- All Categories
- Bibliography
- Chromogenic monopack
- Chromolytic multilayer
- Color separation
- Double-coated / bi-pack
- Edge Codes and Identification
- Hand coloring
- Other
- Printing / dye-transfer
- Printing / pigment process
- Screen processes
- Spatial synthesis (multiple lenses, beam splitter)
- Stencil coloring (pochoir, Pathécolor)
- Temporal synthesis (rotary filters)
- Theory
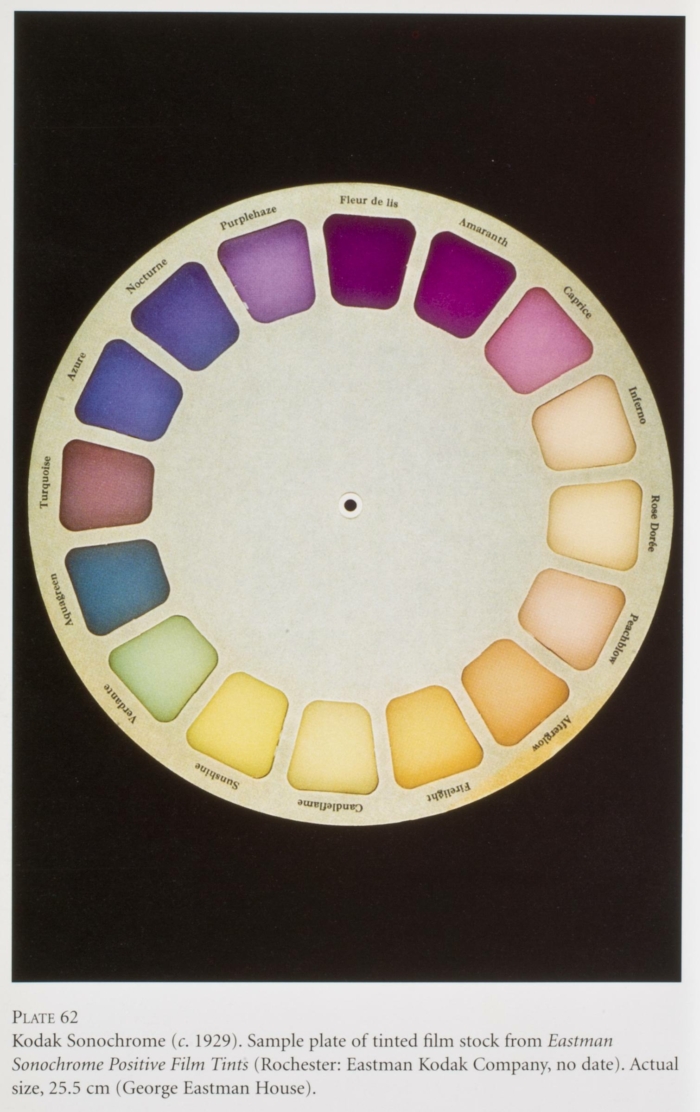
- Tinting
- Toning
-
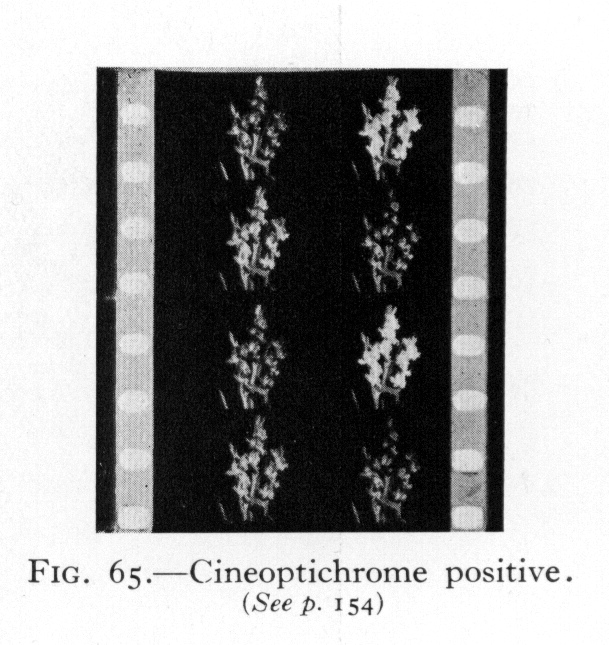
![]() Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Source: Coe, Brian (1981): The History of Movie Photography. Westfield, N.J.: Eastview Editions.
- Schmidt, Richard / Kochs, Adolf (1943): Farbfilmtechnik. Eine Einführung für Filmschaffende. Berlin: Hesse, pp. 54-72. (Schriftenreihe der Reichsfilmkammer, 10.) (in German) [quote id='5']
- Schmidt, Richard / Kochs, Adolf (1943): Farbfilmtechnik. Eine Einführung für Filmschaffende. Berlin: Hesse, pp. 54-72. (Schriftenreihe der Reichsfilmkammer, 10.) (in German) [quote id='5']
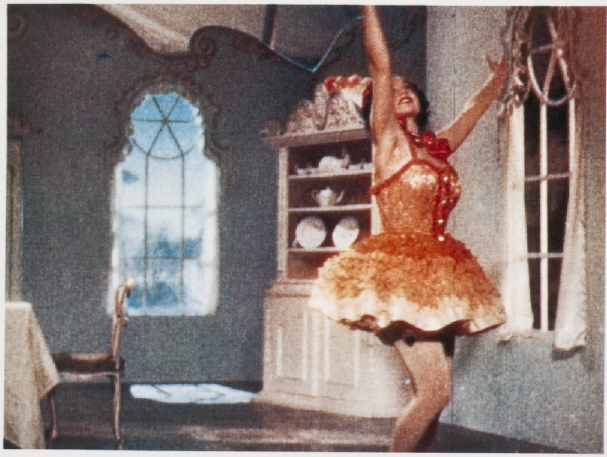
9 Images in 1 Gallery
“In 1930 Mannes and Godowsky were invited to join the staff of the Kodak Research Laboratory, where they concentrated on methods of processing multilayer films, while their colleagues worked out ways of manufacturing them. The result was the new Kodachrome film, launched in 1935. Three very thin emulsion layers were coated on film base, the emulsions being sensitised with non-wandering dyes to red, green and blue light, the red-sensitive layer being at the bottom.” (Coe, Brian (1978): Colour Photography. The First Hundred Years 1840-1940. London: Ash & Grant, pp. 121 ff.)
-
![]() Credit: Lichtspiel / Kinemathek Bern. Film: New York, Taufe und Ausflug (CH 1954, Donald Brun).
Credit: Lichtspiel / Kinemathek Bern. Film: New York, Taufe und Ausflug (CH 1954, Donald Brun).
- Surface emulsion side, raking light. Credit: Carsta Knaack, HTW Berlin. Film: Regular 8mm home movie, anonymous 1975.
92 Images in 6 Galleries
-
![]() Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
- Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
- Source: Kistler, L. R. (1945): The Projection of Thomascolor Motion Pictures. In: International Projectionist, 20,7, Jul., pp. 12–14.
- Source: Kistler, L. R. (1945): The Projection of Thomascolor Motion Pictures. In: International Projectionist, 20,7, Jul., pp. 12–14.
- Left: Thomascolor camera lens mount for converting standard motion picture camera into Thomascolor. Right: A closeup of the Thomascolor projector lens mount for standard film projectors. The inventor points out that this is all that is needed to convert a standard projector to Thomascolor. Source: Anonymous (1944): Thomascolor. Four-Color Process For Motion Pictures. In: International Projectionist, 19,10, Oct., pp. 7–9.
5 Images
-
![]() Cross-section of the optical system displaying the different lenses, the prism and the four filters. Source: Pierotti, Federico (2016): Un'archeologia del colore nel cinema italiano. Dal Technicolor ad Antonioni. Pisa: Edizioni ETS, p. 71.
Cross-section of the optical system displaying the different lenses, the prism and the four filters. Source: Pierotti, Federico (2016): Un'archeologia del colore nel cinema italiano. Dal Technicolor ad Antonioni. Pisa: Edizioni ETS, p. 71.
- 35mm black and white film strip with four equal-sized images (left) and 16mm projector with Cristiani-Mascarini optical system. Source: Pierotti, Federico (2016): Un'archeologia del colore nel cinema italiano. Dal Technicolor ad Antonioni. Pisa: Edizioni ETS, p. 71.
2 Images
-
![]() Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. A History of Motion Picture Color Technology.
Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. A History of Motion Picture Color Technology.
- Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
2 Images
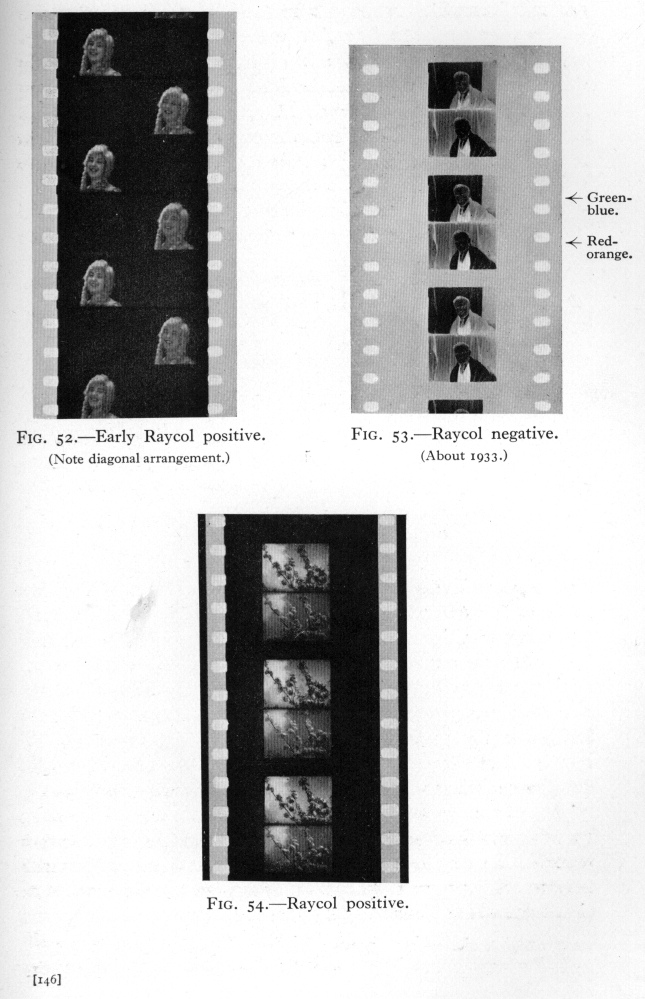
Dufaycolor was a regular line screen process whereby the incident light was filtered through a pattern of tiny color patches created by lines in red, green and blue, the so called réseau.
-
![]() Reversal Colour Positive. Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: A Colour Box (GB 1935, Len Lye).
Reversal Colour Positive. Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: A Colour Box (GB 1935, Len Lye).
- Microscopic image of the filter structure of a Dufaycolor film. The Emulsion has been removed. The visible structures are not silver grain but the structure of the filter layers. Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Microscopic images of Dufaycolor film with the focus set at different points within the emulsion and filter layers. The images have been chained to show a travelling through the 3-dimensional structure of the layers. Credit: David Pfluger, conversion to video by Martin Weiss, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
231 Images in 9 Galleries
-
![]() Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
3 Images
-
![]() Source: Dubray, J.A. (1933): The Morgana Process In: Journal of the Society of Motion Picture Engineers 21,5, 1933, pp. 403-412.
Source: Dubray, J.A. (1933): The Morgana Process In: Journal of the Society of Motion Picture Engineers 21,5, 1933, pp. 403-412.
1 Image
-
![]() Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
40 Images
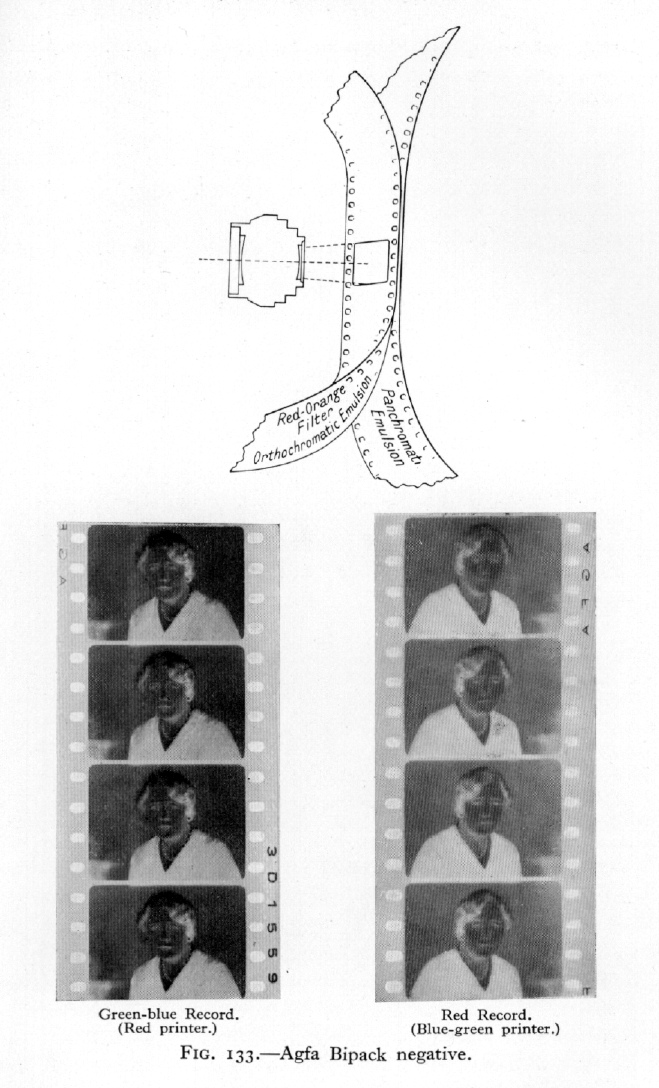
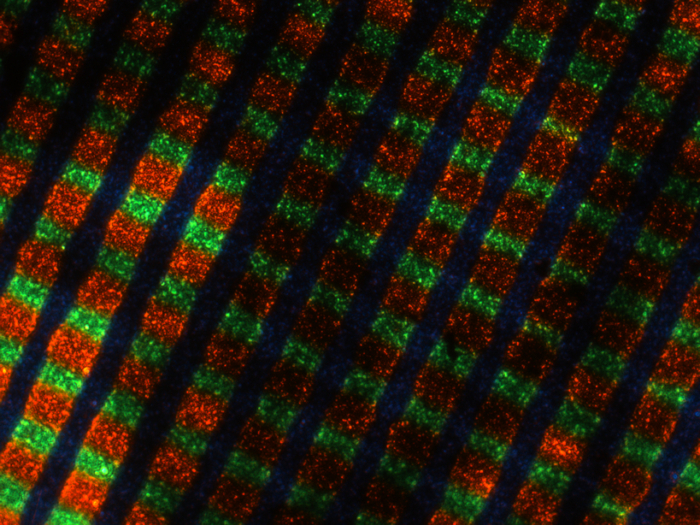
Gasparcolor was the first three-color multi-layer monopack film available for practical use. It was a double-coated print film with a cyan layer on one side and two layers dyed magenta and yellow on the other side (see illustrations).
-
![]() Uit het rijk der kristallen (NDL 1927?, J.C. Mol). Credit: EYE Film Museum. Photographs of the Dufaycolor and Gasparcolor nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
Uit het rijk der kristallen (NDL 1927?, J.C. Mol). Credit: EYE Film Museum. Photographs of the Dufaycolor and Gasparcolor nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Kreise (English title Circles) (Oskar Fischinger, GER 1933-34) Oskar Fischinger's own nitrate print. Credit: Library of Congress, (c) Fischinger Trust, courtesy Center for Visual Music. Photograph Fischinger's own nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Credit: (c) Fischinger Trust, courtesy Center for Visual Music. Film: Allegretto by Oskar Fischinger (1936-1943).
- Credit: (c) Fischinger Trust, courtesy Center for Visual Music. Film: Gasparcolor tests by Oskar Fischinger, c. 1933-34.
- Credit: Cinémathèque suisse. Film: Komposition in Blau (Composition in Blue) AKA Lichtkonzert Nr. 1 (Light-Concert No. 1) (GER 1935, Oskar Fischinger).
- Credit: Cinémathèque suisse. © Fischinger Trust, courtesy Center for Visual Music. Film: Komposition in Blau (Composition in Blue) AKA Lichtkonzert Nr. 1 (Light-Concert No. 1) (GER 1935, Oskar Fischinger).
- Credit: Cinémathèque suisse. © Fischinger Trust, courtesy Center for Visual Music. Film: Komposition in Blau (Composition in Blue) AKA Lichtkonzert Nr. 1 (Light-Concert No. 1) (GER 1935, Oskar Fischinger).
- Source: Coe, Brian (1981): The History of Movie Photography. Westfield, N.J.: Eastview Editions.
- Color chart on Agfa Tripofilm. This was the raw stock used for Gasparcolor in Germany until about 1939. Source: Arens, Hans; Heymer, Gerd (1939): Die „Agfa-Farbentafel für Farbenphotographie“. In: Veröffentlichungen des wissenschaftlichen Zentral-Laboratoriums der photographischen Abteilung Agfa, Vol. 6, 1939, pp. 225-229. Leipzig: Hirzel. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 213.
398 Images in 24 Galleries
-
![]() Projection of lenticular film in Bocca-Rudatis. Refraction of light beams through lens. Source: Pierotti, Federico (2016): Un'archeologia del colore nel cinema italiano. Dal Technicolor ad Antonioni. Pisa: Edizioni ETS, p. 81.
Projection of lenticular film in Bocca-Rudatis. Refraction of light beams through lens. Source: Pierotti, Federico (2016): Un'archeologia del colore nel cinema italiano. Dal Technicolor ad Antonioni. Pisa: Edizioni ETS, p. 81.
1 Image
-
![]() Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 72.
Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 72.
1 Image
-
![]() Source: Coe, Brian (1981): The History of Movie Photography. Westfield, N.J.: Eastview Editions. Film: Pagliacci (1937).
Source: Coe, Brian (1981): The History of Movie Photography. Westfield, N.J.: Eastview Editions. Film: Pagliacci (1937).
9 Images in 2 Galleries
-
![]() Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 76.
Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 76.
1 Image
-
![]() Credit: Image courtesy of the Academy Film Archive. Film: Gone with the Wind (USA 1939, Victor Fleming). Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
Credit: Image courtesy of the Academy Film Archive. Film: Gone with the Wind (USA 1939, Victor Fleming). Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Film: Samson and Delilah (US 1949, Cecil B. DeMille), trailer.
- Photomicrograph, 50x. Credit: Norbert Wey, Institute of Pathology, University of Zurich.
- Photomicrograph, 100x. Credit: Norbert Wey, Institute of Pathology, University of Zurich.
1881 Images in 65 Galleries
-
![]() Color reconstruction. Credit: Gisela Harich-Hamburger, Diplomrestauratorin (FH).
Color reconstruction. Credit: Gisela Harich-Hamburger, Diplomrestauratorin (FH).
- Source: Heymer, Gerd (1933): Auflösungsvermögen und Farbwiedergabe in der Farbrasterphotographie. In: Veröffentlichungen des wissenschaftlichen Zentral-Laboratoriums der photographischen Abteilung Agfa, 3, 1933, pp. 188-207.
- Source: Weil, F. (1933): The Optical-Photographic Principles of the Agfacolor Process. In: Journal of the Society of Motion Picture Engineers, 20, (April, 1933), No. 4, p. 301-308.
- Both the Kodak and Agfa lenticular processes required the correct banded filter to be used with each different batch of panchromatic film. These two filters were for different batches of Agfacolor used in a Leica camera.. Source: Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ede, François (1994): Jour de fête ou la couleur retrouvée. Cahiers du Cinéma: Paris.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Magnification 5x, front. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification 10x, back. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification 20x, front. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Reflection on Agfacolor lenticular film. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. In: Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Reconstruction of lenticular film by Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland in the framework of their research project doLCE
- Agfacolor Lenticular sample from the Kodak Film Samples Collection at the National Science and Media Museum in Bradford. Credit: National Science and Media Museum Bradford. Photographs by Barbara Flueckiger in collaboration with Noemi Daugaard.
- Analog reconstruction by Giorgio Trumpy, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors
15 Images
-
![]() Credit: Harvard Film Archive, George Huizinga Collection, item no. 10454. Film: Prehistoric Women (1951).
Credit: Harvard Film Archive, George Huizinga Collection, item no. 10454. Film: Prehistoric Women (1951).
- Credit: Harvard Film Archive, George Huizinga Collection, item no. 10454. Film: Prehistoric Women (1951).
- Source: Coe, Brian (1981): The History of Movie Photography. Westfield, N.J.: Eastview Editions.
- Reflection on Cinecolor print. Credit: Image courtesy of the 20th Century Fox Collection at the Academy Film Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger
- Reflection on Cinecolor 16 mm print. Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger
93 Images in 9 Galleries
-
![]() Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
2 Images
-
![]() Screenshot from Mayorov, Nikolai (2012): Soviet Colours. Translated by Birgit Beumers. In: Studies in Russian & Soviet Cinema, 6:2, pp. 241–255. doi: 10.1386/srsc.6.2.241_1 Courtesy of Nikolai Mayorov.
Screenshot from Mayorov, Nikolai (2012): Soviet Colours. Translated by Birgit Beumers. In: Studies in Russian & Soviet Cinema, 6:2, pp. 241–255. doi: 10.1386/srsc.6.2.241_1 Courtesy of Nikolai Mayorov.
1 Image
-
![]() Rota Farbenfilm Samples (Kodak Film Samples Collection). Credit: National Science and Media Museum Bradford. Photographs of the Rotacolor Prints by Josephine Diecke, SNSF project Film Colors. Technologies, Cultures, Institutions and Joëlle Kost, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
Rota Farbenfilm Samples (Kodak Film Samples Collection). Credit: National Science and Media Museum Bradford. Photographs of the Rotacolor Prints by Josephine Diecke, SNSF project Film Colors. Technologies, Cultures, Institutions and Joëlle Kost, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
13 Images in 2 Galleries
-
![]() Magnification of an image area. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
Magnification of an image area. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Color chart. Credit: Guido Seeber Nachlass, Deutsche Kinemathek, Berlin. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92.
- Credit: Guido Seeber Nachlass, Deutsche Kinemathek, Berlin. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Credit: Bundesarchiv-Filmarchiv, photo: Marian Stefanowski. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92. Film: Bunte Tierwelt. Studien in Hagebecks Tierpark in Stellingen (1931).
- Credit: Bundesarchiv-Filmarchiv, photo: Marian Stefanowski. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92. Film: Karneval (1936).
- Credit: Bundesarchiv-Filmarchiv, photo: Jeanpaul Goergen. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92. Film: Bunte Fischwelt (1936).
- Credit: Bundesarchiv-Filmarchiv, photo: Marian Stefanowski. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92. Film: Karneval (1936).
- Credit: Deutsches Filminstitut DIF (Vicas Nachlass), photo: Jeanpaul Goergen. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92. Film: Potsdam (1934).
- Credit: Bundesarchiv-Filmarchiv, photo: Marian Stefanowski. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92. Film: Farben machen froh (1938).
- Magnification 5x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification 10x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification 20x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. In:Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Magnification of an image area. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. In:Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Reflection on Ufacolor film. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. In:Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- An opened splice of an Ufacolor positive shows the two colors used in the process. Credit: David Pfluger. Source: David Pfluger’s collection.
136 Images in 7 Galleries
-
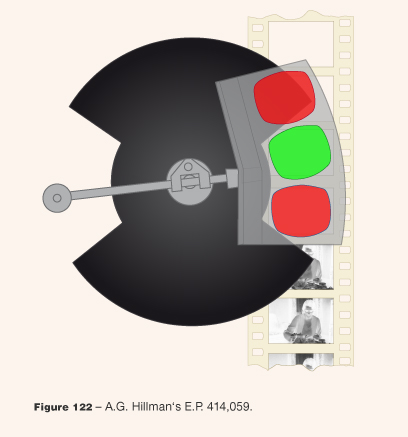
![]() Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
2 Images
-
![]() Mysore Yesterday and Tomorrow Credit: Image courtesy of the 20th Century Fox Collection at the Academy Film Archive. Photograph: Barbara Flueckiger.
Mysore Yesterday and Tomorrow Credit: Image courtesy of the 20th Century Fox Collection at the Academy Film Archive. Photograph: Barbara Flueckiger.
23 Images in 2 Galleries
-
![]() Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
3 Images
-
![]() Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
42 Images
-
![]() Strange Birds (US 1930, Mack Sennett). Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph of the nitrate print: Barbara Flueckiger
Strange Birds (US 1930, Mack Sennett). Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph of the nitrate print: Barbara Flueckiger
- Magnification. Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Strange Birds (1930)
18 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
1 Image
-
![]() Dyes of Brewster color. Credit: Brian Pritchard.
Dyes of Brewster color. Credit: Brian Pritchard.
- Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
52 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Rotating filters permitting to adjust tonality and intensity of the colors. Source: Pierotti, Federico (2016): Un'archeologia del colore nel cinema italiano. Dal Technicolor ad Antonioni. Pisa: Edizioni ETS, p. 62
Rotating filters permitting to adjust tonality and intensity of the colors. Source: Pierotti, Federico (2016): Un'archeologia del colore nel cinema italiano. Dal Technicolor ad Antonioni. Pisa: Edizioni ETS, p. 62
1 Image
-
![]() Credit: Technicolor Collection. George Eastman House Moving Image Department. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
Credit: Technicolor Collection. George Eastman House Moving Image Department. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Credit: Technicolor Collection. George Eastman House Moving Image Department. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Credit: Technicolor Collection. George Eastman House Moving Image Department. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
3 Images
-
![]() Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
11 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 70.
Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 70.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 70.
- Photomicrograph (20x) of a Finlay screen. Credit: Courtesy of George Eastman House, International Museum of Photography and Film.
- Finlay box. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 39.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 39.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 40.
9 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
13 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Magnification, 20x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
Magnification, 20x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification, 10x. Credit: Photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification, 5x. Credit: Photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. In: Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Magnification of an image area. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Reflection on the Sirius film, front. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Reflection on the Sirius film, back. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
142 Images in 4 Galleries
-
![]() Kodacolor lenticular filter for the projector. Lichtspiel / Kinemathek Bern.
Kodacolor lenticular filter for the projector. Lichtspiel / Kinemathek Bern.
- Credit: Rudolf Gschwind, Imaging and Media Lab, University of Basel.
- Magnification of an area. Credit: Rudolf Gschwind, Imaging and Media Lab, University of Basel.
- Color reconstruction test. Credit: Rudolf Gschwind, Imaging and Media Lab, University of Basel.
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Microscopic linear lens structure of Kodacolor lenticular film. Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Acetate plastic base of Kodacolor lenticular film embedded in epoxide resin. The emulsion layer usually placed on the opposite side of the acetate base has been removed beforehand and is therefore not visible. Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Focal travelling through the 3-dimensional structure of Kodacolor lenticular film. In the beginning the linear lenticular structure is visible and towards the end the emulsion layer comes into focus and the granular structure defined by the density of the silver is visible. In this shot the lenticules were showing towards the light source and the emulsion towards the camera. This enables an undistorted recording of the emulsion layer. Credit: David Pfluger, editing by Martin Weiss, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Focal travelling through the 3-dimensional structure of Kodacolor lenticular film. In the beginning the linear lenticular structure is visible and towards the end the emulsion layer comes into focus. In this shot the lenticules were allocated towards the lens of the microscope and the light source at the side of the emulsion similar to the configuration in projection. As a consequence the graininess of the emulsion is not visible as with the film flipped to the other side. The structure is optically distorted perpendicular to the linear structure of the lenticules. Credit: David Pfluger, editing by Martin Weiss, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
24 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Cinécolor, mosaic screen, ca. 1929. Credit: Gert Koshofer Collection. Sample No. 68. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Magnification of an image area. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
27 Images in 2 Galleries
-
![]() Iridescence on Multicolor print, reflection properties. Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger
Iridescence on Multicolor print, reflection properties. Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger
- Magnification 20x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification 10x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification 5x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Fox Movietone Follies of 1929.
- Source: Coe, Brian (1981): The History of Movie Photography. Westfield, N.J.: Eastview Editions.
- Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Magnification of an area. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Reflection properties. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
72 Images in 6 Galleries
-
![]() Credit: Paolo Cherchi Usai. Source: Cherchi Usai, Paolo (2000): Silent Cinema. London: BFI.
Credit: Paolo Cherchi Usai. Source: Cherchi Usai, Paolo (2000): Silent Cinema. London: BFI.
- Source: The International Photographer, July 1929
- Source: The International Photographer, July 1929
- Source: The International Photographer, July 1929
- Source: The International Photographer, July 1929
79 Images in 3 Galleries
-
![]() Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress.
Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress.
2 Images
The third Technicolor process used the same camera as process no. II to combine a pair of frames of the red and green record respectively on the b/w negative (see image). In contrast to the former process, however, the two images were printed on one side of the positive by the dye transfer or imbibition process.
-
![]() King of Jazz (USA 1930, John Murray Anderson). Credit: Library of Congress. Photographs of the Technicolor No. III dye-tranfer nitrate print from 1930 and 1931 by Olivia Kristina Stutz, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
King of Jazz (USA 1930, John Murray Anderson). Credit: Library of Congress. Photographs of the Technicolor No. III dye-tranfer nitrate print from 1930 and 1931 by Olivia Kristina Stutz, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
- Credit: Images courtesy of the Margaret Herrick Library. Film: Corrine Griffith in The Garden of Eden. Photograph: Barbara Flueckiger.
- Credit: George Eastman House Motion Picture Department Collection. Film: Buffalo Bill’s Last Fight (USA 1927, John W. Noble).
- Technicolor ad in Photoplay, 1930. Source: Photoplay, 1930, see Media History Digital Library
- Technicolor ad in Photoplay, 1930. Source: Photoplay, 1930, see Media History Digital Library
- Photomicrograph, 10x. Credit: Silvana Konermann.
- Photomicrograph, 20x. Credit: Silvana Konermann.
- Doctor X (USA 1932, Michael Curtiz). Credit: UCLA Film & Television Archive. Photographs of the Technicolor No. III dye-tranfer nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Doctor X (USA 1932, Michael Curtiz). Credit: UCLA Film & Television Archive. Photographs of the Technicolor No. III dye-tranfer nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
1298 Images in 38 Galleries
-
![]() Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 74.
Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 74.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 44.
2 Images
-
![]() Credit: Gert Koshofer Collection. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
Credit: Gert Koshofer Collection. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
5 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
2 Images
-
![]() Magnification 20x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
Magnification 20x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Magnification 10x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Magnification 5x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. In: Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Source: Coe, Brian (1981): The History of Movie Photography. Westfield, N.J.: Eastview Editions.
- Magnification of an image area. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
78 Images in 2 Galleries
-
![]() Credit: George Eastman House Motion Picture Department Collection. Film: The Old Family Toothbrush (USA 1925).
Credit: George Eastman House Motion Picture Department Collection. Film: The Old Family Toothbrush (USA 1925).
1 Image
-
![]() Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 73.
Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 73.
1 Image
-
![]() Russian Ideas in Clothes! (USA 1922). Credit: UCLA Film & Television Archive. Photographs of the nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
Russian Ideas in Clothes! (USA 1922). Credit: UCLA Film & Television Archive. Photographs of the nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
21 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ede, François (1994): Jour de fête ou la couleur retrouvée. Cahiers du Cinéma: Paris.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Microscopic image of a piece of Keller-Dorian lenticular film embedded in epoxide resin. The 3-dimensional structure of the lenticules is visible as well as the thin emulsion layer on the other side of the acetate base. Credit: Sample preparation and imaging by the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Lenticular surface of the acetate plastic base of Keller-Dorian lenticular film. On the back plane of the acetate layer and therefore out of focus in this image, structures defined by the silver image in the emulsion layer can be perceived. Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Hexagonal structure of the lenticules of Keller-Dorian lenticular film. Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Microscopic images of the Keller-Dorian lenticular structure with the focus set at different points. The images have been chained to show a travelling through the 3-dimensional structure of the bee-hive shaped lenticules. Credit: David Pfluger, conversion to video by Martin Weiss, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
14 Images in 2 Galleries
The first subtractive 2 color process introduced by Technicolor captured the incoming light through a beam splitter with red and green filters also. However, in contrast to the first Technicolor process, the two b/w images were recorded on one negative strip. This was achieved by the pull-down of two frames simultaneously, a process that required the double speed in the camera. These two frames were arranged in pairs, whereby the green record was inverted up-side down (see image).
-
![]() The Phantom of the Opera (USA 1925, Rupert Julian). Credit: UCLA Film & Television Archive. Photographs of the nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
The Phantom of the Opera (USA 1925, Rupert Julian). Credit: UCLA Film & Television Archive. Photographs of the nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Credit: Images courtesy of the Margaret Herrick Library. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Source: Coe, Brian (1981): The History of Movie Photography. Westfield, N.J.: Eastview Editions.
- Apparently test pieces, these clippings may well be the oldest surviving samples of the process in existence. Ruedel (2009: 55). Credit: George Eastman House Motion Picture Department Collection. Source: Ruedel, Ulrich (2009): The Technicolor Notebooks at the George Eastman House. In: Film History, Volume 21, Number 1, 2009, pp. 47-60.
- Apparently test pieces, these clippings may well be the oldest surviving samples of the process in existence. Ruedel (2009: 55); color reconstruction of the images shown above. Credit: George Eastman House Motion Picture Department Collection. Source: Ruedel, Ulrich (2009): The Technicolor Notebooks at the George Eastman House. In: Film History, Volume 21, Number 1, 2009, pp. 47-60.
- Apparently test pieces, these clippings may well be the oldest surviving samples of the process in existence. Ruedel (2009: 55). Credit: George Eastman House Motion Picture Department Collection. Source: Ruedel, Ulrich (2009): The Technicolor Notebooks at the George Eastman House. In: Film History, Volume 21, Number 1, 2009, pp. 47-60.
- Arrangement of the two records on the camera negative. Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress.
- Film: Stage Struck (USA 1925, Allan Dwan). Credit: Nitrate Frame Collection. George Eastman House Moving Image Collection. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Film: Irene (USA 1926, Alfred E. Green). Credit: Nitrate Frame Collection. George Eastman House Moving Image Collection. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Film: Irene (USA 1926, Alfred E. Green). Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Film: Irene (USA 1926, Alfred E. Green). Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Film: Irene (USA 1926, Alfred E. Green). Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Film: Irene (USA 1926, Alfred E. Green). Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Film: Irene (USA 1926, Alfred E. Green). Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
133 Images in 8 Galleries
-
![]() Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 103.
Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 103.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 277.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 138.
3 Images
-
![]() Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Source: Coe, Brian (1981): The History of Movie Photography. Westfield, N.J.: Eastview Editions.
- Credit: Collection Gert Koshofer, Bergisch Gladbach (Germany).
16 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() The two colors visible at a splice. Credit: EYE Film Institute Amsterdam. Film: [Kleurenpracht].
The two colors visible at a splice. Credit: EYE Film Institute Amsterdam. Film: [Kleurenpracht].
- Credit: George Eastman House. Preserved by Carole Fodor, Haghefilm Digitaal fellow and graduate of The L. Jeffrey Selznick School of Film Preservation. Film: A Day with John Burroughs (Prizma, 1919).
- Credit: George Eastman House. Preserved by Carole Fodor, Haghefilm Digitaal fellow and graduate of The L. Jeffrey Selznick School of Film Preservation. Film: A Day with John Burroughs (Prizma, 1919).
- Credit: George Eastman House Motion Picture Department Collection. Film: The Land of the Great Spirit (1919).
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Orange.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Orange.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Orange.
399 Images in 14 Galleries
-
![]() Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
1 Image
-
![]() Polychromide samples from the Kodak Film Samples Collection at the National Science and Media Museum in Bradford.
Credit: National Science and Media Museum Bradford.
Photographs by Barbara Flueckiger in collaboration with Noemi Daugaard.
Polychromide samples from the Kodak Film Samples Collection at the National Science and Media Museum in Bradford.
Credit: National Science and Media Museum Bradford.
Photographs by Barbara Flueckiger in collaboration with Noemi Daugaard.
- Credit: Brian Pritchard
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 279.
66 Images in 2 Galleries
-
![]() Knowing Men (GB 1930, Elinor Glyn), negative. Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
Knowing Men (GB 1930, Elinor Glyn), negative. Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
3 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
- Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
2 Images
During the capturing of the film a beam-splitter in combination with filters in the camera divided the incoming light into a red and a green separation negative on black-and-white stock. When projected in the cinema the two images were combined simultaneously by additive mixture through corresponding red and green filters into one picture consisting of red and green colored light. The reduction of the whole color range to two colors (and their additive combinations) was necessary because of the complex optical arrangement.
-
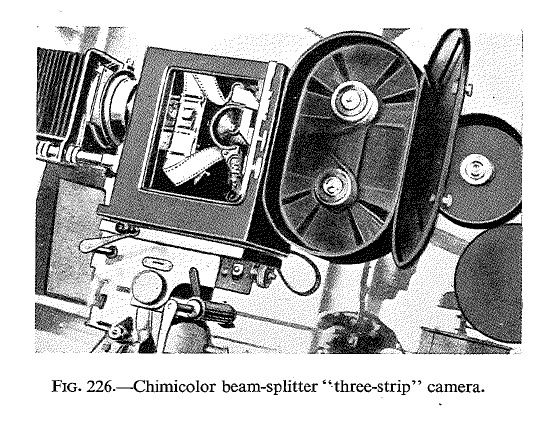
![]() The beam-splitter prism. Source: Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press.
The beam-splitter prism. Source: Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press.
6 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Magnification. Source: Coe, Brian (1978): Colour Photography. The First Hundred Years 1840-1940. London: Ash & Grant.
Magnification. Source: Coe, Brian (1978): Colour Photography. The First Hundred Years 1840-1940. London: Ash & Grant.
- Source: Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press.
- Source: Heymer, Gerd (1943): Die neuere Entwicklung der Farbphotographie. In: Ergänzungswerk zum Handbuch der wissenschaftlichen und angewandten Photographie. Wien: Julius Springer 1943, pp. 337-463.
- Source: Finger, Ehrhard (1998): Die Pioniere des Wolfener Farbfilms. In: Industrie- und Filmmuseum Wolfen e. V. (ed.), Die Filmfabrik Wolfen. Aus der Geschichte, Heft 2, pp. 16-36. (in German) [quote id='4']
- Source: Finger, Ehrhard (1998): Die Pioniere des Wolfener Farbfilms. In: Industrie- und Filmmuseum Wolfen e. V. (ed.), Die Filmfabrik Wolfen. Aus der Geschichte, Heft 2, pp. 16-36. (in German) [quote id='4']
- Source: Finger, Ehrhard (1998): Die Pioniere des Wolfener Farbfilms. In: Industrie- und Filmmuseum Wolfen e. V. (ed.), Die Filmfabrik Wolfen. Aus der Geschichte, Heft 2, pp. 16-36. (in German) [quote id='4']
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 73.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 73.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 72.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 76.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 42.
11 Images
-
![]() Black-and-white with Handschiegl in Lights of Old Broadway (USA 1925, Monta Bell). Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph of the nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
Black-and-white with Handschiegl in Lights of Old Broadway (USA 1925, Monta Bell). Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph of the nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Trail of '98 (USA 1929, Clarence Brown).
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Trail of '98 (USA 1929, Clarence Brown).
- Credit: Paolo Cherchi Usai. Source: Cherchi Usai, Paolo (2000): Silent Cinema. London: BFI. Film: Greed (USA 1925, Erich von Stroheim).
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Forbidden Fruit (USA 1921, Cecil B. DeMille).
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Forbidden Fruit (USA 1921, Cecil B. DeMille).
- Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press, p. 24.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Trail of '98 (USA 1929, Clarence Brown).
141 Images in 8 Galleries
-
![]() Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press. Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press. Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
- Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press. Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
3 Images
The Kodachrome process was invented in 1913 by John G. Capstaff for still photography and subsequently adapted to motion pictures. For the process two frames were advanced simultaneously, one located above the other. The light passed either through two lenses or through a beam-splitter, fitted with red and green filters. The release print was exposed through a beam-splitter whereby the alternate frames were projected onto either side of double-coated stock. After development by a usual b/w process, the film was tanned to harden the exposed areas. The soft areas were dyed red-orange and blue-green respectively.
-
![]() Two-Color Kodachrome Print (USA ca. 1925 to 1927, Anonymous). Credit: George Eastman Museum. Photographs of the Kodachrome two-color double coated stock from 1925 and 1927 by Olivia Kristina Stutz, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
Two-Color Kodachrome Print (USA ca. 1925 to 1927, Anonymous). Credit: George Eastman Museum. Photographs of the Kodachrome two-color double coated stock from 1925 and 1927 by Olivia Kristina Stutz, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. In:Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Magnification 5x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification 10x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification 20x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Kodachrome Two-color test from 1922, YouTube channel of the George Eastman House.
350 Images in 12 Galleries
-
![]() Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: Cinechrome Colour Test with Soap Boxes and Packets (1920)
Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: Cinechrome Colour Test with Soap Boxes and Packets (1920)
- Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: Cinechrome Colour Test with Soap Boxes and Packets (1920)
- Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: Cinechrome Colour Test with Soap Boxes and Packets (1920)