Select Category▼×
- All Categories
- Bibliography
- Chromogenic monopack
- Chromolytic multilayer
- Color separation
- Double-coated / bi-pack
- Edge Codes and Identification
- Hand coloring
- Other
- Printing / dye-transfer
- Printing / pigment process
- Screen processes
- Spatial synthesis (multiple lenses, beam splitter)
- Stencil coloring (pochoir, Pathécolor)
- Temporal synthesis (rotary filters)
- Theory
- Tinting
- Toning
Not to be confused with the Eastman Color Print Film 5381 from 1950.
Not to be confused with the Eastman Color Print Film 5381 / 7381 from 1970.
-
![]() Cross section scheme of Eastman Color Negative, Type 5250. Scource: Dundon, Merle L./Zwick, Daan M. (1959): A High Speed Color Negative Film. In: JSMPTE Vol 68, p. 736.
Cross section scheme of Eastman Color Negative, Type 5250. Scource: Dundon, Merle L./Zwick, Daan M. (1959): A High Speed Color Negative Film. In: JSMPTE Vol 68, p. 736.
1 Image
-
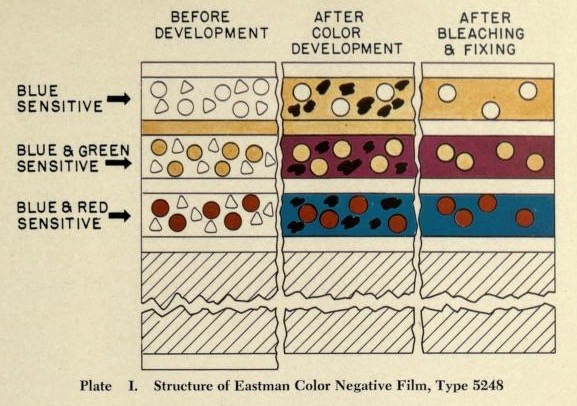
![]() Cross section scheme of Eastman Color Type 5248. Scource: Hanson, W. T., Jr.; Kisner, W. I. (1953): Improved Color Films for Color Motion-Picture Production. In: Journal SMPTE, Vol. 61, Dec. 1953, p. 699.
Cross section scheme of Eastman Color Type 5248. Scource: Hanson, W. T., Jr.; Kisner, W. I. (1953): Improved Color Films for Color Motion-Picture Production. In: Journal SMPTE, Vol. 61, Dec. 1953, p. 699.
1 Image
“The Eastman Colour Films are multilayer films of the type in which the layers are not separated after exposure. Films of this class are known as Multilayer, Monopack or Integral Tripack. “Multilayer” is descriptive not only of this ...
-
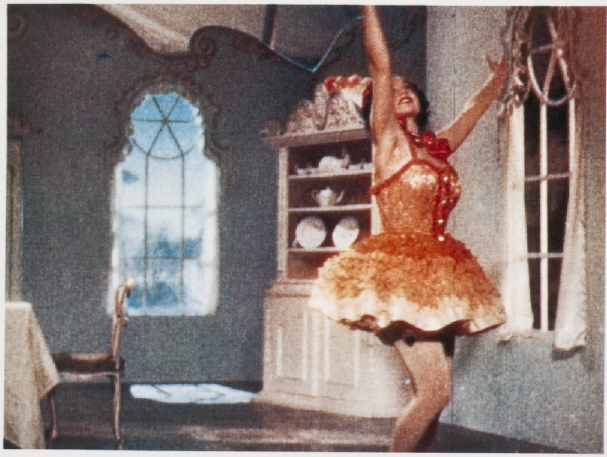
![]() Alien (USA 1979, Ridley Scott). Credit: Library of Congress. Photographs of the Eastman Color Print Film from 1979 by Joëlle Kost, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
Alien (USA 1979, Ridley Scott). Credit: Library of Congress. Photographs of the Eastman Color Print Film from 1979 by Joëlle Kost, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
- Photomicrograph of modern chromogenic stock, . Credit: Silvana Konermann.
- Eastman Color chromogenic monopack. Source: Craig, G.J. (1953): Eastman Colour Films for Professional Motion Picture Work. In: British Kinematography, 22,5, 1953, pp. 146-158.
- Color fading of Eastmancolor stock. Credit: Collection Gert Koshofer, Bergisch Gladbach (Germany). Source: Schultze, Werner (1953): Farbenphotographie und Farbenfilm. Wissenschaftliche Grundlagen und technische Gestaltung. Berlin: Springer.
- Color reconstruction by Rudolf Gschwind, University of Basel. Credit: Collection Gert Koshofer, Bergisch Gladbach (Germany).
- Color fading of Eastmancolor stock.
- Source: Schultze, Werner (1953): Farbenphotographie und Farbenfilm. Wissenschaftliche Grundlagen und technische Gestaltung. Berlin/Göttingen /Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag. Photograph by Martin Weiss, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
- Source: Schultze, Werner (1953): Farbenphotographie und Farbenfilm. Wissenschaftliche Grundlagen und technische Gestaltung. Berlin/Göttingen /Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag. Photograph by Martin Weiss, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
707 Images in 23 Galleries
-
![]() Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson.
Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson.
1 Image
“One of the most elegant solutions to the problem of forming a colored image, lies in the utilization of the products formed by the action of the developer upon the latent image. By this means there is formed a dye image whose intensity follows ...
-
![]() Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 161.
Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 161.
1 Image
-
![]() Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
- Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
2 Images
-
![]() Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
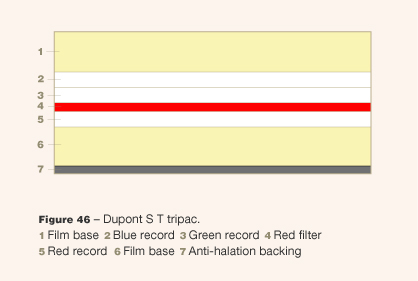
- Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
- Source: Sease, V. B. (1949): DuPont's New Color Film. In:American Cinematographer, 30: 240, 257-258.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Sease, V. B. (1949): DuPont's New Color Film. In:American Cinematographer, 30: 240, 257-258.
8 Images in 1 Gallery
Dufaycolor was a regular line screen process whereby the incident light was filtered through a pattern of tiny color patches created by lines in red, green and blue, the so called réseau.
-
![]() Reversal Colour Positive. Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: A Colour Box (GB 1935, Len Lye).
Reversal Colour Positive. Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: A Colour Box (GB 1935, Len Lye).
- Microscopic image of the filter structure of a Dufaycolor film. The Emulsion has been removed. The visible structures are not silver grain but the structure of the filter layers. Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Microscopic images of Dufaycolor film with the focus set at different points within the emulsion and filter layers. The images have been chained to show a travelling through the 3-dimensional structure of the layers. Credit: David Pfluger, conversion to video by Martin Weiss, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
231 Images in 9 Galleries
(see detail page on Dufaycolor)
-
![]() Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press,
Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press,
- Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Source: Ede, François (1994): Jour de fête ou la couleur retrouvée. Cahiers du Cinéma: Paris.
- Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 71.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 73.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 31.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 32.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 33.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 48.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 69.
10 Images
“Douglass Color No. 2 (1919). The two negatives of the Douglass Color system No. 1 were printed on a positive. In this updated version of the process, rather than projecting the frames through red and green filters, both latent images were ...
“This two-color additive system for color cinematography was invented in 1916 by Leon Forrest Douglass of San Rafael, California. A special beam splitter camera would advance each roll of film two frames per exposure with its double frame pull down ...
-
![]() Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press. Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press. Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
- Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press. Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
3 Images
The film is recorded through alternating red and green filters, creating two color separations. After development, the print is placed in two alternating dye-baths, toning the blacks green and the whites red. Additionally, a black-and-white copy is ...
-
![]() Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
- Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
2 Images
“The principle of the subtractive colour process was described first by Louis Ducos du Hauron in 1868.
Although eminently suitable for colour motion pictures, the principle could not be applied until means were found of producing several colour ...
-
![]() Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press, p. 67.
Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press, p. 67.
1 Image
-
![]() Russian Ideas in Clothes! (USA 1922). Credit: UCLA Film & Television Archive. Photographs of the nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
Russian Ideas in Clothes! (USA 1922). Credit: UCLA Film & Television Archive. Photographs of the nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
21 Images in 1 Gallery
“Coloratura. This is the process of Pathé Exchange at Bound Brook, N. J. Negatives are made by the bi-pack method. Prints are made on double-sided film and are dye-toned on one side and metallic-toned on the other. The double-sided film, ...
“In a lecture on the theory of three primary colors, given at the Royal Institution of Great Britain on May 17, 1861, Maxwell presented the first demonstration of a photograph in color. According to the records of that meeting (Maxwell, 1890c, ...
-
![]() Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress.
Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress.
2 Images
“The first two-colour additive method in which the two components were taken and projected simultaneously was the Colcin process, in 1913. The result of a Franco-Japanese collaboration, it was demonstrated at the International Kinematographic ...
-
![]() Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. A History of Motion Picture Color Technology.
Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. A History of Motion Picture Color Technology.
- Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
2 Images
-
![]() Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
2 Images
-
![]() Credit: Harvard Film Archive, George Huizinga Collection, item no. 10454. Film: Prehistoric Women (1951).
Credit: Harvard Film Archive, George Huizinga Collection, item no. 10454. Film: Prehistoric Women (1951).
- Credit: Harvard Film Archive, George Huizinga Collection, item no. 10454. Film: Prehistoric Women (1951).
- Source: Coe, Brian (1981): The History of Movie Photography. Westfield, N.J.: Eastview Editions.
- Reflection on Cinecolor print. Credit: Image courtesy of the 20th Century Fox Collection at the Academy Film Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger
- Reflection on Cinecolor 16 mm print. Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger
93 Images in 9 Galleries
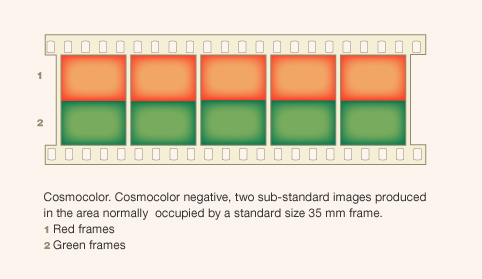
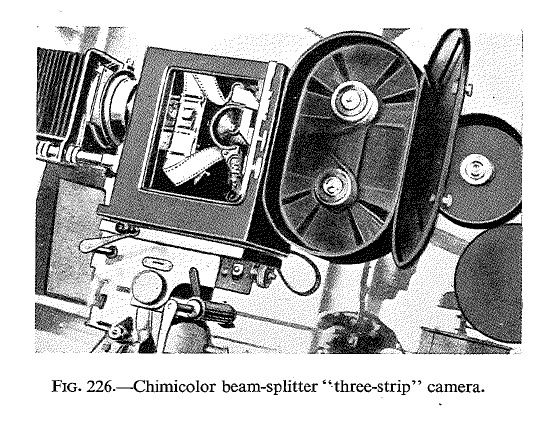
“[…] pictures were taken side by side, full-size, on double-width film, the film not only being perforated on the edges but also down the centre between the pairs of images.”
(Klein, Adrian Bernhard = Cornwell-Clyne (1940): Colour ...
-
![]() Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: Cinechrome Colour Test with Soap Boxes and Packets (1920)
Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: Cinechrome Colour Test with Soap Boxes and Packets (1920)
- Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: Cinechrome Colour Test with Soap Boxes and Packets (1920)
- Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: Cinechrome Colour Test with Soap Boxes and Packets (1920)
3 Images
Widely used in print media around 1900, the chromolithographic printing process was first adapted for the Laterna Magica and then utilized to produce early animated films primarily aimed at children. These films were usually very short ...
-
![]() [U-Boot]. Credit: Deutsches Filminstitut DIF. Photograph of the chromolithographic nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
[U-Boot]. Credit: Deutsches Filminstitut DIF. Photograph of the chromolithographic nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Box Der Film fürs Heimkino. Credit: Deutsches Filminstitut DIF. iPhone photo by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Box "Film for Home Cinema". Credit: Deutsches Filminstitut DIF. iPhone photo by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Box "Attention! Celluloid Film". Credit: Deutsches Filminstitut DIF. iPhone photo by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Boxes and loops. Credit: Deutsches Filminstitut DIF. iPhone photo by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Box and loops. Credit: Deutsches Filminstitut DIF. iPhone photo by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Film can for Chromolithographic Loop. Credit: Deutsches Filminstitut DIF. iPhone photo by Noemi Daugaard, SNSF Filmcolors
- Film can for Chromolithographic Loop. Credit: Deutsches Filminstitut DIF. iPhone photo by Noemi Daugaard, SNSF Filmcolors
119 Images in 3 Galleries
-
![]() Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
2 Images
“Chemicoior was the name under which the German Ufacolor Process was marketed in Britain. Ufacolor was also marketed under the name Spectracolor. The process used Agfa bipack negatives loaded with the emulsion sides facing and separated by a ...
-
![]() Source: Coe, Brian (1981): The History of Movie Photography. Westfield, N.J.: Eastview Editions. Film: Pagliacci (1937).
Source: Coe, Brian (1981): The History of Movie Photography. Westfield, N.J.: Eastview Editions. Film: Pagliacci (1937).
9 Images in 2 Galleries
Process for still photography in which light is filtered through a screen or transparent plate covered in lines or dots in the primary colors orange, green and violet. For the positive, the process relies on a support material which includes an ...
-
![]() Credit: Gert Koshofer Collection. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
Credit: Gert Koshofer Collection. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
5 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
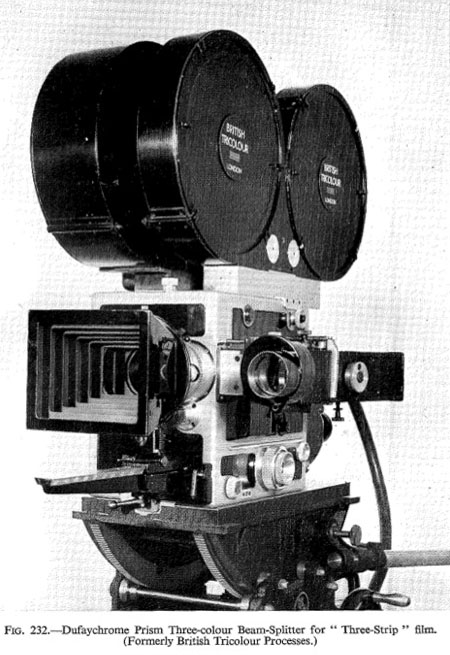
- Coote, Jack (1948): New Three-Color Camera, In: Journal of the Society of Motion Picture Engineers, vol. 50, June 1948, pp. 543-553.
- Coote, Jack (1948): New Three-Color Camera, In: Journal of the Society of Motion Picture Engineers, vol. 50, June 1948, pp. 543-553.
19 Images in 3 Galleries
“Following the premises of one of William Friese-Greene’s systems, this two-colour subtractive process required that two reels of film be printed in parallel through a lens fitted with a prism that split light in two directions, through red ...
“The Brewster Process.
(U.S.P. 1,752,477. 1930-)
Camera. – P. D. Brewster, an American inventor, who was one of the first to apply the bipack system to colour cinematography, has a number of patents to his credit covering various cameras and ...
-
![]() Dyes of Brewster color. Credit: Brian Pritchard.
Dyes of Brewster color. Credit: Brian Pritchard.
- Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
52 Images in 1 Gallery
The procedure for obtaining the lenticular elements in relief required a series of steps: starting from three black and white positive color separations, obtained with any of the available methods, three matrices were printed, from which the film to ...
-
![]() Projection of lenticular film in Bocca-Rudatis. Refraction of light beams through lens. Source: Pierotti, Federico (2016): Un'archeologia del colore nel cinema italiano. Dal Technicolor ad Antonioni. Pisa: Edizioni ETS, p. 81.
Projection of lenticular film in Bocca-Rudatis. Refraction of light beams through lens. Source: Pierotti, Federico (2016): Un'archeologia del colore nel cinema italiano. Dal Technicolor ad Antonioni. Pisa: Edizioni ETS, p. 81.
1 Image
“Inevitably, the success of Kinemacolor led to the appearance of imitations. One company, Friese Greene Patents Ltd had been formed in 1908 to exploit several patents, mostly impractical, filed by Friese Greene. From this came a new company, ...
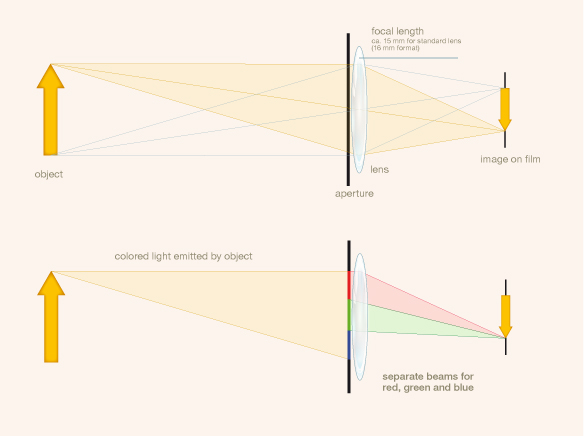
A. Gurtner (Eng. P. 7924/03; U.S.P. 730454), used a front element that was sensitive only to the blue, and a rear element that was sensitive up to but not including the red. He was the first person to suggest that the two films or plates be placed ...
-
![]() Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ede, François (1994): Jour de fête ou la couleur retrouvée. Cahiers du Cinéma: Paris.
- Schmidt, Richard / Kochs, Adolf (1943): Farbfilmtechnik. Eine Einführung für Filmschaffende. Berlin: Hesse, pp. 54-72. (Schriftenreihe der Reichsfilmkammer, 10.) (in German) [quote id='6']
5 Images
“R. Berthon patented the use of a lens diaphragm with three apertures, covered respectively with red, green and blue-violet filters, and a sensitive surface on a support, the other side of which was impressed with hemi-spherical, transparent, ...
-
![]() Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ede, François (1994): Jour de fête ou la couleur retrouvée. Cahiers du Cinéma: Paris.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Source: Heymer, Gerd (1933): Auflösungsvermögen und Farbwiedergabe in der Farbrasterphotographie. In: Veröffentlichungen des wissenschaftlichen Zentral-Laboratoriums der photographischen Abteilung Agfa, 3, 1933, pp. 188-207.
4 Images
“Camera.—An interesting camera has been made by the Société Chromofilm, Paris. An astonishing mechanism moves the entire gate, and film within it, at each exposure, with reference to the normal fixed objective. Three miniature negatives are ...
-
![]() Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
3 Images in 1 Gallery
Several attempts were made to apply the Autochrome process invented by the Lumière brothers to motion pictures.
Transparent potato starch grains with a diameter of 15–20 micrometer were colored in the additive primaries red, green and blue. The ...
-
![]() Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Cinécolor, mosaic screen, ca. 1929. Credit: Gert Koshofer Collection. Sample No. 68. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Magnification of an image area. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
27 Images in 2 Galleries
“The Autochrome process was the first fully practical single-plate colour process to reach the photographic public. It was easy to use. The plate was loaded into a conventional holder, glass to the front. The exposure was made through a yellow ...
-
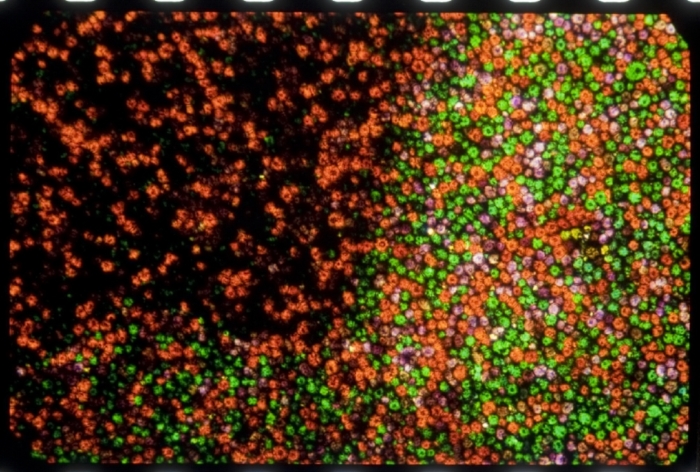
![]() Photomicrograph (50x) of an Autochrome mosaic screen. Credit: Courtesy of George Eastman House, International Museum of Photography and Film.
Photomicrograph (50x) of an Autochrome mosaic screen. Credit: Courtesy of George Eastman House, International Museum of Photography and Film.
- Source: Lavédrine, Bertrand (2009): Photographs of the Past. Process and Preservation. Los Angeles: Getty Publications.
- Source: Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press.
- Source: Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press.
- Source: Holme, Charles (1908): Colour Photography, and Other Recent Developments of the Art of the Camera. London, Paris, New York.: Offices of The Studio.
- Source: Holme, Charles (1908): Colour Photography, and Other Recent Developments of the Art of the Camera. London, Paris, New York.: Offices of The Studio.
- Credit: Klosterarchiv Einsiedeln. http://www.klosterarchiv.ch/earchiv_liste.php?Objektyp_physisch=Glasautochrom&start=1
- Credit: Klosterarchiv Einsiedeln. http://www.klosterarchiv.ch/earchiv_liste.php?Objektyp_physisch=Glasautochrom&start=1
- Credit: Klosterarchiv Einsiedeln. http://www.klosterarchiv.ch/earchiv_liste.php?Objektyp_physisch=Glasautochrom&start=1
- Credit: Klosterarchiv Einsiedeln. http://www.klosterarchiv.ch/earchiv_liste.php?Objektyp_physisch=Glasautochrom&start=1
- Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 70.
- Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 26.
- Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 65.
- Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 27.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 235.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 64.
16 Images
“R. Berthon and M. Audibert patented a method of obtaining a virtual image by means of an anterior lens and prisms or mirrors. This idea was further improved upon in E.P. 17,023, 1913. In F.P. 458,040 Audibert proposed to use a negative front lens ...
-
![]() Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
2 Images
-
![]() Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.