-
![]() Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 70.
Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 70.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 70.
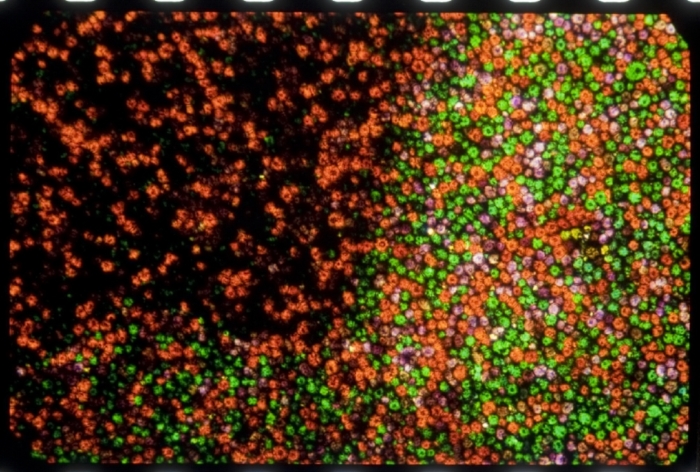
- Photomicrograph (20x) of a Finlay screen. Credit: Courtesy of George Eastman House, International Museum of Photography and Film.
- Finlay box. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 39.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 39.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 40.
Category: Mosaic screen▼×
- All Categories
- Bibliography
- Chromogenic monopack
- Chromolytic multilayer
- Color separation
- Double-coated / bi-pack
- Edge Codes and Identification
- Hand coloring
- Other
- Printing / dye-transfer
- Printing / pigment process
- Screen processes
- Spatial synthesis (multiple lenses, beam splitter)
- Stencil coloring (pochoir, Pathécolor)
- Temporal synthesis (rotary filters)
- Theory
- Tinting
- Toning
“The Autochrome process was the first fully practical single-plate colour process to reach the photographic public. It was easy to use. The plate was loaded into a conventional holder, glass to the front. The exposure was made through a yellow ...
-
![]() Photomicrograph (50x) of an Autochrome mosaic screen. Credit: Courtesy of George Eastman House, International Museum of Photography and Film.
Photomicrograph (50x) of an Autochrome mosaic screen. Credit: Courtesy of George Eastman House, International Museum of Photography and Film.
- Source: Lavédrine, Bertrand (2009): Photographs of the Past. Process and Preservation. Los Angeles: Getty Publications.
- Source: Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press.
- Source: Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press.
- Source: Holme, Charles (1908): Colour Photography, and Other Recent Developments of the Art of the Camera. London, Paris, New York.: Offices of The Studio.
- Source: Holme, Charles (1908): Colour Photography, and Other Recent Developments of the Art of the Camera. London, Paris, New York.: Offices of The Studio.
- Credit: Klosterarchiv Einsiedeln. http://www.klosterarchiv.ch/earchiv_liste.php?Objektyp_physisch=Glasautochrom&start=1
- Credit: Klosterarchiv Einsiedeln. http://www.klosterarchiv.ch/earchiv_liste.php?Objektyp_physisch=Glasautochrom&start=1
- Credit: Klosterarchiv Einsiedeln. http://www.klosterarchiv.ch/earchiv_liste.php?Objektyp_physisch=Glasautochrom&start=1
- Credit: Klosterarchiv Einsiedeln. http://www.klosterarchiv.ch/earchiv_liste.php?Objektyp_physisch=Glasautochrom&start=1
- Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 70.
- Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 26.
- Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 65.
- Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 27.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 235.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 64.
16 Images
Several attempts were made to apply the Autochrome process invented by the Lumière brothers to motion pictures.
Transparent potato starch grains with a diameter of 15–20 micrometer were colored in the additive primaries red, green and blue. The ...
-
![]() Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Cinécolor, mosaic screen, ca. 1929. Credit: Gert Koshofer Collection. Sample No. 68. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Magnification of an image area. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
27 Images in 2 Galleries
“New Agfa Color Plate (1923–1932): colored particles very small and not visible to the naked eye, but clumps of particles of the same color give the image a pointillist effect (Fig. 2.62). Unlike with the autochromes, in which the grains ...
-
![]() Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 73.
Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 73.
1 Image
“Agfacolor Plate (1932-1938): colored particles very small and not visible to the naked eye; clumps of particles of the same color give the image a pointillist effect (Fig. 2.63). Unlike with the autochromes, in which the grains are remarkably ...
-
![]() Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 72.
Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 72.
1 Image
“Agfacolor Film (1932–1934): individual colored particles cannot be seen with the naked eye, but clumps of grains of the same color give the image a pointillist effect (Fig. 2.70). There is no black pigment filler. The film has a thick base ...
-
![]() Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 76.
Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 76.
1 Image
-
![]() Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 74.
Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 74.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 44.
2 Images
“During the war, an important new screen plate appeared, based on patents taken out by J. H. Christensen in 1908. He proposed to make a concentrated solution of gum in alcohol. Divided into three parts, the gum solutions were dyed red, green ...
-
![]() Magnification. Source: Coe, Brian (1978): Colour Photography. The First Hundred Years 1840-1940. London: Ash & Grant.
Magnification. Source: Coe, Brian (1978): Colour Photography. The First Hundred Years 1840-1940. London: Ash & Grant.
- Source: Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press.
- Source: Heymer, Gerd (1943): Die neuere Entwicklung der Farbphotographie. In: Ergänzungswerk zum Handbuch der wissenschaftlichen und angewandten Photographie. Wien: Julius Springer 1943, pp. 337-463.
- Source: Finger, Ehrhard (1998): Die Pioniere des Wolfener Farbfilms. In: Industrie- und Filmmuseum Wolfen e. V. (ed.), Die Filmfabrik Wolfen. Aus der Geschichte, Heft 2, pp. 16-36. (in German) [quote id='4']
- Source: Finger, Ehrhard (1998): Die Pioniere des Wolfener Farbfilms. In: Industrie- und Filmmuseum Wolfen e. V. (ed.), Die Filmfabrik Wolfen. Aus der Geschichte, Heft 2, pp. 16-36. (in German) [quote id='4']
- Source: Finger, Ehrhard (1998): Die Pioniere des Wolfener Farbfilms. In: Industrie- und Filmmuseum Wolfen e. V. (ed.), Die Filmfabrik Wolfen. Aus der Geschichte, Heft 2, pp. 16-36. (in German) [quote id='4']
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 73.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 73.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 72.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 76.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 42.