-
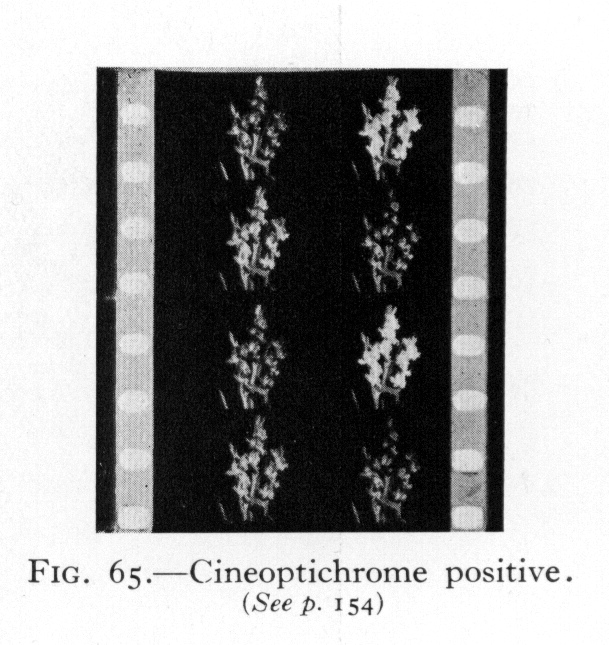
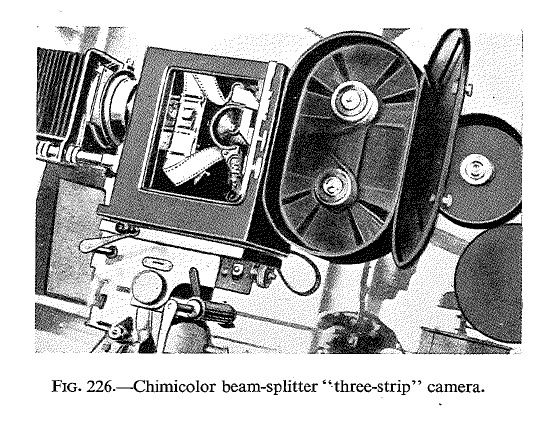
![]() Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
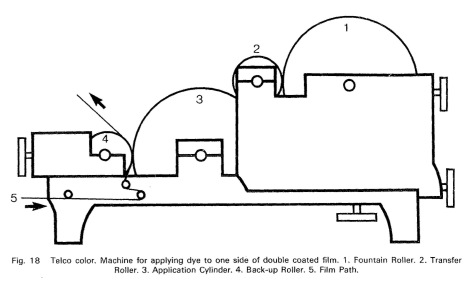
Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- All Categories
- Bibliography
- Chromogenic monopack
- Chromolytic multilayer
- Color separation
- Double-coated / bi-pack
- Edge Codes and Identification
- Hand coloring
- Other
- Printing / dye-transfer
- Printing / pigment process
- Screen processes
- Spatial synthesis (multiple lenses, beam splitter)
- Stencil coloring (pochoir, Pathécolor)
- Temporal synthesis (rotary filters)
- Theory
- Tinting
- Toning
-
![]() Knowing Men (GB 1930, Elinor Glyn), negative. Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
Knowing Men (GB 1930, Elinor Glyn), negative. Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
3 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Dyes of Brewster color. Credit: Brian Pritchard.
Dyes of Brewster color. Credit: Brian Pritchard.
- Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
52 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Zaveshchanie/The Testament (7 June 1937). Credit: Courtesy of Nikolai Mayorov.
Zaveshchanie/The Testament (7 June 1937). Credit: Courtesy of Nikolai Mayorov.
- Zaveshchanie/The Testament (7 June 1937). Credit: Courtesy of Nikolai Mayorov. Credit: Courtesy of Nikolai Mayorov.
- The Miraculous Traffic Light (1938). Credit: courtesy of Nikolai Mayorov
- The Wolf and Seven Goat-Kids (1938). Credit: Courtesy of Nikolai Mayorov.
- The Fox and the Wolf (1937). Credit: Courtesy of Nikolai Mayorov.
- The Fox and the Wolf (1937). Credit: Courtesy of Nikolai Mayorov.
6 Images
-
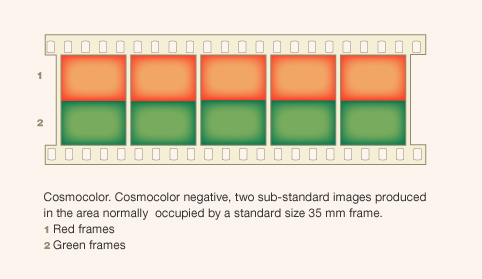
![]() Source: Wall, E.J. (1925): The History of Three-color Photography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
Source: Wall, E.J. (1925): The History of Three-color Photography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
1 Image
-
![]() Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. A History of Motion Picture Color Technology.
Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. A History of Motion Picture Color Technology.
- Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
2 Images
-
![]() Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
- Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
2 Images
-
![]() Screenshot from Mayorov, Nikolai (2012): Soviet Colours. Translated by Birgit Beumers. In: Studies in Russian & Soviet Cinema, 6:2, pp. 241–255. doi: 10.1386/srsc.6.2.241_1 Courtesy of Nikolai Mayorov.
Screenshot from Mayorov, Nikolai (2012): Soviet Colours. Translated by Birgit Beumers. In: Studies in Russian & Soviet Cinema, 6:2, pp. 241–255. doi: 10.1386/srsc.6.2.241_1 Courtesy of Nikolai Mayorov.
1 Image
-
![]() Black-and-white with Handschiegl in Lights of Old Broadway (USA 1925, Monta Bell). Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph of the nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
Black-and-white with Handschiegl in Lights of Old Broadway (USA 1925, Monta Bell). Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph of the nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Trail of '98 (USA 1929, Clarence Brown).
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Trail of '98 (USA 1929, Clarence Brown).
- Credit: Paolo Cherchi Usai. Source: Cherchi Usai, Paolo (2000): Silent Cinema. London: BFI. Film: Greed (USA 1925, Erich von Stroheim).
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Forbidden Fruit (USA 1921, Cecil B. DeMille).
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Forbidden Fruit (USA 1921, Cecil B. DeMille).
- Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press, p. 24.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Trail of '98 (USA 1929, Clarence Brown).
141 Images in 8 Galleries
-
![]() Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
3 Images
-
![]() Cross-section of the optical system displaying the different lenses, the prism and the four filters. Source: Pierotti, Federico (2016): Un'archeologia del colore nel cinema italiano. Dal Technicolor ad Antonioni. Pisa: Edizioni ETS, p. 71.
Cross-section of the optical system displaying the different lenses, the prism and the four filters. Source: Pierotti, Federico (2016): Un'archeologia del colore nel cinema italiano. Dal Technicolor ad Antonioni. Pisa: Edizioni ETS, p. 71.
- 35mm black and white film strip with four equal-sized images (left) and 16mm projector with Cristiani-Mascarini optical system. Source: Pierotti, Federico (2016): Un'archeologia del colore nel cinema italiano. Dal Technicolor ad Antonioni. Pisa: Edizioni ETS, p. 71.
2 Images
-
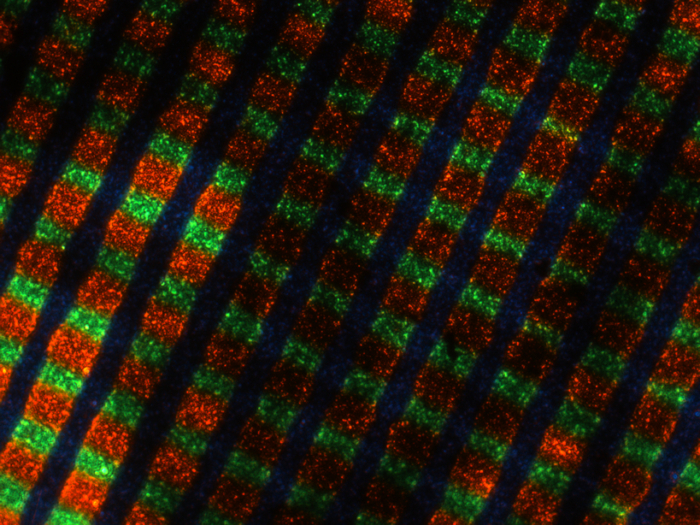
![]() Magnification, 20x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
Magnification, 20x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification, 10x. Credit: Photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification, 5x. Credit: Photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. In: Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Magnification of an image area. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Reflection on the Sirius film, front. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Reflection on the Sirius film, back. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
142 Images in 4 Galleries
-
![]() Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
2 Images
Dufaycolor was a regular line screen process whereby the incident light was filtered through a pattern of tiny color patches created by lines in red, green and blue, the so called réseau.
-
![]() Reversal Colour Positive. Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: A Colour Box (GB 1935, Len Lye).
Reversal Colour Positive. Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: A Colour Box (GB 1935, Len Lye).
- Microscopic image of the filter structure of a Dufaycolor film. The Emulsion has been removed. The visible structures are not silver grain but the structure of the filter layers. Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Microscopic images of Dufaycolor film with the focus set at different points within the emulsion and filter layers. The images have been chained to show a travelling through the 3-dimensional structure of the layers. Credit: David Pfluger, conversion to video by Martin Weiss, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
231 Images in 9 Galleries
-
![]() Magnification 20x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
Magnification 20x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Magnification 10x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Magnification 5x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. In: Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Source: Coe, Brian (1981): The History of Movie Photography. Westfield, N.J.: Eastview Editions.
- Magnification of an image area. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
78 Images in 2 Galleries
-
![]() Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press,
Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press,
- Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Source: Ede, François (1994): Jour de fête ou la couleur retrouvée. Cahiers du Cinéma: Paris.
- Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 71.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 73.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 31.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 32.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 33.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 48.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 69.
10 Images
-
![]() "Du Hauron invented his Chromographoscope in 1874. It could be used either as a camera or an additive viewer." Source: Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press.
"Du Hauron invented his Chromographoscope in 1874. It could be used either as a camera or an additive viewer." Source: Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press.
- An early three-color print by Louis Ducros Du Hauron, 1877.
2 Images
“In 1930 Mannes and Godowsky were invited to join the staff of the Kodak Research Laboratory, where they concentrated on methods of processing multilayer films, while their colleagues worked out ways of manufacturing them. The result was the new Kodachrome film, launched in 1935. Three very thin emulsion layers were coated on film base, the emulsions being sensitised with non-wandering dyes to red, green and blue light, the red-sensitive layer being at the bottom.” (Coe, Brian (1978): Colour Photography. The First Hundred Years 1840-1940. London: Ash & Grant, pp. 121 ff.)
-
![]() Credit: Lichtspiel / Kinemathek Bern. Film: New York, Taufe und Ausflug (CH 1954, Donald Brun).
Credit: Lichtspiel / Kinemathek Bern. Film: New York, Taufe und Ausflug (CH 1954, Donald Brun).
- Surface emulsion side, raking light. Credit: Carsta Knaack, HTW Berlin. Film: Regular 8mm home movie, anonymous 1975.
92 Images in 6 Galleries
-
![]() Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.