Select Category▼×
- All Categories
- Bibliography
- Chromogenic monopack
- Chromolytic multilayer
- Color separation
- Double-coated / bi-pack
- Edge Codes and Identification
- Hand coloring
- Other
- Printing / dye-transfer
- Printing / pigment process
- Screen processes
- Spatial synthesis (multiple lenses, beam splitter)
- Stencil coloring (pochoir, Pathécolor)
- Temporal synthesis (rotary filters)
- Theory
- Tinting
- Toning
-
![]() Photomicrograph 1000x, Agfachrome cross section. Credit: Carsta Knaack.
Photomicrograph 1000x, Agfachrome cross section. Credit: Carsta Knaack.
- Photomicrograph 500x, Agfachrome cross section. Credit: Carsta Knaack.
2 Images
Kodachrome II was introduced in 1961. It was the first film stock since 1936 that was specifically meant for amateur use. Eastman Kodak presented the material as superior to the ‘regular Kodachrome’. It supposedly had a higher speed of 25 ...
-
![]() La perception et l'imaginaire (FRA 1964, Éric Duvivier). Credit: Image'Est. Photographs of the Kodachrome II camera material by Bregt Lameris, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
La perception et l'imaginaire (FRA 1964, Éric Duvivier). Credit: Image'Est. Photographs of the Kodachrome II camera material by Bregt Lameris, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
- Les autopathes (FRA 1971, Éric Duvivier). Credit: Image'Est. Photographs of the kodachrome reversal by Bregt Lameris, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
- Hallucinations: Images du monde visionnaire (FRA 1963, Éric Duvivier). Credit: Image'Est. Photographs of undated Kodachrome II projection print by Bregt Lameris, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
84 Images in 5 Galleries
-
![]() cross section scheme of Ektachrome Type 5257 (and 5258). Scource: Groet, N.H./Murray, T.J./Osborne, C.E. (1960): Two High-Speed Color Films and a Reversal Print Film for Motion Picture Use. In: JSMPTE Vol. 69, p. 816.
cross section scheme of Ektachrome Type 5257 (and 5258). Scource: Groet, N.H./Murray, T.J./Osborne, C.E. (1960): Two High-Speed Color Films and a Reversal Print Film for Motion Picture Use. In: JSMPTE Vol. 69, p. 816.
1 Image
-
![]() Cross section scheme of Eastman Color Negative, Type 5250. Scource: Dundon, Merle L./Zwick, Daan M. (1959): A High Speed Color Negative Film. In: JSMPTE Vol 68, p. 736.
Cross section scheme of Eastman Color Negative, Type 5250. Scource: Dundon, Merle L./Zwick, Daan M. (1959): A High Speed Color Negative Film. In: JSMPTE Vol 68, p. 736.
1 Image
See Anscochrome and Super Anscochrome Daylight, type 225.
-
![]() Cross section of Ektachrome Commercial, Type 7255. Scource: Groet, N. H./Liberman, M./ Richey, F. (1959): An Improved Professional 16mm Reversal Camera Film. In: JSMPTE, Vol. 68, January 1959, p. 9.
Cross section of Ektachrome Commercial, Type 7255. Scource: Groet, N. H./Liberman, M./ Richey, F. (1959): An Improved Professional 16mm Reversal Camera Film. In: JSMPTE, Vol. 68, January 1959, p. 9.
1 Image
A chromogenic process based on Agfacolor, see detail page Agfacolor Neu / Agfacolor.
-
![]() Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jen počkej X (Nu, pogodi!) (Vjačeslav Kotěnočkin, USSR, 1976).
Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jen počkej X (Nu, pogodi!) (Vjačeslav Kotěnočkin, USSR, 1976).
- Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jen počkej X (Nu, pogodi!) (Vjačeslav Kotěnočkin, USSR, 1976).
- Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jen počkej X (Nu, pogodi!) (Vjačeslav Kotěnočkin, USSR, 1976).
- Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jen počkej X (Nu, pogodi!) (Vjačeslav Kotěnočkin, USSR, 1976).
- Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jen počkej X (Nu, pogodi!) (Vjačeslav Kotěnočkin, USSR, 1976).
- Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jen počkej X (Nu, pogodi!) (Vjačeslav Kotěnočkin, USSR, 1976).
- Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jak se Žofka postarala o svatbu (Adolf Born, Jaroslav Doubrava, Miloš Macourek, Czechoslovakia 1988).
- Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jak se Žofka postarala o svatbu (Adolf Born, Jaroslav Doubrava, Miloš Macourek, Czechoslovakia 1988).
- Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jak se Žofka postarala o svatbu (Adolf Born, Jaroslav Doubrava, Miloš Macourek, Czechoslovakia 1988).
- Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jak se Žofka postarala o svatbu (Adolf Born, Jaroslav Doubrava, Miloš Macourek, Czechoslovakia 1988).
- Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jak se Žofka postarala o svatbu (Adolf Born, Jaroslav Doubrava, Miloš Macourek, Czechoslovakia 1988).
- Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jak se Žofka postarala o svatbu (Adolf Born, Jaroslav Doubrava, Miloš Macourek, Czechoslovakia 1988).
- Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jak se Žofka postarala o svatbu (Adolf Born, Jaroslav Doubrava, Miloš Macourek, Czechoslovakia 1988).
- Eastmancolor negative on Fomacolor positive. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Slunečná laguna (Mirko Kačena, Czechoslovakia 1990).
- Eastmancolor negative on Fomacolor positive. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Slunečná laguna (Mirko Kačena, Czechoslovakia 1990).
- Eastmancolor negative on Fomacolor positive. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Slunečná laguna (Mirko Kačena, Czechoslovakia 1990).
- Eastmancolor negative on Fomacolor positive. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Slunečná laguna (Mirko Kačena, Czechoslovakia 1990).
- Eastmancolor negative on Fomacolor positive. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Slunečná laguna (Mirko Kačena, Czechoslovakia 1990).
18 Images
See Anscochrome and Super Anscochrome Tungsten, type 226.
-
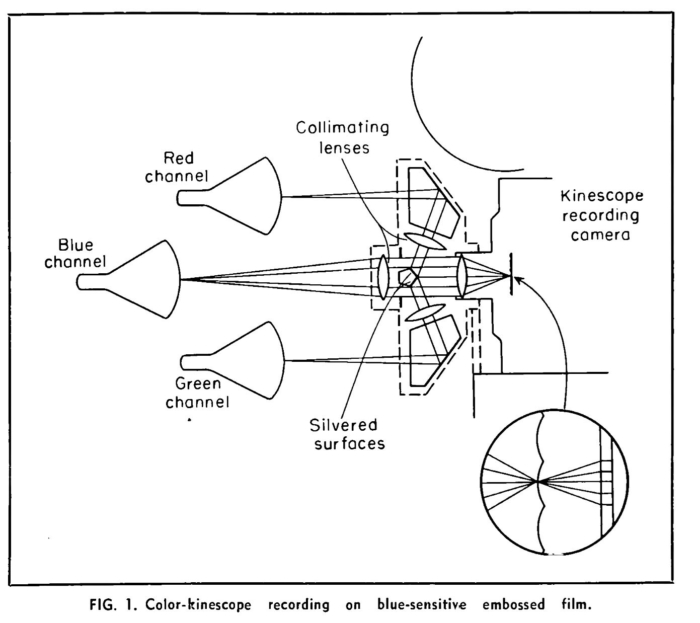
![]() Recording of a color video signal onto lenticular film.
Recording of a color video signal onto lenticular film.
- Playback of the color image on the lenticular film as a television signal.