-
![]() Source: Coe, Brian (1981): The History of Movie Photography. Westfield, N.J.: Eastview Editions. Film: Pagliacci (1937).
Source: Coe, Brian (1981): The History of Movie Photography. Westfield, N.J.: Eastview Editions. Film: Pagliacci (1937).
- All Categories
- Bibliography
- Chromogenic monopack
- Chromolytic multilayer
- Color separation
- Edge Codes and Identification
- Hand coloring
- Other
- Printing / dye-transfer
- Printing / pigment process
- Screen processes
- Spatial synthesis (multiple lenses, beam splitter)
- Stencil coloring (pochoir, Pathécolor)
- Temporal synthesis (rotary filters)
- Theory
- Tinting
- Toning
-
![]() Rota Farbenfilm Samples (Kodak Film Samples Collection). Credit: National Science and Media Museum Bradford. Photographs of the Rotacolor Prints by Josephine Diecke, SNSF project Film Colors. Technologies, Cultures, Institutions and Joëlle Kost, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
Rota Farbenfilm Samples (Kodak Film Samples Collection). Credit: National Science and Media Museum Bradford. Photographs of the Rotacolor Prints by Josephine Diecke, SNSF project Film Colors. Technologies, Cultures, Institutions and Joëlle Kost, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
13 Images in 2 Galleries
-
![]() Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
11 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress.
Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress.
2 Images
-
![]() Russian Ideas in Clothes! (USA 1922). Credit: UCLA Film & Television Archive. Photographs of the nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
Russian Ideas in Clothes! (USA 1922). Credit: UCLA Film & Television Archive. Photographs of the nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
21 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Mysore Yesterday and Tomorrow Credit: Image courtesy of the 20th Century Fox Collection at the Academy Film Archive. Photograph: Barbara Flueckiger.
Mysore Yesterday and Tomorrow Credit: Image courtesy of the 20th Century Fox Collection at the Academy Film Archive. Photograph: Barbara Flueckiger.
23 Images in 2 Galleries
-
![]() Iridescence on Multicolor print, reflection properties. Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger
Iridescence on Multicolor print, reflection properties. Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger
- Magnification 20x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification 10x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification 5x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Fox Movietone Follies of 1929.
- Source: Coe, Brian (1981): The History of Movie Photography. Westfield, N.J.: Eastview Editions.
- Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Magnification of an area. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Reflection properties. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
72 Images in 6 Galleries
-
![]() Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
42 Images
-
![]() Strange Birds (US 1930, Mack Sennett). Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph of the nitrate print: Barbara Flueckiger
Strange Birds (US 1930, Mack Sennett). Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph of the nitrate print: Barbara Flueckiger
- Magnification. Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Strange Birds (1930)
18 Images in 1 Gallery
The first subtractive 2 color process introduced by Technicolor captured the incoming light through a beam splitter with red and green filters also. However, in contrast to the first Technicolor process, the two b/w images were recorded on one negative strip. This was achieved by the pull-down of two frames simultaneously, a process that required the double speed in the camera. These two frames were arranged in pairs, whereby the green record was inverted up-side down (see image).
-
![]() The Phantom of the Opera (USA 1925, Rupert Julian). Credit: UCLA Film & Television Archive. Photographs of the nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
The Phantom of the Opera (USA 1925, Rupert Julian). Credit: UCLA Film & Television Archive. Photographs of the nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Credit: Images courtesy of the Margaret Herrick Library. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Source: Coe, Brian (1981): The History of Movie Photography. Westfield, N.J.: Eastview Editions.
- Apparently test pieces, these clippings may well be the oldest surviving samples of the process in existence. Ruedel (2009: 55). Credit: George Eastman House Motion Picture Department Collection. Source: Ruedel, Ulrich (2009): The Technicolor Notebooks at the George Eastman House. In: Film History, Volume 21, Number 1, 2009, pp. 47-60.
- Apparently test pieces, these clippings may well be the oldest surviving samples of the process in existence. Ruedel (2009: 55); color reconstruction of the images shown above. Credit: George Eastman House Motion Picture Department Collection. Source: Ruedel, Ulrich (2009): The Technicolor Notebooks at the George Eastman House. In: Film History, Volume 21, Number 1, 2009, pp. 47-60.
- Apparently test pieces, these clippings may well be the oldest surviving samples of the process in existence. Ruedel (2009: 55). Credit: George Eastman House Motion Picture Department Collection. Source: Ruedel, Ulrich (2009): The Technicolor Notebooks at the George Eastman House. In: Film History, Volume 21, Number 1, 2009, pp. 47-60.
- Arrangement of the two records on the camera negative. Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress.
- Film: Stage Struck (USA 1925, Allan Dwan). Credit: Nitrate Frame Collection. George Eastman House Moving Image Collection. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Film: Irene (USA 1926, Alfred E. Green). Credit: Nitrate Frame Collection. George Eastman House Moving Image Collection. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Film: Irene (USA 1926, Alfred E. Green). Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Film: Irene (USA 1926, Alfred E. Green). Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Film: Irene (USA 1926, Alfred E. Green). Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Film: Irene (USA 1926, Alfred E. Green). Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Film: Irene (USA 1926, Alfred E. Green). Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
133 Images in 8 Galleries
-
![]() Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
40 Images
-
![]() Polychromide samples from the Kodak Film Samples Collection at the National Science and Media Museum in Bradford.
Credit: National Science and Media Museum Bradford.
Photographs by Barbara Flueckiger in collaboration with Noemi Daugaard.
Polychromide samples from the Kodak Film Samples Collection at the National Science and Media Museum in Bradford.
Credit: National Science and Media Museum Bradford.
Photographs by Barbara Flueckiger in collaboration with Noemi Daugaard.
- Credit: Brian Pritchard
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 279.
66 Images in 2 Galleries
-
![]() Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
13 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press, p. 67.
Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press, p. 67.
1 Image
-
![]() Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Source: Wall, E.J. (1925): The History of Three-color Photography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
2 Images
-
![]() Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
2 Images
-
![]() Credit: Gert Koshofer Collection. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
Credit: Gert Koshofer Collection. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
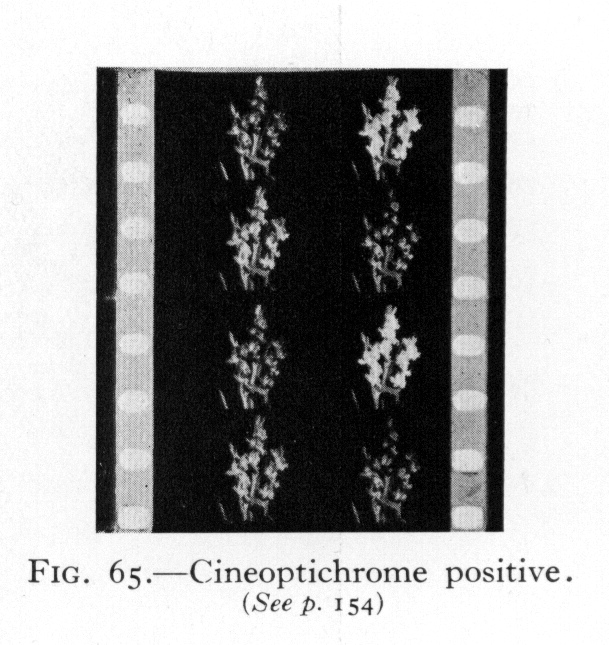
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
5 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Captain Calamity (1936)
Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Captain Calamity (1936)
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Captain Calamity (1936)
2 Images
-
![]() Credit: Technicolor Collection. George Eastman House Moving Image Department. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
Credit: Technicolor Collection. George Eastman House Moving Image Department. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Credit: Technicolor Collection. George Eastman House Moving Image Department. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Credit: Technicolor Collection. George Eastman House Moving Image Department. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
3 Images
-
![]() Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
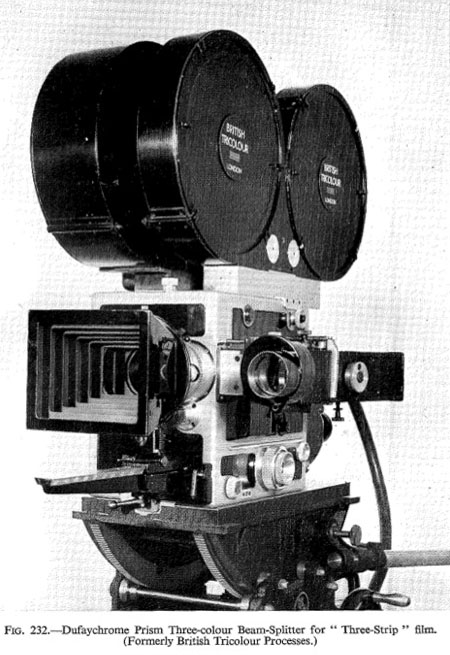
- Coote, Jack (1948): New Three-Color Camera, In: Journal of the Society of Motion Picture Engineers, vol. 50, June 1948, pp. 543-553.
- Coote, Jack (1948): New Three-Color Camera, In: Journal of the Society of Motion Picture Engineers, vol. 50, June 1948, pp. 543-553.
19 Images in 3 Galleries
The Kodachrome process was invented in 1913 by John G. Capstaff for still photography and subsequently adapted to motion pictures. For the process two frames were advanced simultaneously, one located above the other. The light passed either through two lenses or through a beam-splitter, fitted with red and green filters. The release print was exposed through a beam-splitter whereby the alternate frames were projected onto either side of double-coated stock. After development by a usual b/w process, the film was tanned to harden the exposed areas. The soft areas were dyed red-orange and blue-green respectively.
-
![]() Two-Color Kodachrome Print (USA ca. 1925 to 1927, Anonymous). Credit: George Eastman Museum. Photographs of the Kodachrome two-color double coated stock from 1925 and 1927 by Olivia Kristina Stutz, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
Two-Color Kodachrome Print (USA ca. 1925 to 1927, Anonymous). Credit: George Eastman Museum. Photographs of the Kodachrome two-color double coated stock from 1925 and 1927 by Olivia Kristina Stutz, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. In:Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Magnification 5x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification 10x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification 20x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Kodachrome Two-color test from 1922, YouTube channel of the George Eastman House.
350 Images in 12 Galleries
-
![]() Magnification of an image area. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
Magnification of an image area. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Color chart. Credit: Guido Seeber Nachlass, Deutsche Kinemathek, Berlin. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92.
- Credit: Guido Seeber Nachlass, Deutsche Kinemathek, Berlin. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Credit: Bundesarchiv-Filmarchiv, photo: Marian Stefanowski. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92. Film: Bunte Tierwelt. Studien in Hagebecks Tierpark in Stellingen (1931).
- Credit: Bundesarchiv-Filmarchiv, photo: Marian Stefanowski. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92. Film: Karneval (1936).
- Credit: Bundesarchiv-Filmarchiv, photo: Jeanpaul Goergen. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92. Film: Bunte Fischwelt (1936).
- Credit: Bundesarchiv-Filmarchiv, photo: Marian Stefanowski. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92. Film: Karneval (1936).
- Credit: Deutsches Filminstitut DIF (Vicas Nachlass), photo: Jeanpaul Goergen. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92. Film: Potsdam (1934).
- Credit: Bundesarchiv-Filmarchiv, photo: Marian Stefanowski. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92. Film: Farben machen froh (1938).
- Magnification 5x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification 10x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification 20x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. In:Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Magnification of an image area. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. In:Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Reflection on Ufacolor film. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. In:Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- An opened splice of an Ufacolor positive shows the two colors used in the process. Credit: David Pfluger. Source: David Pfluger’s collection.
136 Images in 7 Galleries
-
![]() Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
1 Image
-
![]() Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
2 Images
-
![]() Magnification, 20x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
Magnification, 20x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification, 10x. Credit: Photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification, 5x. Credit: Photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. In: Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Magnification of an image area. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Reflection on the Sirius film, front. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Reflection on the Sirius film, back. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
142 Images in 4 Galleries
-
![]() Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
3 Images
-
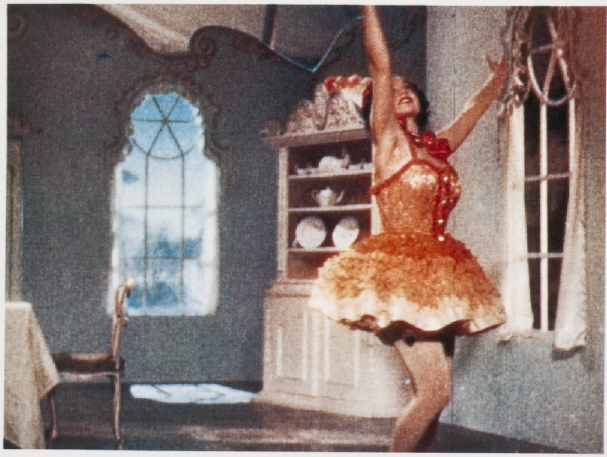
![]() Screenshot from Mayorov, Nikolai (2012): Soviet Colours. Translated by Birgit Beumers. In: Studies in Russian & Soviet Cinema, 6:2, pp. 241–255. doi: 10.1386/srsc.6.2.241_1 Courtesy of Nikolai Mayorov.
Screenshot from Mayorov, Nikolai (2012): Soviet Colours. Translated by Birgit Beumers. In: Studies in Russian & Soviet Cinema, 6:2, pp. 241–255. doi: 10.1386/srsc.6.2.241_1 Courtesy of Nikolai Mayorov.