-
![]() Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Captain Calamity (1936)
Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Captain Calamity (1936)
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Captain Calamity (1936)
Category: Double-coated / bi-pack▼×
- All Categories
- Bibliography
- Chromogenic monopack
- Chromolytic multilayer
- Color separation
- Edge Codes and Identification
- Hand coloring
- Other
- Printing / dye-transfer
- Printing / pigment process
- Screen processes
- Spatial synthesis (multiple lenses, beam splitter)
- Stencil coloring (pochoir, Pathécolor)
- Temporal synthesis (rotary filters)
- Theory
- Tinting
- Toning
-
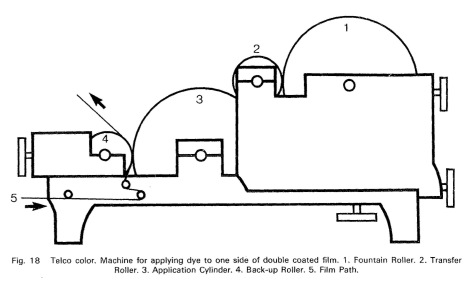
![]() Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
1 Image
-
![]() Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
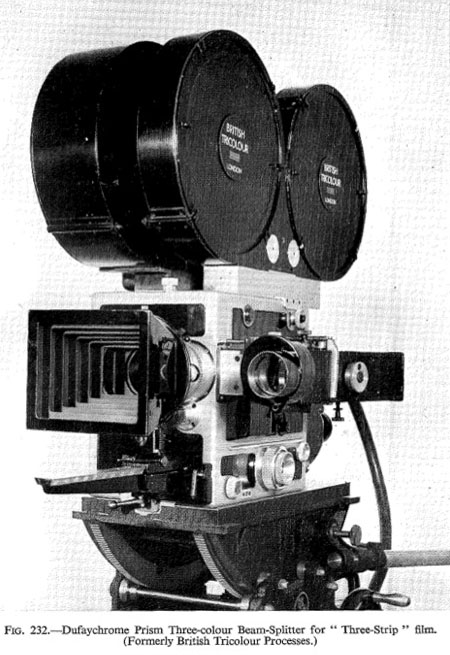
- Coote, Jack (1948): New Three-Color Camera, In: Journal of the Society of Motion Picture Engineers, vol. 50, June 1948, pp. 543-553.
- Coote, Jack (1948): New Three-Color Camera, In: Journal of the Society of Motion Picture Engineers, vol. 50, June 1948, pp. 543-553.
19 Images in 3 Galleries
“By the 1940s, most of the two-colour subtractive processes, apart from Cinecolor, were obsolete. The widespread use of the high-quality Technicolor process showed up the serious deficiencies in the simpler methods. The only significant new ...