-
![]() Photomicrograph 500x, faded 3M print, cross section. Credit: Karsta Knaack.
Photomicrograph 500x, faded 3M print, cross section. Credit: Karsta Knaack.
- Photomicrograph 500x, faded 3M print, cross section. Credit: Karsta Knaack.
- Faded 3M positive. Credit: Carsta Knaack, HTW Berlin.
- Faded 3M positive. Credit: Carsta Knaack, HTW Berlin.
Select Category▼×
- All Categories
- Bibliography
- Chromogenic monopack
- Chromolytic multilayer
- Color separation
- Double-coated / bi-pack
- Edge Codes and Identification
- Hand coloring
- Other
- Printing / dye-transfer
- Printing / pigment process
- Screen processes
- Spatial synthesis (multiple lenses, beam splitter)
- Stencil coloring (pochoir, Pathécolor)
- Temporal synthesis (rotary filters)
- Theory
- Tinting
- Toning
“In 1956, after the failure of the French venture, Gaspar resumed his own production of printing materials and chemicals (Koshofer 1981a). In the late 1950s he entered into an agreement with 3M Company of St. Paul, Minnesota, to explore the ...
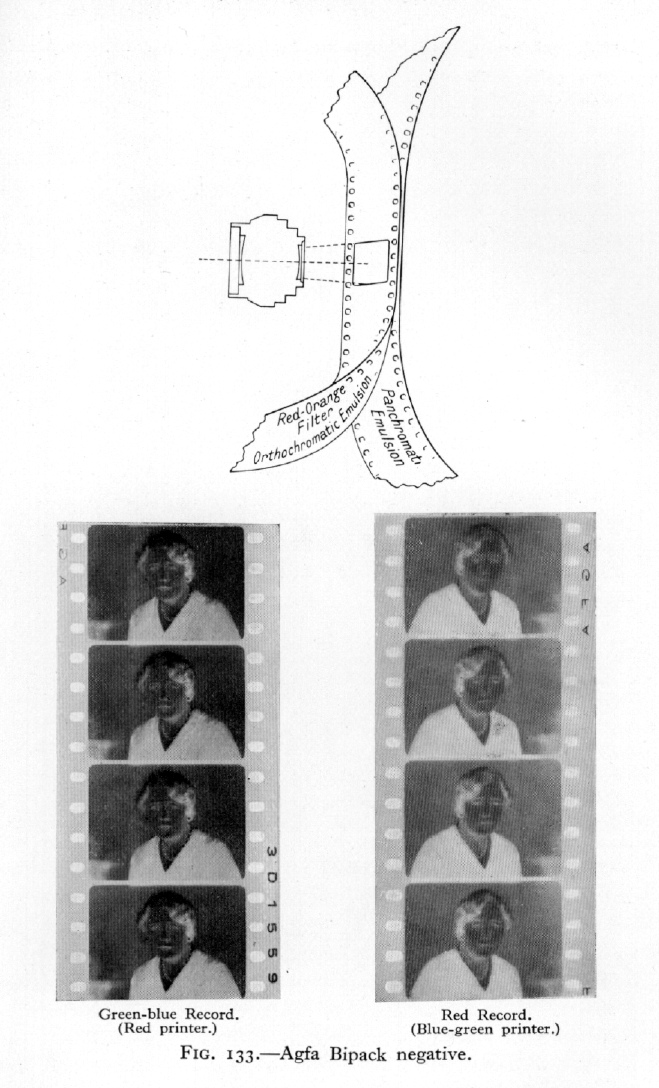
AGFA BIPACK FILM
The front film is orthochromatic and sensitive, therefore, to green and blue. The rear film is panchromatic and records red-orange only, there being a red-orange filter on the orthochromatic emulsion. In fact, this is a bipack of the ...
-
![]() Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
11 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Photomicrograph 1000x, Agfachrome cross section. Credit: Carsta Knaack.
Photomicrograph 1000x, Agfachrome cross section. Credit: Carsta Knaack.
- Photomicrograph 500x, Agfachrome cross section. Credit: Carsta Knaack.
2 Images
“Between 1970 and 1976, Agfa-Gevaert produced its own silver dye-bleach printing material on a white-pigmented acetate base called Agfachrome CU 410.28 Only available to a few photofinishers in Germany, it was used to print amateurs’ ...
-
![]() Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 218.
Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 218.
1 Image
L stands for the Leverkusen brand of Agfacolor. N for negative, K for tungsten (Kunstlicht) and T for daylight (Tageslicht).
-
![]() Credit: By courtesy of Deutsche Kinemathek, Berlin. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: Commercial Denkt rechtzeitig daran (GER 1952).
Credit: By courtesy of Deutsche Kinemathek, Berlin. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: Commercial Denkt rechtzeitig daran (GER 1952).
- Credit: By courtesy of Deutsche Kinemathek, Berlin. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: 1/50 Sekunde, commercial for Niggemeyer Foto/Kino (1952).
13 Images in 2 Galleries
The basic idea of the lenticular film was developed by the German Raphaël Liesegang in 1896 and applied to still photography by the French Rodolphe Berthon in 1908.
The lenticular process applies tiny cylindrical lenses embossed on the film support ...
-
![]() Color reconstruction. Credit: Gisela Harich-Hamburger, Diplomrestauratorin (FH).
Color reconstruction. Credit: Gisela Harich-Hamburger, Diplomrestauratorin (FH).
- Source: Heymer, Gerd (1933): Auflösungsvermögen und Farbwiedergabe in der Farbrasterphotographie. In: Veröffentlichungen des wissenschaftlichen Zentral-Laboratoriums der photographischen Abteilung Agfa, 3, 1933, pp. 188-207.
- Source: Weil, F. (1933): The Optical-Photographic Principles of the Agfacolor Process. In: Journal of the Society of Motion Picture Engineers, 20, (April, 1933), No. 4, p. 301-308.
- Both the Kodak and Agfa lenticular processes required the correct banded filter to be used with each different batch of panchromatic film. These two filters were for different batches of Agfacolor used in a Leica camera.. Source: Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ede, François (1994): Jour de fête ou la couleur retrouvée. Cahiers du Cinéma: Paris.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Magnification 5x, front. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification 10x, back. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification 20x, front. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Reflection on Agfacolor lenticular film. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. In: Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Reconstruction of lenticular film by Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland in the framework of their research project doLCE
- Agfacolor Lenticular sample from the Kodak Film Samples Collection at the National Science and Media Museum in Bradford. Credit: National Science and Media Museum Bradford. Photographs by Barbara Flueckiger in collaboration with Noemi Daugaard.
- Analog reconstruction by Giorgio Trumpy, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors
15 Images
For more information on the Agfacolor process see the detail page Agfacolor Neu / Agfacolor.
-
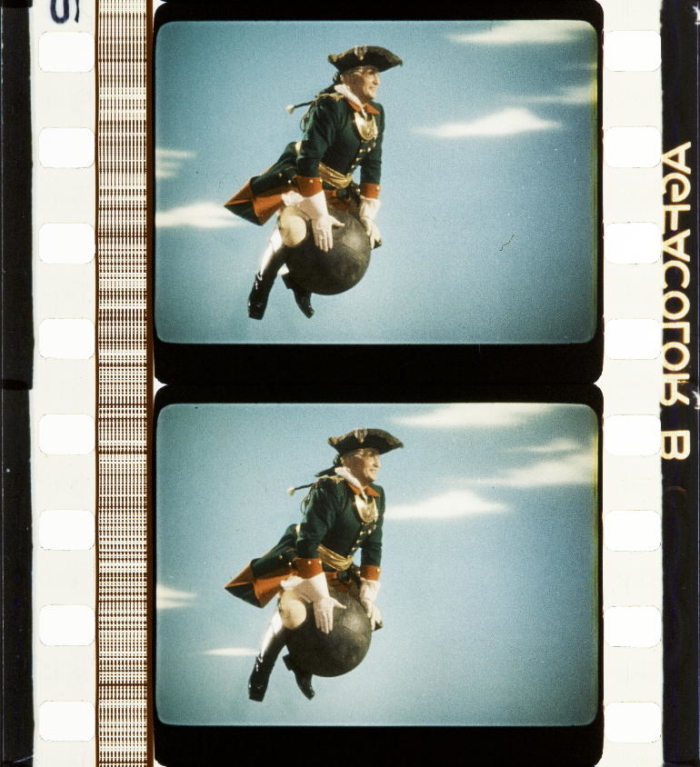
![]() Agfacolor B original negative. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jan Roháč z Dubé (Czechoslovakia 1947, Vladimír Borsky).
Agfacolor B original negative. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jan Roháč z Dubé (Czechoslovakia 1947, Vladimír Borsky).
- Faded Agfacolor period nitrate print. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jan Roháč z Dubé (Czechoslovakia 1947, Vladimír Borský).
- Agfacolor B original negative. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jan Roháč z Dubé (Czechoslovakia 1947, Vladimír Borsky).
- Faded Agfacolor period nitrate print. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jan Roháč z Dubé (Czechoslovakia 1947, Vladimír Borský).
- Agfacolor B original negative. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jan Roháč z Dubé (Czechoslovakia 1947, Vladimír Borsky).
- Agfacolor B original negative. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Kvítí z Čech (Czechoslovakia 1947, dir. Václav Jan Staněk).
- Agfacolor positive nitrate print. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Kvítí z Čech (Czechoslovakia 1947, dir. Václav Jan Staněk).
- Agfacolor positive nitrate print. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Kvítí z Čech (Czechoslovakia 1947, dir. Václav Jan Staněk).
- Agfacolor B original negative. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Mistr třeboňský (Czechoslovakia 1950, dir. František Kudláč).
- Agfacolor B original negative. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Mistr třeboňský (Czechoslovakia 1950, dir. František Kudláč).
- Agfacolor positive nitrate print. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Mistr třeboňský (Czechoslovakia 1950, dir. František Kudláč).
- Agfacolor B original negative. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Praha v říjnu (Czechoslovakia 1945, dir. František Sádek).
- Faded Agfacolor period nitrate print. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Praha v říjnu (Czechoslovakia 1945, dir. František Sádek).
- Agfacolor B original negative. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Praha v říjnu (Czechoslovakia 1945, dir. František Sádek).
- Agfacolor B original negative. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Zasadil dědek řepu (Czechoslovakia 1945, dir. Jiří Trnka).
- Agfacolor positive nitrate print. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Zasadil dědek řepu (Czechoslovakia 1945, Jiří Trnka).
- Agfacolor positive nitrate print. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Zasadil dědek řepu (Czechoslovakia 1945, Jiří Trnka).
- Credit: By courtesy of Deutsche Kinemathek, Berlin. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: 1/50 Sekunde, commercial for Niggemeyer Foto/Kino (1952).
- Schmidt, Richard / Kochs, Adolf (1943): Farbfilmtechnik. Eine Einführung für Filmschaffende. Berlin: Hesse, pp. 77-98. (Schriftenreihe der Reichsfilmkammer, 10.) (in German) [quote cite='35875']
- Schmidt, Richard / Kochs, Adolf (1943): Farbfilmtechnik. Eine Einführung für Filmschaffende. Berlin: Hesse, pp. 77-98. (Schriftenreihe der Reichsfilmkammer, 10.) (in German) [quote cite='35875']
- Schmidt, Richard / Kochs, Adolf (1943): Farbfilmtechnik. Eine Einführung für Filmschaffende. Berlin: Hesse, pp. 77-98. (Schriftenreihe der Reichsfilmkammer, 10.) (in German) [quote cite='35875']
21 Images
For more information on the Agfacolor chromogenic process see Agfacolor Neu / Agfacolor.
-
![]() Agfacolor B negative on Agfacolor positive. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Tábor (Oldřich Mirad, Czechoslovakia 1953). Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
Agfacolor B negative on Agfacolor positive. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Tábor (Oldřich Mirad, Czechoslovakia 1953). Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
37 Images in 2 Galleries
Agfacolor Negative type G was a chromogenic camera negative balanced for Tungsten illumination.
-
![]() Original Agfacolor negative G. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Neposlušný zajíček (German title Klein, aber Oho!, Horst von Möllendorff, Czechoslovakia 1944).
Original Agfacolor negative G. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Neposlušný zajíček (German title Klein, aber Oho!, Horst von Möllendorff, Czechoslovakia 1944).
- Schmidt, Richard / Kochs, Adolf (1943): Farbfilmtechnik. Eine Einführung für Filmschaffende. Berlin: Hesse, pp. 77-98. (Schriftenreihe der Reichsfilmkammer, 10.) (in German) [quote cite='35875']
- Schmidt, Richard / Kochs, Adolf (1943): Farbfilmtechnik. Eine Einführung für Filmschaffende. Berlin: Hesse, pp. 77-98. (Schriftenreihe der Reichsfilmkammer, 10.) (in German) [quote cite='35875']
14 Images in 2 Galleries
For more information on the Agfacolor chromogenic process see Agfacolor Neu / Agfacolor.
-
![]() Negative. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Princezna se zlatou hvězdou (Martin Frič, Czechoslovakia 1959).
Negative. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Princezna se zlatou hvězdou (Martin Frič, Czechoslovakia 1959).
- Negative. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Princezna se zlatou hvězdou (Martin Frič, Czechoslovakia 1959).
- Negative. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Princezna se zlatou hvězdou (Martin Frič, Czechoslovakia 1959).
- Negative. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Princezna se zlatou hvězdou (Martin Frič, Czechoslovakia 1959).
- Princezna se zlatou hvězdou (CZE 1959, Martin Frič). Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Photographs of the Agfacolor B negative on Orwocolor positive by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Princezna se zlatou hvězdou (CZE 1959, Martin Frič). Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Photographs of the Agfacolor B negative on Orwocolor positive by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Princezna se zlatou hvězdou (CZE 1959, Martin Frič). Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Photographs of the Agfacolor B negative on Orwocolor positive by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Princezna se zlatou hvězdou (CZE 1959, Martin Frič). Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Photographs of the Agfacolor B negative on Orwocolor positive by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Princezna se zlatou hvězdou (CZE 1959, Martin Frič). Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Photographs of the Agfacolor B negative on Orwocolor positive by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Princezna se zlatou hvězdou (CZE 1959, Martin Frič). Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Photographs of the Agfacolor B negative on Orwocolor positive by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Princezna se zlatou hvězdou (CZE 1959, Martin Frič). Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Photographs of the Agfacolor B negative on Orwocolor positive by Barbara Flueckiger.
11 Images
“The New Agfacolor Process;
Agfa Ansco Corp., Binghamton, N. Y.
A survey of the history of monopack or multilayer photographic color processes is given, including the coloring methods of greatest importance at the present time. These are: (a) ...
-
![]() Münchhausen (Josef von Báky, Germany 1943). Credit: Bundesarchiv Filmarchiv and Friedrich-Wilhelm-Murnau-Stiftung. Photographs of the Agfacolor safety print (acetate) by Barbara Flueckiger.
Münchhausen (Josef von Báky, Germany 1943). Credit: Bundesarchiv Filmarchiv and Friedrich-Wilhelm-Murnau-Stiftung. Photographs of the Agfacolor safety print (acetate) by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Opfergang (GER 1944, Veit Harlan), magnification. Credit: Print from the Filmmuseum Düsseldorf. © Friedrich Wilhelm Murnau Foundation, Wiesbaden. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Paper print. Source: Serda, Charlott (1941): Das Farbfoto-Buch vom Film. Breitkopf & Härtel: Leipzig.
- Parade (1960). Credit: Harvard Film Archive, Brandon Film Library Collection, item no. 14303. Photographs of Agfacolor negative on Orwocolor reversal print by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Parade (1960). Credit: Harvard Film Archive, Brandon Film Library Collection, item no. 14303. Photographs of Agfacolor negative on Orwocolor reversal print by Barbara Flueckiger.
640 Images in 21 Galleries
-
![]() Cross section scheme, Agfacolor Positive Type 5. Scource: Brune, Wolfgang (1955): Ein neues Agfacolor-Positivmaterial (Agfacolor-Positivfilm Typ 5).
Cross section scheme, Agfacolor Positive Type 5. Scource: Brune, Wolfgang (1955): Ein neues Agfacolor-Positivmaterial (Agfacolor-Positivfilm Typ 5).
1 Image
“During the war, an important new screen plate appeared, based on patents taken out by J. H. Christensen in 1908. He proposed to make a concentrated solution of gum in alcohol. Divided into three parts, the gum solutions were dyed red, green ...
-
![]() Magnification. Source: Coe, Brian (1978): Colour Photography. The First Hundred Years 1840-1940. London: Ash & Grant.
Magnification. Source: Coe, Brian (1978): Colour Photography. The First Hundred Years 1840-1940. London: Ash & Grant.
- Source: Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press.
- Source: Heymer, Gerd (1943): Die neuere Entwicklung der Farbphotographie. In: Ergänzungswerk zum Handbuch der wissenschaftlichen und angewandten Photographie. Wien: Julius Springer 1943, pp. 337-463.
- Source: Finger, Ehrhard (1998): Die Pioniere des Wolfener Farbfilms. In: Industrie- und Filmmuseum Wolfen e. V. (ed.), Die Filmfabrik Wolfen. Aus der Geschichte, Heft 2, pp. 16-36. (in German) [quote id='4']
- Source: Finger, Ehrhard (1998): Die Pioniere des Wolfener Farbfilms. In: Industrie- und Filmmuseum Wolfen e. V. (ed.), Die Filmfabrik Wolfen. Aus der Geschichte, Heft 2, pp. 16-36. (in German) [quote id='4']
- Source: Finger, Ehrhard (1998): Die Pioniere des Wolfener Farbfilms. In: Industrie- und Filmmuseum Wolfen e. V. (ed.), Die Filmfabrik Wolfen. Aus der Geschichte, Heft 2, pp. 16-36. (in German) [quote id='4']
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 73.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 73.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 72.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 72.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 42.