-
![]() Cyan and magenta combined, third layer, yellow missing. Source: Meister Lucius & Brüning (1905): Pinatypie. Positiv-Verfahren für die Dreifarbenphotographie. Höchst am Main.
Cyan and magenta combined, third layer, yellow missing. Source: Meister Lucius & Brüning (1905): Pinatypie. Positiv-Verfahren für die Dreifarbenphotographie. Höchst am Main.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 235.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 235.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 132.
- All Categories
- Bibliography
- Chromogenic monopack
- Chromolytic multilayer
- Color separation
- Double-coated / bi-pack
- Edge Codes and Identification
- Hand coloring
- Other
- Printing / dye-transfer
- Printing / pigment process
- Screen processes
- Spatial synthesis (multiple lenses, beam splitter)
- Stencil coloring (pochoir, Pathécolor)
- Temporal synthesis (rotary filters)
- Theory
- Tinting
- Toning
-
![]() Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Source: Wall, E.J. (1925): The History of Three-color Photography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
2 Images
-
![]() Source: Wall, E.J. (1925): The History of Three-color Photography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
Source: Wall, E.J. (1925): The History of Three-color Photography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
1 Image
-
![]() Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 161.
Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 161.
1 Image
-
![]() Photomicrograph (50x) of an Autochrome mosaic screen. Credit: Courtesy of George Eastman House, International Museum of Photography and Film.
Photomicrograph (50x) of an Autochrome mosaic screen. Credit: Courtesy of George Eastman House, International Museum of Photography and Film.
- Source: Lavédrine, Bertrand (2009): Photographs of the Past. Process and Preservation. Los Angeles: Getty Publications.
- Source: Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press.
- Source: Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press.
- Source: Holme, Charles (1908): Colour Photography, and Other Recent Developments of the Art of the Camera. London, Paris, New York.: Offices of The Studio.
- Source: Holme, Charles (1908): Colour Photography, and Other Recent Developments of the Art of the Camera. London, Paris, New York.: Offices of The Studio.
- Credit: Klosterarchiv Einsiedeln. http://www.klosterarchiv.ch/earchiv_liste.php?Objektyp_physisch=Glasautochrom&start=1
- Credit: Klosterarchiv Einsiedeln. http://www.klosterarchiv.ch/earchiv_liste.php?Objektyp_physisch=Glasautochrom&start=1
- Credit: Klosterarchiv Einsiedeln. http://www.klosterarchiv.ch/earchiv_liste.php?Objektyp_physisch=Glasautochrom&start=1
- Credit: Klosterarchiv Einsiedeln. http://www.klosterarchiv.ch/earchiv_liste.php?Objektyp_physisch=Glasautochrom&start=1
- Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 70.
- Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 26.
- Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 65.
- Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 27.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 235.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 64.
16 Images
Kinemacolor was an additive process operated with alternating red and green filters that were applied to the shutter in front of the camera and in front of the projector. With at least 32 fps the frame rate was double the minimal frame rate of 16 fps. Time parallax with small differences between the red and green record resulted in color fringes that became visible when objects or scenes were moving.
-
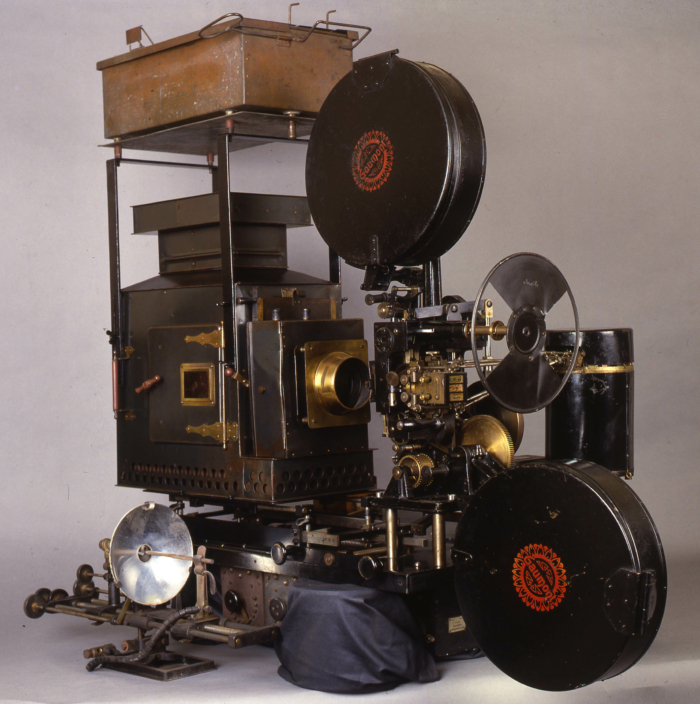
![]() Kinemacolor projector used for David Cleveland's and Brian Pritchard's reconstruction. Credit: Brian Pritchard.
Kinemacolor projector used for David Cleveland's and Brian Pritchard's reconstruction. Credit: Brian Pritchard.
13 Images in 3 Galleries
-
![]() Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press,
Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press,
- Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Source: Ede, François (1994): Jour de fête ou la couleur retrouvée. Cahiers du Cinéma: Paris.
- Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 71.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 73.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 31.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 32.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 33.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 48.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 69.
10 Images
-
![]() Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ede, François (1994): Jour de fête ou la couleur retrouvée. Cahiers du Cinéma: Paris.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Source: Heymer, Gerd (1933): Auflösungsvermögen und Farbwiedergabe in der Farbrasterphotographie. In: Veröffentlichungen des wissenschaftlichen Zentral-Laboratoriums der photographischen Abteilung Agfa, 3, 1933, pp. 188-207.
4 Images
-
![]() Virages sur mordançage, Bleu (blue mordant toning), backlight, Swiss collectors'copy. Source: Didiée, L. (1926): Le Film vierge Pathé. Manuel de développement et de tirage. Paris: Pathé. [quote id='7']
Virages sur mordançage, Bleu (blue mordant toning), backlight, Swiss collectors'copy. Source: Didiée, L. (1926): Le Film vierge Pathé. Manuel de développement et de tirage. Paris: Pathé. [quote id='7']
- Photomicrograph, 25x. Credit: Norbert Wey, Institute of Pathology, University of Zurich.
- Photomicrograph, 50x. Credit: Norbert Wey, Institute of Pathology, University of Zurich.
- Photomicrograph, 100x. Credit: Norbert Wey, Institute of Pathology, University of Zurich.
- Photomicrograph, 100x. Credit: Norbert Wey, Institute of Pathology, University of Zurich.
171 Images in 7 Galleries
-
![]() Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
3 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
2 Images
-
![]() Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Source: Ede, François (1994): Jour de fête ou la couleur retrouvée. Cahiers du Cinéma: Paris.
- Credit: Paolo Cherchi Usai. Source: Cherchi Usai, Paolo (2000): Silent Cinema. London: BFI.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ede, François (1994): Jour de fête ou la couleur retrouvée. Cahiers du Cinéma: Paris.
- Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Source: Gaumont, Léon (1959): Gaumont Chronochrome Process Described by the Inventor. In: Raymond Fielding (ed.): A Technological History of Motion Pictures and Television. An Anthology from the Pages of The Journal of the Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers. Berkeley; Los Angeles: University of California Press, 1967, pp. 65-67.
- Source: Gaumont, Léon (1959): Gaumont Chronochrome Process Described by the Inventor. In: Raymond Fielding (ed.): A Technological History of Motion Pictures and Television. An Anthology from the Pages of The Journal of the Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers. Berkeley; Los Angeles: University of California Press, 1967, pp. 65-67.
12 Images in 2 Galleries
-
![]() Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press, p. 67.
Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press, p. 67.
1 Image
-
![]() Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: Cinechrome Colour Test with Soap Boxes and Packets (1920)
Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: Cinechrome Colour Test with Soap Boxes and Packets (1920)
- Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: Cinechrome Colour Test with Soap Boxes and Packets (1920)
- Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: Cinechrome Colour Test with Soap Boxes and Packets (1920)
3 Images
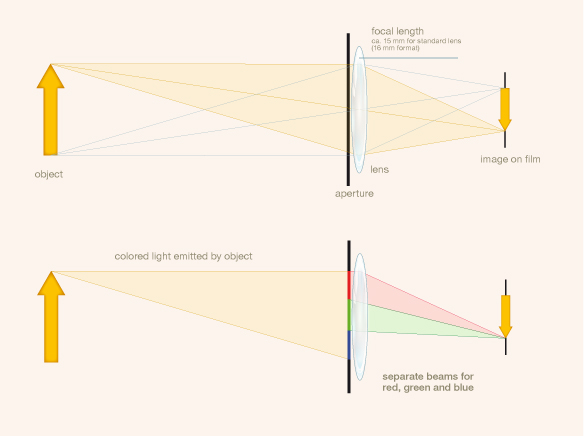
The Kodachrome process was invented in 1913 by John G. Capstaff for still photography and subsequently adapted to motion pictures. For the process two frames were advanced simultaneously, one located above the other. The light passed either through two lenses or through a beam-splitter, fitted with red and green filters. The release print was exposed through a beam-splitter whereby the alternate frames were projected onto either side of double-coated stock. After development by a usual b/w process, the film was tanned to harden the exposed areas. The soft areas were dyed red-orange and blue-green respectively.
-
![]() Two-Color Kodachrome Print (USA ca. 1925 to 1927, Anonymous). Credit: George Eastman Museum. Photographs of the Kodachrome two-color double coated stock from 1925 and 1927 by Olivia Kristina Stutz, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
Two-Color Kodachrome Print (USA ca. 1925 to 1927, Anonymous). Credit: George Eastman Museum. Photographs of the Kodachrome two-color double coated stock from 1925 and 1927 by Olivia Kristina Stutz, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. In:Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
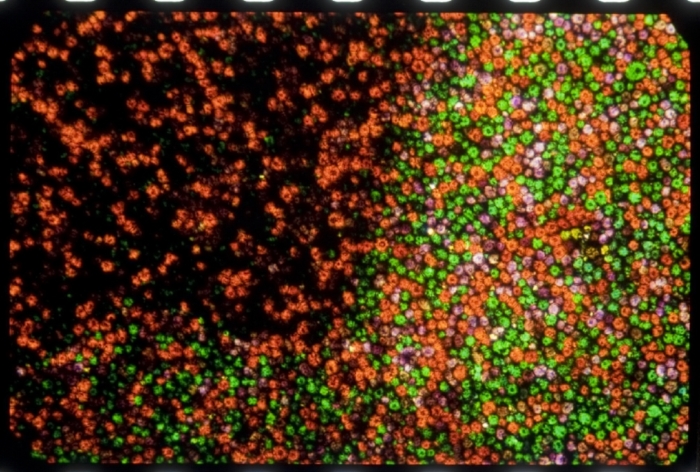
- Magnification 5x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification 10x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification 20x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Kodachrome Two-color test from 1922, YouTube channel of the George Eastman House.
350 Images in 12 Galleries
-
![]() Magnification. Source: Coe, Brian (1978): Colour Photography. The First Hundred Years 1840-1940. London: Ash & Grant.
Magnification. Source: Coe, Brian (1978): Colour Photography. The First Hundred Years 1840-1940. London: Ash & Grant.
- Source: Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press.
- Source: Heymer, Gerd (1943): Die neuere Entwicklung der Farbphotographie. In: Ergänzungswerk zum Handbuch der wissenschaftlichen und angewandten Photographie. Wien: Julius Springer 1943, pp. 337-463.
- Source: Finger, Ehrhard (1998): Die Pioniere des Wolfener Farbfilms. In: Industrie- und Filmmuseum Wolfen e. V. (ed.), Die Filmfabrik Wolfen. Aus der Geschichte, Heft 2, pp. 16-36. (in German) [quote id='4']
- Source: Finger, Ehrhard (1998): Die Pioniere des Wolfener Farbfilms. In: Industrie- und Filmmuseum Wolfen e. V. (ed.), Die Filmfabrik Wolfen. Aus der Geschichte, Heft 2, pp. 16-36. (in German) [quote id='4']
- Source: Finger, Ehrhard (1998): Die Pioniere des Wolfener Farbfilms. In: Industrie- und Filmmuseum Wolfen e. V. (ed.), Die Filmfabrik Wolfen. Aus der Geschichte, Heft 2, pp. 16-36. (in German) [quote id='4']
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 73.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 73.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 72.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 76.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 42.