Category: Screen processes▼×
- All Categories
- Bibliography
- Chromogenic monopack
- Chromolytic multilayer
- Color separation
- Double-coated / bi-pack
- Edge Codes and Identification
- Hand coloring
- Other
- Printing / dye-transfer
- Printing / pigment process
- Spatial synthesis (multiple lenses, beam splitter)
- Stencil coloring (pochoir, Pathécolor)
- Temporal synthesis (rotary filters)
- Theory
- Tinting
- Toning
“The Warner-Powrie process patented in 1905 was the earliest commercial process using a screen made with bichromated colloid. A glass plate was thinly coated with bichromated gelatin or fish glue and exposed to light through a screen having ...
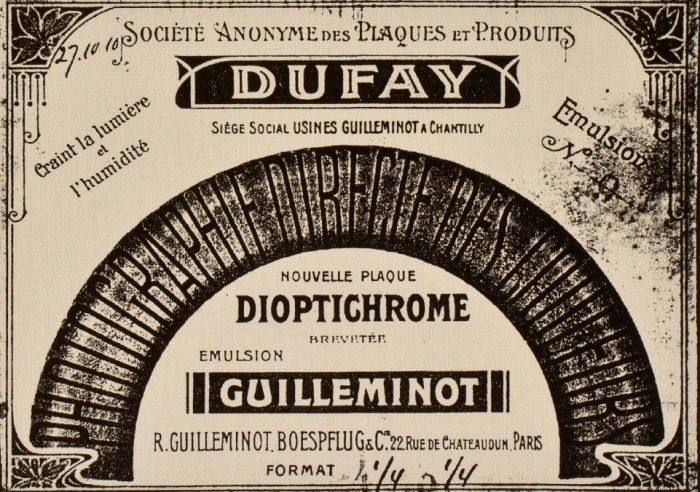
“The most successful of all the screen processes was the one initiated by Louis Dufay. Today the product is known as Dufaycolor, but it was first introduced about 1910 as the Dioptichrome plate. The first Dufay patents were assigned to an ...
-
![]() Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris. Film: Test for Jour de Fête.
Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris. Film: Test for Jour de Fête.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
3 Images
For a description of Spicer-Dufay see detail page on Dufaycolor)
-
![]() Magnification 20x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
Magnification 20x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Magnification 10x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Magnification 5x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. In: Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Source: Coe, Brian (1981): The History of Movie Photography. Westfield, N.J.: Eastview Editions.
- Magnification of an image area. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
78 Images in 2 Galleries
-
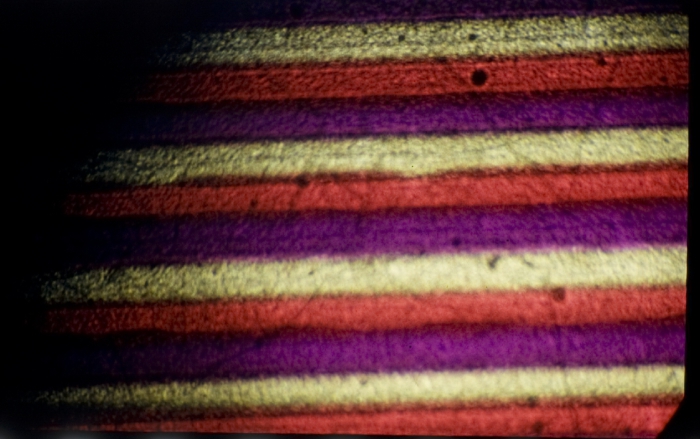
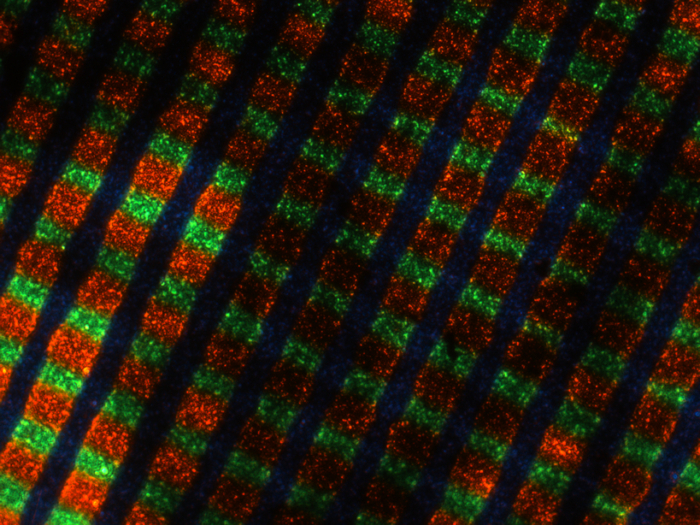
![]() Linear filter structure in Polavision instant Super8 film. The filter lines are running along the film strip. According to the image placement of the Super-8 motion picture standard the image is divided vertically into triplets of R, G and B filter lines. The emulsion layer has been removed before this image was taken.
Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
Linear filter structure in Polavision instant Super8 film. The filter lines are running along the film strip. According to the image placement of the Super-8 motion picture standard the image is divided vertically into triplets of R, G and B filter lines. The emulsion layer has been removed before this image was taken.
Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Linear filter structure in Polavision instant Super8 film with an emulsion layer of a high photographic density. With the focus set on the emulsion the linear structure of the coloured filters is not visible in this image. Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Comparision of the linear filter structure of Polachrome 35mm instant slide film and Polavision Super-8 motion picture film. While the technical concept behind the two film stocks is the same, the Super-8 film was produced with linear filters of a smaller width. Based on the given width of an RGB filter triplet and the 135 still image size there are about 920 horizontal RGB-triplets per image for a Polachrome slide. The Super-8 film image is rotated by 90° compared to the 135 film still image and has about 340 vertical RGB-triplets per frame. The positioning of the image content compared to the filter lines is indicated in the picture. Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Excerpt of a Polavision Super-8 home movie scanned on a Kinetta scanner in 4.8K resolution edge to edge. In post production a zoom in and out was applied to show the linear filter structure of Polavision film in motion. The zoom was based on image detail from the scan. No upres procedure was applied. Credit: Scanning and editing by Martin Weiss.
- A comparison of the colour filter structures of Dufaycolor, Autochrome and Polavision from Anonymous (1978): Ma il Polavision e' un'altra cosa!. Phototest Italiana, 41, Oct., pp 72–77.
- A comparison of the colour filter structures of Dufaycolor, Autochrome and Polavision from Anonymous (1978): Ma il Polavision e' un'altra cosa!. Phototest Italiana, 41, Oct., pp 72–77. Translation: David Pfluger and Giorgio Trumpy.
- The process of exposure and development of Polavision instant Super-8 film. From Anonymous (1978): Ma il Polavision e' un'altra cosa!. Phototest Italiana, 41, Oct., p. 74.
- The process of exposure and development of Polavision instant Super-8 film. From Anonymous (1978): Ma il Polavision e' un'altra cosa!. Phototest Italiana, 41, Oct., p. 74. Translation: David Pfluger and Giorgio Trumpy.
- "Polavision (top) vs. Kodachrome 40: These are blowups from closely matching frames of Debra Goldie, filmed simultaneously with a Polavision and a conventional super 8 camera, side by side, with the Twi Light quartz lamp mounted on top of the former. Subject distance was 6 ft., but the super 8 camera was focused for 10 ft. – same as the Polavision camera at its close-up setting. Both Polavision and Kodachrome 40 are closely equal in speed, but differ distinctly in structure, faithfulness of color rendition, and latitude, as is obvious from these frame reproductions. What can't be seen is the relative opacity of Polavision: according to our measurement, it transmits less than 9 percent as Kodachrome 40. However, the lab that made the duplicate transparency blow-ups of the frames found that it had to give a full six stops extra exposure." (Leavitt, Don; Drukker Leendert (1978): First Look: Polavision instant movies. In: Popular Photography, Feb., p. 68.)
- "C'est devant un immense agrandissement de l'intérieur d'une cassette Polavision sur la-quelle se découpe la silhouette de l'orateur (ci-contre à gauche) que le Dr Land présenta son invention. Ce document permet de distinguer les poulies de guidage du film (1 et 2), la réserve de produit de traitement et son bec ré-partiteur (3), la bobine débitrice (4), l'ensemble formé par le presseur de film et le prisme (5), la poulie d'entraînement du film (6)." "It was in front of a huge enlargement of the interior of a Polavision cassette on which the silhouette of the speaker was cut out (opposite left) that Dr Land presented his invention. This document makes it possible to distinguish the guide pulleys of the film (1 and 2), the supply of treatment product and its distribution nozzle (3), the supply reel (4), the assembly formed by the presser of film and the prism (5), the film drive pulley (6)." (Anonymous (1977): Naissance du cinéma instantané. In: L'auto-journal, Rubrique realisée sous la direction de Pierre Marais, 12, Jul., pp. 94–95.)
- The production of the Filter structure on Polavision film includes the use of a lenticular surface, which is removed after the process. The lenticules are not involved in recording the color information during the taking of images in the camera. Figure 10 and Figure 11 from: Land, Edwin H. (1997): An Introduction to Polavision. In: Photographic Science and Engineering, 21,5, Sept., Oct., pp. 228–236, on p. 228.
- Comparison of thickness of the image carrying layer in a Kodak fine grain positive and Polavision film. Figure 24 from: Land, Edwin H. (1997): An Introduction to Polavision. In: Photographic Science and Engineering, 21,5, Sept., Oct., pp. 228–236, on p. 235.
- In the Polavision instant color film process the negative image recorded during the exposure of the film is neither developed from a latent image to a visible negative nor is it removed from the film. The latent negative stays as a layer in the film and is responsible for a slight attenuation of the image’s highlights. Figure 25 from: Land, Edwin H. (1997): An Introduction to Polavision. In: Photographic Science and Engineering, 21,5, Sept., Oct., pp. 228–236, on p. 236.
- Single frame of a Polavision home movie scanned in 3.5K resolution.
14 Images
-
![]() Linear filter structure in Polachrome 35mm instant slide film. The blue filter strips are slightly larger compared to the red and green filters. The filter lines are running along the film strip. According to the image placement of the 135 film format for still photography the image is divided horizontally into triplets of R, G and B filter lines.
The emulsion layer has been removed before the image was taken.
Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
Linear filter structure in Polachrome 35mm instant slide film. The blue filter strips are slightly larger compared to the red and green filters. The filter lines are running along the film strip. According to the image placement of the 135 film format for still photography the image is divided horizontally into triplets of R, G and B filter lines.
The emulsion layer has been removed before the image was taken.
Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Linear filter structure in Polachrome 35mm instant slide film with a emulsion layer of low photographic density. Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Comparision of the linear filter structure of Polachrome 35mm instant slide film and Polavision Super-8 motion picture film. While the technical concept behind the two film stocks is the same, the Super-8 film was produced with linear filters of a smaller width. Based on the given width of an RGB filter triplet and the 135 still image size there are about 920 horizontal RGB-triplets per image for a Polachrome slide. The Super-8 film image is rotated by 90° compared to the 135 film still image and has about 340 vertical RGB-triplets per frame. The positioning of the image content compared to the filter lines is indicated in the picture. Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
4 Images in 1 Gallery
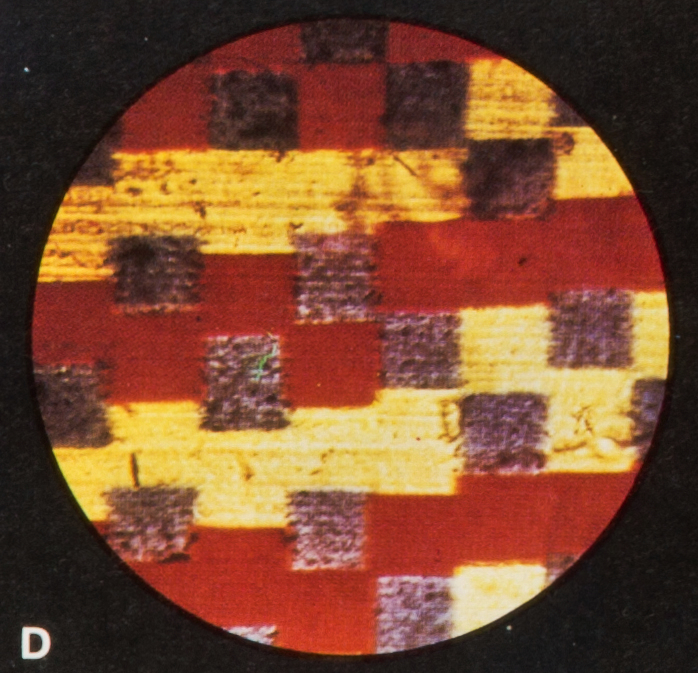
“In October, Eggert of the Agfa Research Department, read a paper at the Berlin meeting of the Deutsche Gesellschaft für photographische Forschung, on the Pantochrom subtractive lenticular bipack tricolor process. (Fig. 1) The green and blue ...
-
![]() Agfa Pantachrom. Source: Arens, Hans; Heymer, Gerd (1939): Die „Agfa-Farbentafel für Farbenphotographie“. In: Veröffentlichungen des wissenschaftlichen Zentral-Laboratoriums der photographischen Abteilung Agfa, Vol. 6, 1939, pp. 225-229. Leipzig: Hirzel. Photograph by Martin Weiss, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
Agfa Pantachrom. Source: Arens, Hans; Heymer, Gerd (1939): Die „Agfa-Farbentafel für Farbenphotographie“. In: Veröffentlichungen des wissenschaftlichen Zentral-Laboratoriums der photographischen Abteilung Agfa, Vol. 6, 1939, pp. 225-229. Leipzig: Hirzel. Photograph by Martin Weiss, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
19 Images in 3 Galleries
“New Agfa Color Plate (1923–1932): colored particles very small and not visible to the naked eye, but clumps of particles of the same color give the image a pointillist effect (Fig. 2.62). Unlike with the autochromes, in which the grains ...
-
![]() Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 73.
Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 73.
1 Image
-
![]() Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 74.
Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 74.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 44.
2 Images
“Every element of a cross-lined screen acts as a pinhole camera, and reproduces an image of the aperture of the objective in whose rear focal plane it is placed. Thus, when using a square stop, the dots in the halftone produced will be square ...
-
![]() Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ede, François (1994): Jour de fête ou la couleur retrouvée. Cahiers du Cinéma: Paris.
Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ede, François (1994): Jour de fête ou la couleur retrouvée. Cahiers du Cinéma: Paris.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
4 Images
“Another method of producing a line screen was patented in 1904 by the German Robert Krayn, and was demonstrated by him in November 1907. Krayn stained very thin celluloid sheets red, green and blue, and cemented them interleaved to form a thick ...
-
![]() Source: Coe, Brian (1978): Colour Photography. The First Hundred Years 1840-1940. London: Ash & Grant, p. 54.
Source: Coe, Brian (1978): Colour Photography. The First Hundred Years 1840-1940. London: Ash & Grant, p. 54.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 34.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 35.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 35.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 36.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 74.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 74.
7 Images
“LENTICULAR PROCESS
In 1896 R. E. Liesegang (Ahriman, 1896) suggested a photographic color process based upon the use of banded filters in the camera aperture.
[…]
In 1909 R. Berthon (British Patent 10,611; see also Berthon, 1910a, b) ...
-
![]() Kodacolor lenticular filter for the projector. Lichtspiel / Kinemathek Bern.
Kodacolor lenticular filter for the projector. Lichtspiel / Kinemathek Bern.
- Credit: Rudolf Gschwind, Imaging and Media Lab, University of Basel.
- Magnification of an area. Credit: Rudolf Gschwind, Imaging and Media Lab, University of Basel.
- Color reconstruction test. Credit: Rudolf Gschwind, Imaging and Media Lab, University of Basel.
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Microscopic linear lens structure of Kodacolor lenticular film. Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Acetate plastic base of Kodacolor lenticular film embedded in epoxide resin. The emulsion layer usually placed on the opposite side of the acetate base has been removed beforehand and is therefore not visible. Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Focal travelling through the 3-dimensional structure of Kodacolor lenticular film. In the beginning the linear lenticular structure is visible and towards the end the emulsion layer comes into focus and the granular structure defined by the density of the silver is visible. In this shot the lenticules were showing towards the light source and the emulsion towards the camera. This enables an undistorted recording of the emulsion layer. Credit: David Pfluger, editing by Martin Weiss, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Focal travelling through the 3-dimensional structure of Kodacolor lenticular film. In the beginning the linear lenticular structure is visible and towards the end the emulsion layer comes into focus. In this shot the lenticules were allocated towards the lens of the microscope and the light source at the side of the emulsion similar to the configuration in projection. As a consequence the graininess of the emulsion is not visible as with the film flipped to the other side. The structure is optically distorted perpendicular to the linear structure of the lenticules. Credit: David Pfluger, editing by Martin Weiss, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
24 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
1 Image
”The process as illustrated in USP 1431309 was a two-color additive process, but it is stated that it could be a three- or four-color process. For the original photography, the negative was exposed through a line screen composed of alternate bands ...
-
![]() Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
1 Image
-
![]() Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ede, François (1994): Jour de fête ou la couleur retrouvée. Cahiers du Cinéma: Paris.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Microscopic image of a piece of Keller-Dorian lenticular film embedded in epoxide resin. The 3-dimensional structure of the lenticules is visible as well as the thin emulsion layer on the other side of the acetate base. Credit: Sample preparation and imaging by the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Lenticular surface of the acetate plastic base of Keller-Dorian lenticular film. On the back plane of the acetate layer and therefore out of focus in this image, structures defined by the silver image in the emulsion layer can be perceived. Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Hexagonal structure of the lenticules of Keller-Dorian lenticular film. Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Microscopic images of the Keller-Dorian lenticular structure with the focus set at different points. The images have been chained to show a travelling through the 3-dimensional structure of the bee-hive shaped lenticules. Credit: David Pfluger, conversion to video by Martin Weiss, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
14 Images in 2 Galleries
“In 1894 Professor John Joly of Dublin patented a process for producing a screen of red, green and blue-violet lines by ruling them on a gelatin-coated glass plate. Joly used ruling machines of great accuracy, with drawing pens trailed across ...
-
![]() Photomicrograph (20x) of a Joly screen. Credit: Courtesy of George Eastman House, International Museum of Photography and Film.
Photomicrograph (20x) of a Joly screen. Credit: Courtesy of George Eastman House, International Museum of Photography and Film.
- Credit: Courtesy of George Eastman House, International Museum of Photography and Film.
- Source: Coe, Brian (1978): Colour Photography. The First Hundred Years 1840-1940. London: Ash & Grant.
- Credit: Gawain Weaver, Photograph Conservator, Gawain Weaver Art Conservation, San Anselmo, CA.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 69.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 22.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 23.
7 Images
-
![]() Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 70.
Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 70.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 70.
- Photomicrograph (20x) of a Finlay screen. Credit: Courtesy of George Eastman House, International Museum of Photography and Film.
- Finlay box. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 39.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 39.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 40.
9 Images in 1 Gallery
-
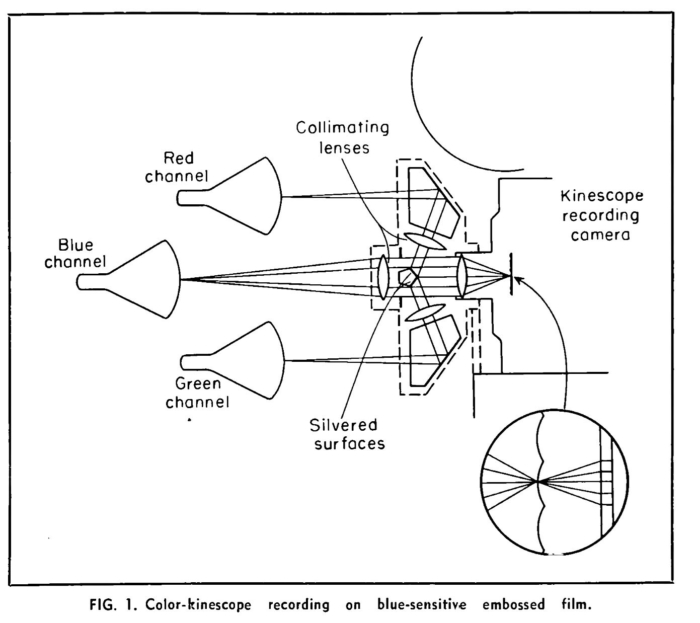
![]() Recording of a color video signal onto lenticular film.
Recording of a color video signal onto lenticular film.
- Playback of the color image on the lenticular film as a television signal.
2 Images
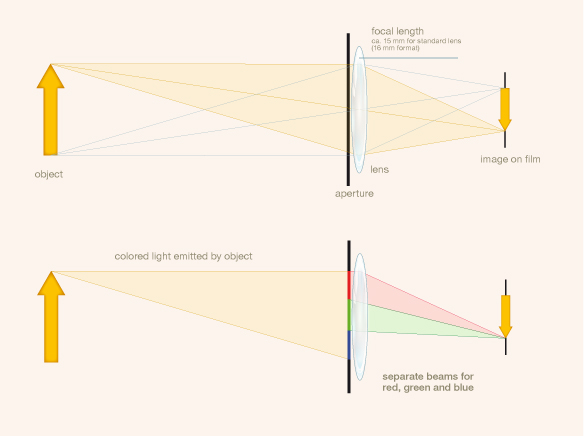
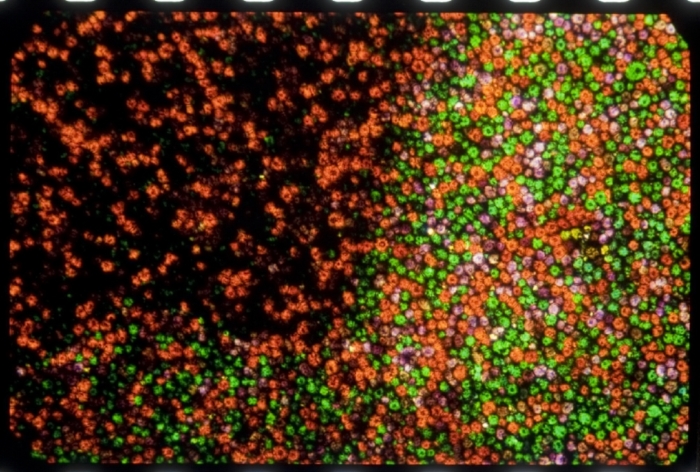
Dufaycolor was a regular line screen process whereby the incident light was filtered through a pattern of tiny color patches created by lines in red, green and blue, the so called réseau.
-
![]() Reversal Colour Positive. Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: A Colour Box (GB 1935, Len Lye).
Reversal Colour Positive. Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: A Colour Box (GB 1935, Len Lye).
- Microscopic image of the filter structure of a Dufaycolor film. The Emulsion has been removed. The visible structures are not silver grain but the structure of the filter layers. Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Microscopic images of Dufaycolor film with the focus set at different points within the emulsion and filter layers. The images have been chained to show a travelling through the 3-dimensional structure of the layers. Credit: David Pfluger, conversion to video by Martin Weiss, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
231 Images in 9 Galleries
(see detail page on Dufaycolor)
-
![]() Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press,
Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press,
- Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Source: Ede, François (1994): Jour de fête ou la couleur retrouvée. Cahiers du Cinéma: Paris.
- Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 71.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 73.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 31.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 32.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 33.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 48.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 69.
10 Images
Process for still photography in which light is filtered through a screen or transparent plate covered in lines or dots in the primary colors orange, green and violet. For the positive, the process relies on a support material which includes an ...
The procedure for obtaining the lenticular elements in relief required a series of steps: starting from three black and white positive color separations, obtained with any of the available methods, three matrices were printed, from which the film to ...
-
![]() Projection of lenticular film in Bocca-Rudatis. Refraction of light beams through lens. Source: Pierotti, Federico (2016): Un'archeologia del colore nel cinema italiano. Dal Technicolor ad Antonioni. Pisa: Edizioni ETS, p. 81.
Projection of lenticular film in Bocca-Rudatis. Refraction of light beams through lens. Source: Pierotti, Federico (2016): Un'archeologia del colore nel cinema italiano. Dal Technicolor ad Antonioni. Pisa: Edizioni ETS, p. 81.
1 Image
-
![]() Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ede, François (1994): Jour de fête ou la couleur retrouvée. Cahiers du Cinéma: Paris.
- Schmidt, Richard / Kochs, Adolf (1943): Farbfilmtechnik. Eine Einführung für Filmschaffende. Berlin: Hesse, pp. 54-72. (Schriftenreihe der Reichsfilmkammer, 10.) (in German) [quote id='6']
5 Images
“R. Berthon patented the use of a lens diaphragm with three apertures, covered respectively with red, green and blue-violet filters, and a sensitive surface on a support, the other side of which was impressed with hemi-spherical, transparent, ...
-
![]() Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ede, François (1994): Jour de fête ou la couleur retrouvée. Cahiers du Cinéma: Paris.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Source: Heymer, Gerd (1933): Auflösungsvermögen und Farbwiedergabe in der Farbrasterphotographie. In: Veröffentlichungen des wissenschaftlichen Zentral-Laboratoriums der photographischen Abteilung Agfa, 3, 1933, pp. 188-207.
4 Images
Several attempts were made to apply the Autochrome process invented by the Lumière brothers to motion pictures.
Transparent potato starch grains with a diameter of 15–20 micrometer were colored in the additive primaries red, green and blue. The ...
-
![]() Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Cinécolor, mosaic screen, ca. 1929. Credit: Gert Koshofer Collection. Sample No. 68. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Magnification of an image area. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
27 Images in 2 Galleries
“The Autochrome process was the first fully practical single-plate colour process to reach the photographic public. It was easy to use. The plate was loaded into a conventional holder, glass to the front. The exposure was made through a yellow ...
-
![]() Photomicrograph (50x) of an Autochrome mosaic screen. Credit: Courtesy of George Eastman House, International Museum of Photography and Film.
Photomicrograph (50x) of an Autochrome mosaic screen. Credit: Courtesy of George Eastman House, International Museum of Photography and Film.
- Source: Lavédrine, Bertrand (2009): Photographs of the Past. Process and Preservation. Los Angeles: Getty Publications.
- Source: Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press.
- Source: Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press.
- Source: Holme, Charles (1908): Colour Photography, and Other Recent Developments of the Art of the Camera. London, Paris, New York.: Offices of The Studio.
- Source: Holme, Charles (1908): Colour Photography, and Other Recent Developments of the Art of the Camera. London, Paris, New York.: Offices of The Studio.
- Credit: Klosterarchiv Einsiedeln. http://www.klosterarchiv.ch/earchiv_liste.php?Objektyp_physisch=Glasautochrom&start=1
- Credit: Klosterarchiv Einsiedeln. http://www.klosterarchiv.ch/earchiv_liste.php?Objektyp_physisch=Glasautochrom&start=1
- Credit: Klosterarchiv Einsiedeln. http://www.klosterarchiv.ch/earchiv_liste.php?Objektyp_physisch=Glasautochrom&start=1
- Credit: Klosterarchiv Einsiedeln. http://www.klosterarchiv.ch/earchiv_liste.php?Objektyp_physisch=Glasautochrom&start=1
- Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 70.
- Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 26.
- Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 65.
- Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 27.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 235.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 64.
16 Images
“During the war, an important new screen plate appeared, based on patents taken out by J. H. Christensen in 1908. He proposed to make a concentrated solution of gum in alcohol. Divided into three parts, the gum solutions were dyed red, green ...
-
![]() Magnification. Source: Coe, Brian (1978): Colour Photography. The First Hundred Years 1840-1940. London: Ash & Grant.
Magnification. Source: Coe, Brian (1978): Colour Photography. The First Hundred Years 1840-1940. London: Ash & Grant.
- Source: Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press.
- Source: Heymer, Gerd (1943): Die neuere Entwicklung der Farbphotographie. In: Ergänzungswerk zum Handbuch der wissenschaftlichen und angewandten Photographie. Wien: Julius Springer 1943, pp. 337-463.
- Source: Finger, Ehrhard (1998): Die Pioniere des Wolfener Farbfilms. In: Industrie- und Filmmuseum Wolfen e. V. (ed.), Die Filmfabrik Wolfen. Aus der Geschichte, Heft 2, pp. 16-36. (in German) [quote id='4']
- Source: Finger, Ehrhard (1998): Die Pioniere des Wolfener Farbfilms. In: Industrie- und Filmmuseum Wolfen e. V. (ed.), Die Filmfabrik Wolfen. Aus der Geschichte, Heft 2, pp. 16-36. (in German) [quote id='4']
- Source: Finger, Ehrhard (1998): Die Pioniere des Wolfener Farbfilms. In: Industrie- und Filmmuseum Wolfen e. V. (ed.), Die Filmfabrik Wolfen. Aus der Geschichte, Heft 2, pp. 16-36. (in German) [quote id='4']
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 73.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 73.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 72.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 76.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 42.
11 Images
“Agfacolor Plate (1932-1938): colored particles very small and not visible to the naked eye; clumps of particles of the same color give the image a pointillist effect (Fig. 2.63). Unlike with the autochromes, in which the grains are remarkably ...
-
![]() Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 72.
Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 72.
1 Image
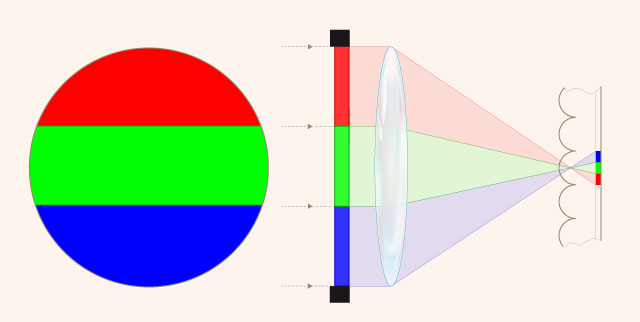
The basic idea of the lenticular film was developed by the German Raphaël Liesegang in 1896 and applied to still photography by the French Rodolphe Berthon in 1908.
The lenticular process applies tiny cylindrical lenses embossed on the film support ...
-
![]() Color reconstruction. Credit: Gisela Harich-Hamburger, Diplomrestauratorin (FH).
Color reconstruction. Credit: Gisela Harich-Hamburger, Diplomrestauratorin (FH).
- Source: Heymer, Gerd (1933): Auflösungsvermögen und Farbwiedergabe in der Farbrasterphotographie. In: Veröffentlichungen des wissenschaftlichen Zentral-Laboratoriums der photographischen Abteilung Agfa, 3, 1933, pp. 188-207.
- Source: Weil, F. (1933): The Optical-Photographic Principles of the Agfacolor Process. In: Journal of the Society of Motion Picture Engineers, 20, (April, 1933), No. 4, p. 301-308.
- Both the Kodak and Agfa lenticular processes required the correct banded filter to be used with each different batch of panchromatic film. These two filters were for different batches of Agfacolor used in a Leica camera.. Source: Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ede, François (1994): Jour de fête ou la couleur retrouvée. Cahiers du Cinéma: Paris.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Magnification 5x, front. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification 10x, back. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification 20x, front. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Reflection on Agfacolor lenticular film. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. In: Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Reconstruction of lenticular film by Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland in the framework of their research project doLCE
- Agfacolor Lenticular sample from the Kodak Film Samples Collection at the National Science and Media Museum in Bradford. Credit: National Science and Media Museum Bradford. Photographs by Barbara Flueckiger in collaboration with Noemi Daugaard.
- Analog reconstruction by Giorgio Trumpy, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors
15 Images
“Agfacolor Film (1932–1934): individual colored particles cannot be seen with the naked eye, but clumps of grains of the same color give the image a pointillist effect (Fig. 2.70). There is no black pigment filler. The film has a thick base ...
-
![]() Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 76.
Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 76.