Select Category▼×
- All Categories
- Bibliography
- Chromogenic monopack
- Chromolytic multilayer
- Color separation
- Double-coated / bi-pack
- Edge Codes and Identification
- Hand coloring
- Other
- Printing / dye-transfer
- Printing / pigment process
- Screen processes
- Spatial synthesis (multiple lenses, beam splitter)
- Stencil coloring (pochoir, Pathécolor)
- Temporal synthesis (rotary filters)
- Theory
- Tinting
- Toning
-
![]() Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
2 Images
“In 1998 Racey Gilbert purchased Polaroid’s stock of pigment films and opened Ataraxia Studio in Bensalem, Pennsylvania, to make high-quality collectors’ carbon prints. Under the direction of Gérard Niemetzky, the studio produced ...
-
![]() Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 98.
Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 98.
1 Image
“Every element of a cross-lined screen acts as a pinhole camera, and reproduces an image of the aperture of the objective in whose rear focal plane it is placed. Thus, when using a square stop, the dots in the halftone produced will be square ...
-
![]() Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ede, François (1994): Jour de fête ou la couleur retrouvée. Cahiers du Cinéma: Paris.
Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ede, François (1994): Jour de fête ou la couleur retrouvée. Cahiers du Cinéma: Paris.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
4 Images
“Probably the first use of the catalytic property of silver was in 1889, when E. Howard Farmer disclosed the action of a silver image upon strong dichromate solutions (Eng. P. 17773/89). When a plate or film, containing a silver image, is immersed ...
Three matrices in the subtractive primary colors are printed on the gelatin of the final print. Supposedly, the used dyes were particularly fast and able to prevent color bleeding. Pokorny started working on color cinematography in the 1920s, often ...
-
![]() Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
- Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
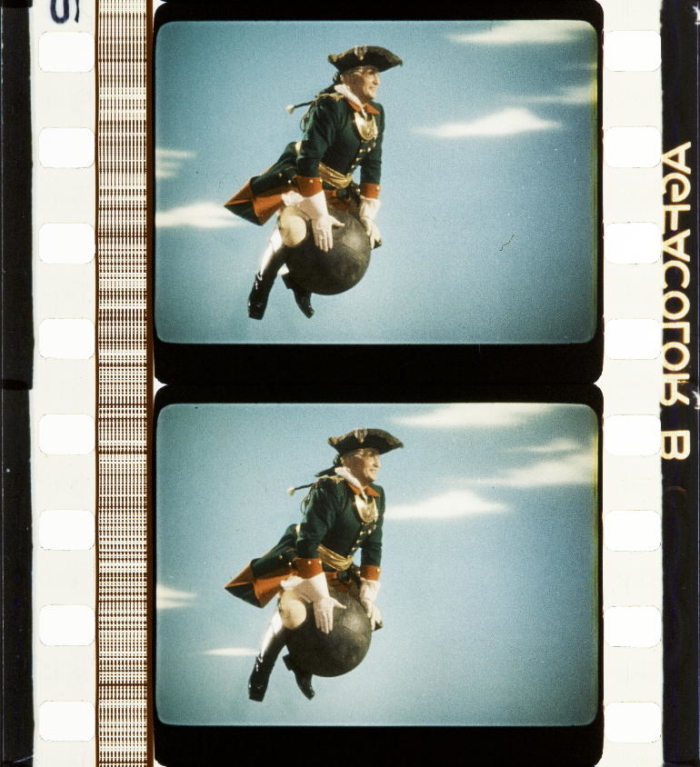
- Source: Kistler, L. R. (1945): The Projection of Thomascolor Motion Pictures. In: International Projectionist, 20,7, Jul., pp. 12–14.
- Source: Kistler, L. R. (1945): The Projection of Thomascolor Motion Pictures. In: International Projectionist, 20,7, Jul., pp. 12–14.
- Left: Thomascolor camera lens mount for converting standard motion picture camera into Thomascolor. Right: A closeup of the Thomascolor projector lens mount for standard film projectors. The inventor points out that this is all that is needed to convert a standard projector to Thomascolor. Source: Anonymous (1944): Thomascolor. Four-Color Process For Motion Pictures. In: International Projectionist, 19,10, Oct., pp. 7–9.
5 Images
“Another method of producing a line screen was patented in 1904 by the German Robert Krayn, and was demonstrated by him in November 1907. Krayn stained very thin celluloid sheets red, green and blue, and cemented them interleaved to form a thick ...
-
![]() Source: Coe, Brian (1978): Colour Photography. The First Hundred Years 1840-1940. London: Ash & Grant, p. 54.
Source: Coe, Brian (1978): Colour Photography. The First Hundred Years 1840-1940. London: Ash & Grant, p. 54.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 34.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 35.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 35.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 36.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 74.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 74.
7 Images
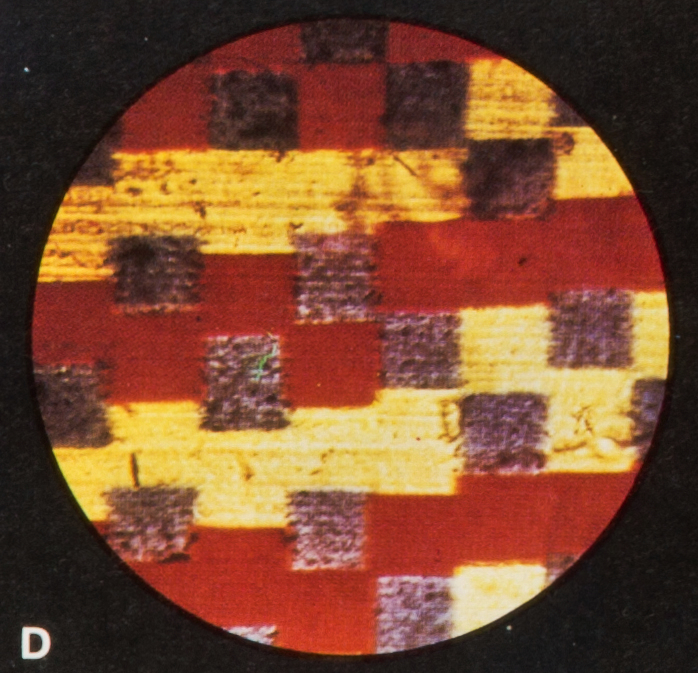
Mordant toning or dye toning is a special case of toning whereby the silver image is replaced by colored compounds. Soluble dyes attach to a colorless (silver ferrocyanide) or nearly colorless (silver iodide) silver salt obtained by bleaching. Dye ...
-
![]() Virages sur mordançage, Bleu (blue mordant toning), backlight, Swiss collectors'copy. Source: Didiée, L. (1926): Le Film vierge Pathé. Manuel de développement et de tirage. Paris: Pathé. [quote id='7']
Virages sur mordançage, Bleu (blue mordant toning), backlight, Swiss collectors'copy. Source: Didiée, L. (1926): Le Film vierge Pathé. Manuel de développement et de tirage. Paris: Pathé. [quote id='7']
- Photomicrograph, 25x. Credit: Norbert Wey, Institute of Pathology, University of Zurich.
- Photomicrograph, 50x. Credit: Norbert Wey, Institute of Pathology, University of Zurich.
- Photomicrograph, 100x. Credit: Norbert Wey, Institute of Pathology, University of Zurich.
- Photomicrograph, 100x. Credit: Norbert Wey, Institute of Pathology, University of Zurich.
171 Images in 7 Galleries
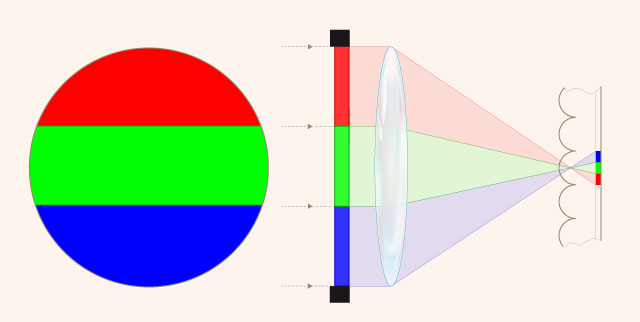
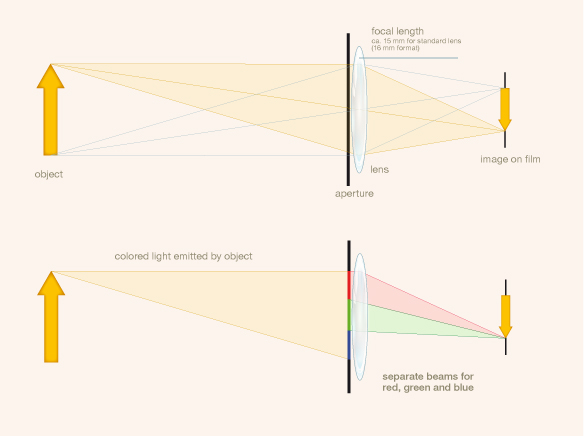
“R. Berthon patented the use of a lens diaphragm with three apertures, covered respectively with red, green and blue-violet filters, and a sensitive surface on a support, the other side of which was impressed with hemi-spherical, transparent, ...
-
![]() Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ede, François (1994): Jour de fête ou la couleur retrouvée. Cahiers du Cinéma: Paris.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Source: Heymer, Gerd (1933): Auflösungsvermögen und Farbwiedergabe in der Farbrasterphotographie. In: Veröffentlichungen des wissenschaftlichen Zentral-Laboratoriums der photographischen Abteilung Agfa, 3, 1933, pp. 188-207.
4 Images
-
![]() Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ede, François (1994): Jour de fête ou la couleur retrouvée. Cahiers du Cinéma: Paris.
- Schmidt, Richard / Kochs, Adolf (1943): Farbfilmtechnik. Eine Einführung für Filmschaffende. Berlin: Hesse, pp. 54-72. (Schriftenreihe der Reichsfilmkammer, 10.) (in German) [quote id='6']
5 Images
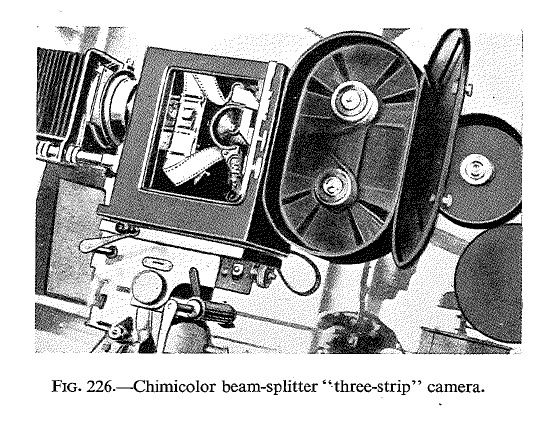
“R. Berthon and M. Audibert patented a method of obtaining a virtual image by means of an anterior lens and prisms or mirrors. This idea was further improved upon in E.P. 17,023, 1913. In F.P. 458,040 Audibert proposed to use a negative front lens ...
-
![]() Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
2 Images
-
![]() Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Source: Coe, Brian (1981): The History of Movie Photography. Westfield, N.J.: Eastview Editions.
- Credit: Collection Gert Koshofer, Bergisch Gladbach (Germany).
16 Images in 1 Gallery
In 1994, Technicolor announced the development of an enhanced dye-transfer process. This process became effective in June 1997. There was no official denomination, so “Technicolor No. VI” is not to be confused with statements from the mid ...
Theory of trichromatic vision proposed by Thomas Young.
-
![]() Cross section scheme, Agfacolor Positive Type 5. Scource: Brune, Wolfgang (1955): Ein neues Agfacolor-Positivmaterial (Agfacolor-Positivfilm Typ 5).
Cross section scheme, Agfacolor Positive Type 5. Scource: Brune, Wolfgang (1955): Ein neues Agfacolor-Positivmaterial (Agfacolor-Positivfilm Typ 5).
1 Image
“The New Agfacolor Process;
Agfa Ansco Corp., Binghamton, N. Y.
A survey of the history of monopack or multilayer photographic color processes is given, including the coloring methods of greatest importance at the present time. These are: (a) ...
-
![]() Münchhausen (Josef von Báky, Germany 1943). Credit: Bundesarchiv Filmarchiv and Friedrich-Wilhelm-Murnau-Stiftung. Photographs of the Agfacolor safety print (acetate) by Barbara Flueckiger.
Münchhausen (Josef von Báky, Germany 1943). Credit: Bundesarchiv Filmarchiv and Friedrich-Wilhelm-Murnau-Stiftung. Photographs of the Agfacolor safety print (acetate) by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Opfergang (GER 1944, Veit Harlan), magnification. Credit: Print from the Filmmuseum Düsseldorf. © Friedrich Wilhelm Murnau Foundation, Wiesbaden. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Paper print. Source: Serda, Charlott (1941): Das Farbfoto-Buch vom Film. Breitkopf & Härtel: Leipzig.
- Parade (1960). Credit: Harvard Film Archive, Brandon Film Library Collection, item no. 14303. Photographs of Agfacolor negative on Orwocolor reversal print by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Parade (1960). Credit: Harvard Film Archive, Brandon Film Library Collection, item no. 14303. Photographs of Agfacolor negative on Orwocolor reversal print by Barbara Flueckiger.
640 Images in 21 Galleries
“In 1898 William Friese-Greene, a professional portrait photographer by trade, demonstrated in London ‘the first process of true natural-color cinematography.’ His program consisted of ‘a series of animated natural-color pictures,’ and although this demonstration aroused considerable interest at the time, Friese-Greene was unable to exploit this system on a profitable basis. Undaunted, he eventually developed a total of four different color methods.”
-
![]() Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: Kino the Girl of Colour (GB 1920, William Friese-Greene, Claude Friese-Greene).
Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: Kino the Girl of Colour (GB 1920, William Friese-Greene, Claude Friese-Greene).
- Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Credit: Paolo Cherchi Usai. Source: Cherchi Usai, Paolo (2000): Silent Cinema. London: BFI.
112 Images in 2 Galleries
“Inevitably, the success of Kinemacolor led to the appearance of imitations. One company, Friese Greene Patents Ltd had been formed in 1908 to exploit several patents, mostly impractical, filed by Friese Greene. From this came a new company, ...
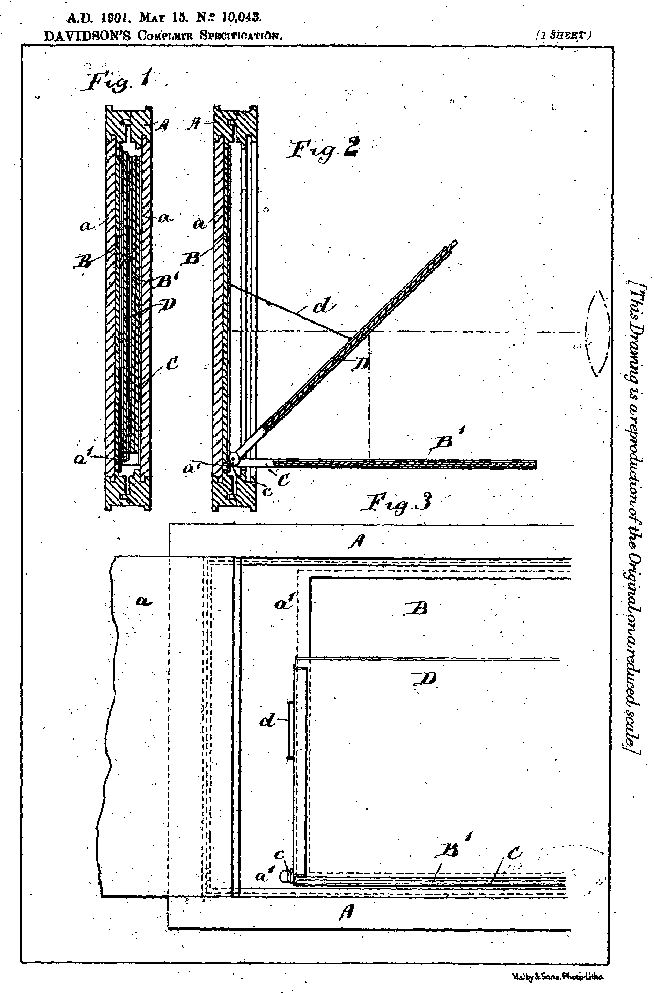
“Apparently, associated with W. Friese-Greene, in the same year, Captain William Norman Lascelles-Davidson, also of Brighton, patented a triple lens motion picture camera (E.P. 23,863, 1898). The colour filters revolved either behind the lenses, ...
-
![]() Credit: Harvard Film Archive, George Huizinga Collection, item no. 10454. Film: Prehistoric Women (1951).
Credit: Harvard Film Archive, George Huizinga Collection, item no. 10454. Film: Prehistoric Women (1951).
- Credit: Harvard Film Archive, George Huizinga Collection, item no. 10454. Film: Prehistoric Women (1951).
- Source: Coe, Brian (1981): The History of Movie Photography. Westfield, N.J.: Eastview Editions.
- Reflection on Cinecolor print. Credit: Image courtesy of the 20th Century Fox Collection at the Academy Film Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger
- Reflection on Cinecolor 16 mm print. Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger
93 Images in 9 Galleries
“In 1919 Kelley produced a series of coloured cartoons which were drawn by Pinto Colvig. In 1924 he introduced “Kelleycolor,” which was an imbibition process. Two colours were imbibed on a black-and-white key image. In 1926 he ...
-
![]() Credit: George Eastman House Motion Picture Department Collection. Film: The Old Family Toothbrush (USA 1925).
Credit: George Eastman House Motion Picture Department Collection. Film: The Old Family Toothbrush (USA 1925).
1 Image
”Kelley’s first color process was a four-color additive system introduced in 1913. Called Panchromotion, Kelley formed a company which would exploit the process commercially and, he hoped, provide strong competition for Kinemacolor. He apparently ...
-
![]() Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
- Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
2 Images
“In its final form Prizma made use of duplitized positive film. As in previous Prizma systems, the original negatives were alternate frame sequential exposures. The Prizma negative was printed on both sides of the positive film in a special ...
-
![]() The two colors visible at a splice. Credit: EYE Film Institute Amsterdam. Film: [Kleurenpracht].
The two colors visible at a splice. Credit: EYE Film Institute Amsterdam. Film: [Kleurenpracht].
- Credit: George Eastman House. Preserved by Carole Fodor, Haghefilm Digitaal fellow and graduate of The L. Jeffrey Selznick School of Film Preservation. Film: A Day with John Burroughs (Prizma, 1919).
- Credit: George Eastman House. Preserved by Carole Fodor, Haghefilm Digitaal fellow and graduate of The L. Jeffrey Selznick School of Film Preservation. Film: A Day with John Burroughs (Prizma, 1919).
- Credit: George Eastman House Motion Picture Department Collection. Film: The Land of the Great Spirit (1919).
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Orange.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Orange.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Orange.