-
![]() Cross-section of the optical system displaying the different lenses, the prism and the four filters. Source: Pierotti, Federico (2016): Un'archeologia del colore nel cinema italiano. Dal Technicolor ad Antonioni. Pisa: Edizioni ETS, p. 71.
Cross-section of the optical system displaying the different lenses, the prism and the four filters. Source: Pierotti, Federico (2016): Un'archeologia del colore nel cinema italiano. Dal Technicolor ad Antonioni. Pisa: Edizioni ETS, p. 71.
- 35mm black and white film strip with four equal-sized images (left) and 16mm projector with Cristiani-Mascarini optical system. Source: Pierotti, Federico (2016): Un'archeologia del colore nel cinema italiano. Dal Technicolor ad Antonioni. Pisa: Edizioni ETS, p. 71.
Select Category▼×
- All Categories
- Bibliography
- Chromogenic monopack
- Chromolytic multilayer
- Color separation
- Double-coated / bi-pack
- Edge Codes and Identification
- Hand coloring
- Other
- Printing / dye-transfer
- Printing / pigment process
- Screen processes
- Spatial synthesis (multiple lenses, beam splitter)
- Stencil coloring (pochoir, Pathécolor)
- Temporal synthesis (rotary filters)
- Theory
- Tinting
- Toning
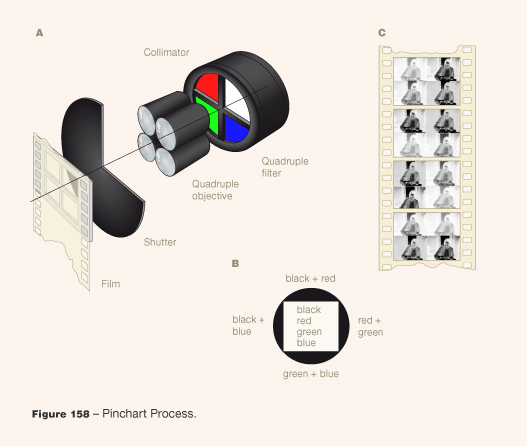
For this four-color process, the light beam was decomposed into four parts, each of which simultaneously exposed an area equal to one quarter of the 35mm frame of a black and white negative. This was obtained optically by placing a diaphragm and a ...
“The Dutch Sirius Color process (1929) used a camera with a beamsplitting system behind the lens to expose a single film, the film passing through two gates at right angles to each other. The double-coated print film was dye-toned. The process ...
-
![]() Magnification, 20x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
Magnification, 20x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification, 10x. Credit: Photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification, 5x. Credit: Photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. In: Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Magnification of an image area. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Reflection on the Sirius film, front. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Reflection on the Sirius film, back. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
142 Images in 4 Galleries
“Probably the first use of the catalytic property of silver was in 1889, when E. Howard Farmer disclosed the action of a silver image upon strong dichromate solutions (Eng. P. 17773/89). When a plate or film, containing a silver image, is immersed ...
“Dr. H. W. Vogel, the discoverer of colour sensitizers, made three-colour photography possible, and has been the first to recognise the relation between colour sensitiveness of plate and printing colour in the following principle made known in ...
“Public showings of the work done at this plant in Hollywood have been given to Los Angeles audiences.
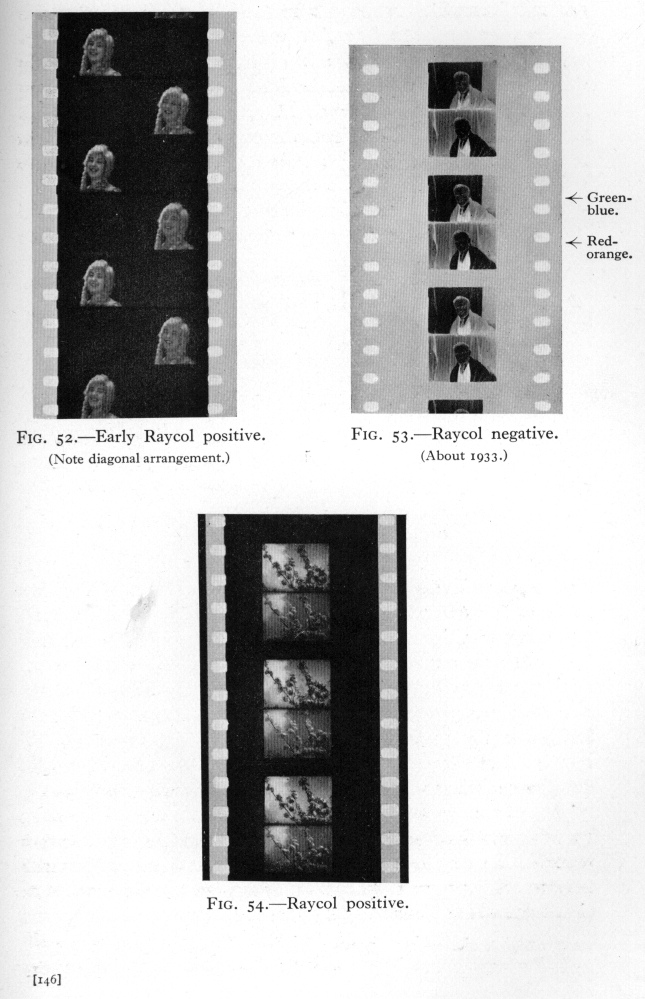
The release prints are made on double sided film. Both sides are developed at one time and then toned red on one side and bluegreen on the ...
-
![]() Strange Birds (US 1930, Mack Sennett). Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph of the nitrate print: Barbara Flueckiger
Strange Birds (US 1930, Mack Sennett). Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph of the nitrate print: Barbara Flueckiger
- Magnification. Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Strange Birds (1930)
18 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Screenshot from Mayorov, Nikolai (2012): Soviet Colours. Translated by Birgit Beumers. In: Studies in Russian & Soviet Cinema, 6:2, pp. 241–255. doi: 10.1386/srsc.6.2.241_1 Courtesy of Nikolai Mayorov.
Screenshot from Mayorov, Nikolai (2012): Soviet Colours. Translated by Birgit Beumers. In: Studies in Russian & Soviet Cinema, 6:2, pp. 241–255. doi: 10.1386/srsc.6.2.241_1 Courtesy of Nikolai Mayorov.
1 Image
-
![]() Zaveshchanie/The Testament (7 June 1937). Credit: Courtesy of Nikolai Mayorov.
Zaveshchanie/The Testament (7 June 1937). Credit: Courtesy of Nikolai Mayorov.
- Zaveshchanie/The Testament (7 June 1937). Credit: Courtesy of Nikolai Mayorov. Credit: Courtesy of Nikolai Mayorov.
- The Miraculous Traffic Light (1938). Credit: courtesy of Nikolai Mayorov
- The Wolf and Seven Goat-Kids (1938). Credit: Courtesy of Nikolai Mayorov.
- The Fox and the Wolf (1937). Credit: Courtesy of Nikolai Mayorov.
- The Fox and the Wolf (1937). Credit: Courtesy of Nikolai Mayorov.
6 Images
-
![]() Rouxcolor, four-color, black and white negative and positive, ca. 1948. Credit: Gert Koshofer Collection. Sample No. 83. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger
Rouxcolor, four-color, black and white negative and positive, ca. 1948. Credit: Gert Koshofer Collection. Sample No. 83. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger
- Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
7 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
2 Images
“The Rotocolor process was an additive system for color cinematography. The process was announced in 1931 by H. Muller. According to an article in Film Daily, April 12, 1931, and The Motion Picture Herald, April 11, 1931, the process consisted of ...
-
![]() Rota Farbenfilm Samples (Kodak Film Samples Collection). Credit: National Science and Media Museum Bradford. Photographs of the Rotacolor Prints by Josephine Diecke, SNSF project Film Colors. Technologies, Cultures, Institutions and Joëlle Kost, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
Rota Farbenfilm Samples (Kodak Film Samples Collection). Credit: National Science and Media Museum Bradford. Photographs of the Rotacolor Prints by Josephine Diecke, SNSF project Film Colors. Technologies, Cultures, Institutions and Joëlle Kost, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
13 Images in 2 Galleries
The Roncarolo system required a camera capable of recording two panchromatic negatives (which became three or four in subsequent patents) through the use of a beam splitter and red and green filters.
The chromatic information registered on the two or ...
-
![]() Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
13 Images in 1 Gallery
“Louis Ducos du Hauron is reported to have become interested in the reproduction of colors by photography in 1859, when he was twentyone years old (Potonniée, 1939). In 1862 he submitted to a friend of his family, M. Lelut, a paper embodying ...
-
![]() "Du Hauron invented his Chromographoscope in 1874. It could be used either as a camera or an additive viewer." Source: Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press.
"Du Hauron invented his Chromographoscope in 1874. It could be used either as a camera or an additive viewer." Source: Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press.
- An early three-color print by Louis Ducros Du Hauron, 1877.
2 Images
Description of a variety of color processes, even for images in motion by the use of a rotary shutter.
Based on four primary colors, the process successively recorded two simultaneous images for two primary colors each. In projection, the four images were combined on screen, supposedly via a regular projector.
“M. F. de Colombier appears to have been the first to suggest the application of this system to cinematography, and like so many French patents it is a little indefinite in phraseology. Three films were employed representing the same view and ...
“In its final form Prizma made use of duplitized positive film. As in previous Prizma systems, the original negatives were alternate frame sequential exposures. The Prizma negative was printed on both sides of the positive film in a special ...
-
![]() The two colors visible at a splice. Credit: EYE Film Institute Amsterdam. Film: [Kleurenpracht].
The two colors visible at a splice. Credit: EYE Film Institute Amsterdam. Film: [Kleurenpracht].
- Credit: George Eastman House. Preserved by Carole Fodor, Haghefilm Digitaal fellow and graduate of The L. Jeffrey Selznick School of Film Preservation. Film: A Day with John Burroughs (Prizma, 1919).
- Credit: George Eastman House. Preserved by Carole Fodor, Haghefilm Digitaal fellow and graduate of The L. Jeffrey Selznick School of Film Preservation. Film: A Day with John Burroughs (Prizma, 1919).
- Credit: George Eastman House Motion Picture Department Collection. Film: The Land of the Great Spirit (1919).
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Orange.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Orange.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Orange.
399 Images in 14 Galleries
“The color experiments were conducted in the basement of a house at 1586 E. Seventeenth St., Brooklyn, N. Y. During this time a double-coated stock and a bleach formula which had much to do with the success of the later Prizma process were ...
-
![]() Source: Wall, E.J. (1925): The History of Three-color Photography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
Source: Wall, E.J. (1925): The History of Three-color Photography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
1 Image
“Then we come upon the name of George Albert Smith, F.R.A.S., of Laboratory Lodge, Roman Crescent, Southwick, Brighton, who in E.P. 26,671, of 1906, patented the method which eventually was commercialized as Kinemacolor.
In this patent he ...
“Polychromide, a two-color subtractive process invented in 1918 by Aron Hamburger, achieved limited commercial success overseas, and was occasionally employed in England as late as 1933. Originally an orthochromatic and a panchromatic negative were ...
-
![]() Polychromide samples from the Kodak Film Samples Collection at the National Science and Media Museum in Bradford.
Credit: National Science and Media Museum Bradford.
Photographs by Barbara Flueckiger in collaboration with Noemi Daugaard.
Polychromide samples from the Kodak Film Samples Collection at the National Science and Media Museum in Bradford.
Credit: National Science and Media Museum Bradford.
Photographs by Barbara Flueckiger in collaboration with Noemi Daugaard.
- Credit: Brian Pritchard
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 279.
66 Images in 2 Galleries
-
![]() Linear filter structure in Polavision instant Super8 film. The filter lines are running along the film strip. According to the image placement of the Super-8 motion picture standard the image is divided vertically into triplets of R, G and B filter lines. The emulsion layer has been removed before this image was taken.
Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
Linear filter structure in Polavision instant Super8 film. The filter lines are running along the film strip. According to the image placement of the Super-8 motion picture standard the image is divided vertically into triplets of R, G and B filter lines. The emulsion layer has been removed before this image was taken.
Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Linear filter structure in Polavision instant Super8 film with an emulsion layer of a high photographic density. With the focus set on the emulsion the linear structure of the coloured filters is not visible in this image. Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Comparision of the linear filter structure of Polachrome 35mm instant slide film and Polavision Super-8 motion picture film. While the technical concept behind the two film stocks is the same, the Super-8 film was produced with linear filters of a smaller width. Based on the given width of an RGB filter triplet and the 135 still image size there are about 920 horizontal RGB-triplets per image for a Polachrome slide. The Super-8 film image is rotated by 90° compared to the 135 film still image and has about 340 vertical RGB-triplets per frame. The positioning of the image content compared to the filter lines is indicated in the picture. Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Excerpt of a Polavision Super-8 home movie scanned on a Kinetta scanner in 4.8K resolution edge to edge. In post production a zoom in and out was applied to show the linear filter structure of Polavision film in motion. The zoom was based on image detail from the scan. No upres procedure was applied. Credit: Scanning and editing by Martin Weiss.
- A comparison of the colour filter structures of Dufaycolor, Autochrome and Polavision from Anonymous (1978): Ma il Polavision e' un'altra cosa!. Phototest Italiana, 41, Oct., pp 72–77.
- A comparison of the colour filter structures of Dufaycolor, Autochrome and Polavision from Anonymous (1978): Ma il Polavision e' un'altra cosa!. Phototest Italiana, 41, Oct., pp 72–77. Translation: David Pfluger and Giorgio Trumpy.
- The process of exposure and development of Polavision instant Super-8 film. From Anonymous (1978): Ma il Polavision e' un'altra cosa!. Phototest Italiana, 41, Oct., p. 74.
- The process of exposure and development of Polavision instant Super-8 film. From Anonymous (1978): Ma il Polavision e' un'altra cosa!. Phototest Italiana, 41, Oct., p. 74. Translation: David Pfluger and Giorgio Trumpy.
- "Polavision (top) vs. Kodachrome 40: These are blowups from closely matching frames of Debra Goldie, filmed simultaneously with a Polavision and a conventional super 8 camera, side by side, with the Twi Light quartz lamp mounted on top of the former. Subject distance was 6 ft., but the super 8 camera was focused for 10 ft. – same as the Polavision camera at its close-up setting. Both Polavision and Kodachrome 40 are closely equal in speed, but differ distinctly in structure, faithfulness of color rendition, and latitude, as is obvious from these frame reproductions. What can't be seen is the relative opacity of Polavision: according to our measurement, it transmits less than 9 percent as Kodachrome 40. However, the lab that made the duplicate transparency blow-ups of the frames found that it had to give a full six stops extra exposure." (Leavitt, Don; Drukker Leendert (1978): First Look: Polavision instant movies. In: Popular Photography, Feb., p. 68.)
- "C'est devant un immense agrandissement de l'intérieur d'une cassette Polavision sur la-quelle se découpe la silhouette de l'orateur (ci-contre à gauche) que le Dr Land présenta son invention. Ce document permet de distinguer les poulies de guidage du film (1 et 2), la réserve de produit de traitement et son bec ré-partiteur (3), la bobine débitrice (4), l'ensemble formé par le presseur de film et le prisme (5), la poulie d'entraînement du film (6)." "It was in front of a huge enlargement of the interior of a Polavision cassette on which the silhouette of the speaker was cut out (opposite left) that Dr Land presented his invention. This document makes it possible to distinguish the guide pulleys of the film (1 and 2), the supply of treatment product and its distribution nozzle (3), the supply reel (4), the assembly formed by the presser of film and the prism (5), the film drive pulley (6)." (Anonymous (1977): Naissance du cinéma instantané. In: L'auto-journal, Rubrique realisée sous la direction de Pierre Marais, 12, Jul., pp. 94–95.)
- The production of the Filter structure on Polavision film includes the use of a lenticular surface, which is removed after the process. The lenticules are not involved in recording the color information during the taking of images in the camera. Figure 10 and Figure 11 from: Land, Edwin H. (1997): An Introduction to Polavision. In: Photographic Science and Engineering, 21,5, Sept., Oct., pp. 228–236, on p. 228.
- Comparison of thickness of the image carrying layer in a Kodak fine grain positive and Polavision film. Figure 24 from: Land, Edwin H. (1997): An Introduction to Polavision. In: Photographic Science and Engineering, 21,5, Sept., Oct., pp. 228–236, on p. 235.
- In the Polavision instant color film process the negative image recorded during the exposure of the film is neither developed from a latent image to a visible negative nor is it removed from the film. The latent negative stays as a layer in the film and is responsible for a slight attenuation of the image’s highlights. Figure 25 from: Land, Edwin H. (1997): An Introduction to Polavision. In: Photographic Science and Engineering, 21,5, Sept., Oct., pp. 228–236, on p. 236.
- Single frame of a Polavision home movie scanned in 3.5K resolution.
14 Images
“Polacolor was commercialized in 1963 and became an immediate success. It was acclaimed as the “most outstanding single advance in photographic science made during this century” (Crawley 1963). Indeed, Polacolor introduced important new ...
-
![]() Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 235.
Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 235.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 235.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 235.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 258.
4 Images
-
![]() Linear filter structure in Polachrome 35mm instant slide film. The blue filter strips are slightly larger compared to the red and green filters. The filter lines are running along the film strip. According to the image placement of the 135 film format for still photography the image is divided horizontally into triplets of R, G and B filter lines.
The emulsion layer has been removed before the image was taken.
Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
Linear filter structure in Polachrome 35mm instant slide film. The blue filter strips are slightly larger compared to the red and green filters. The filter lines are running along the film strip. According to the image placement of the 135 film format for still photography the image is divided horizontally into triplets of R, G and B filter lines.
The emulsion layer has been removed before the image was taken.
Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Linear filter structure in Polachrome 35mm instant slide film with a emulsion layer of low photographic density. Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Comparision of the linear filter structure of Polachrome 35mm instant slide film and Polavision Super-8 motion picture film. While the technical concept behind the two film stocks is the same, the Super-8 film was produced with linear filters of a smaller width. Based on the given width of an RGB filter triplet and the 135 still image size there are about 920 horizontal RGB-triplets per image for a Polachrome slide. The Super-8 film image is rotated by 90° compared to the 135 film still image and has about 340 vertical RGB-triplets per frame. The positioning of the image content compared to the filter lines is indicated in the picture. Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
4 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
2 Images
“In the imbibition process, a dye image is transferred from a gelatin relief image to a receiving layer made either of paper or film. Charles Cros described this method of “hydrotypie” transfer printing in 1880 and suggested it ...
-
![]() Cyan and magenta combined, third layer, yellow missing. Source: Meister Lucius & Brüning (1905): Pinatypie. Positiv-Verfahren für die Dreifarbenphotographie. Höchst am Main.
Cyan and magenta combined, third layer, yellow missing. Source: Meister Lucius & Brüning (1905): Pinatypie. Positiv-Verfahren für die Dreifarbenphotographie. Höchst am Main.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 235.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 235.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 132.