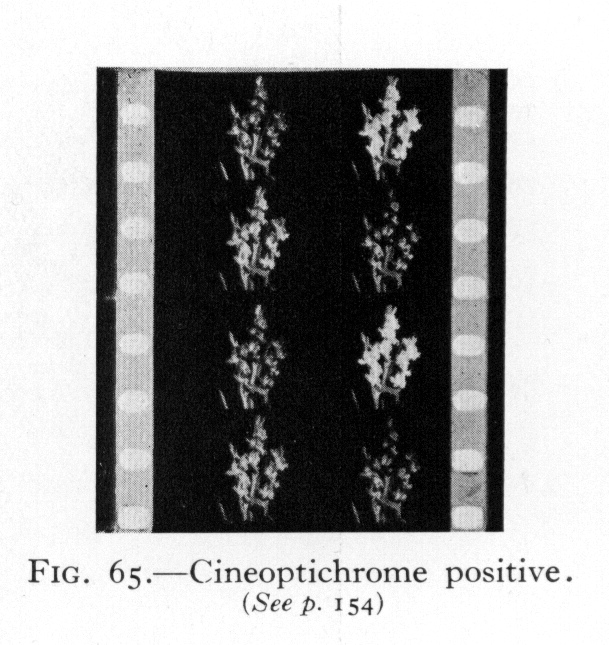
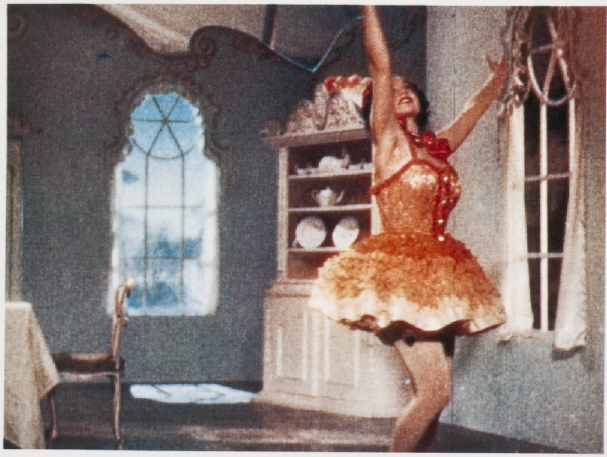
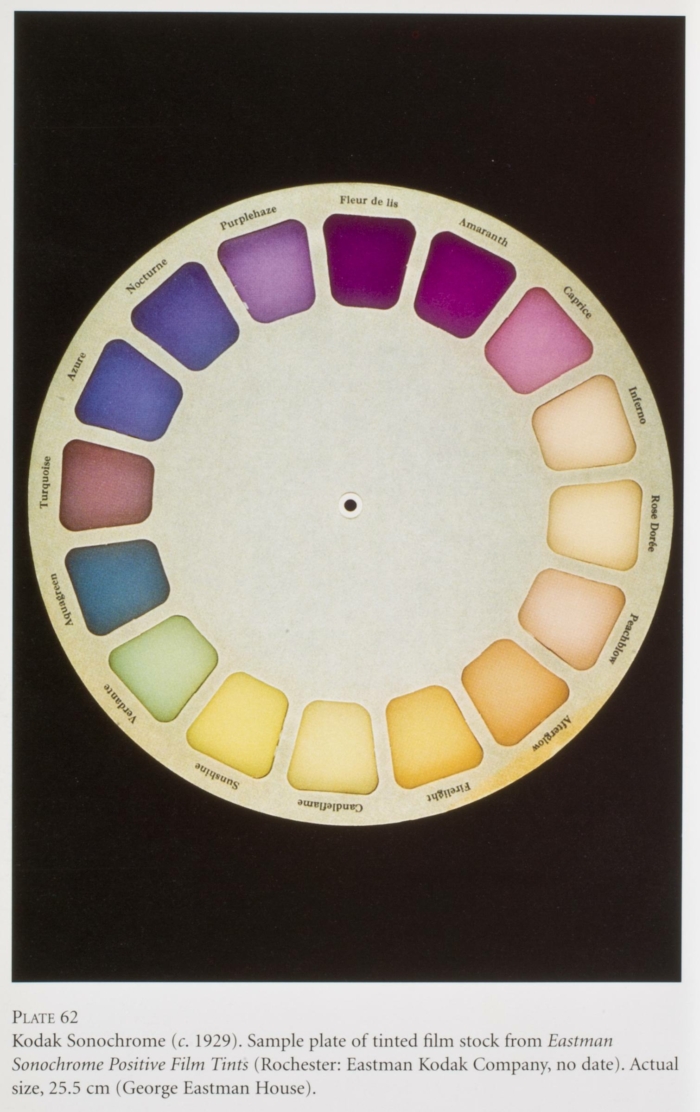
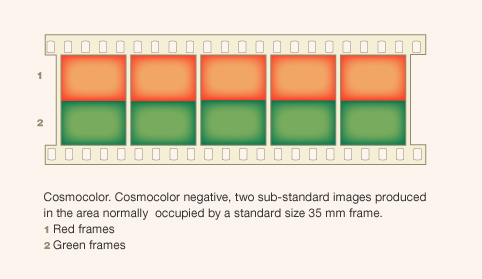
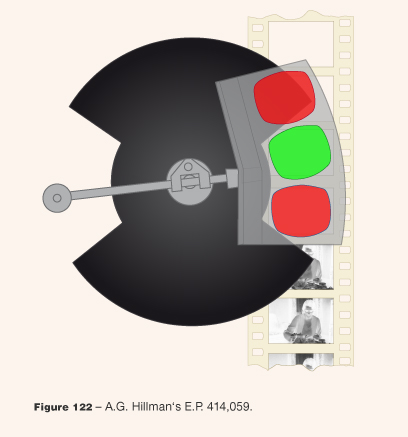
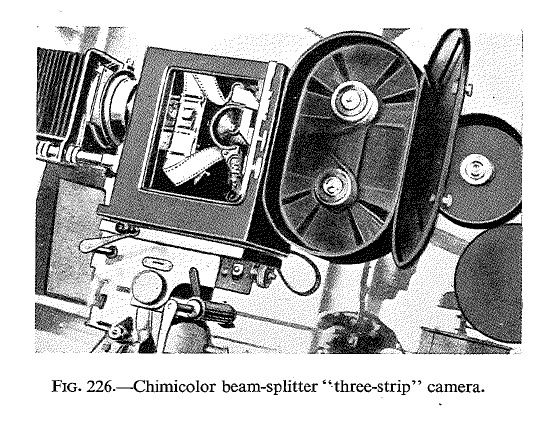
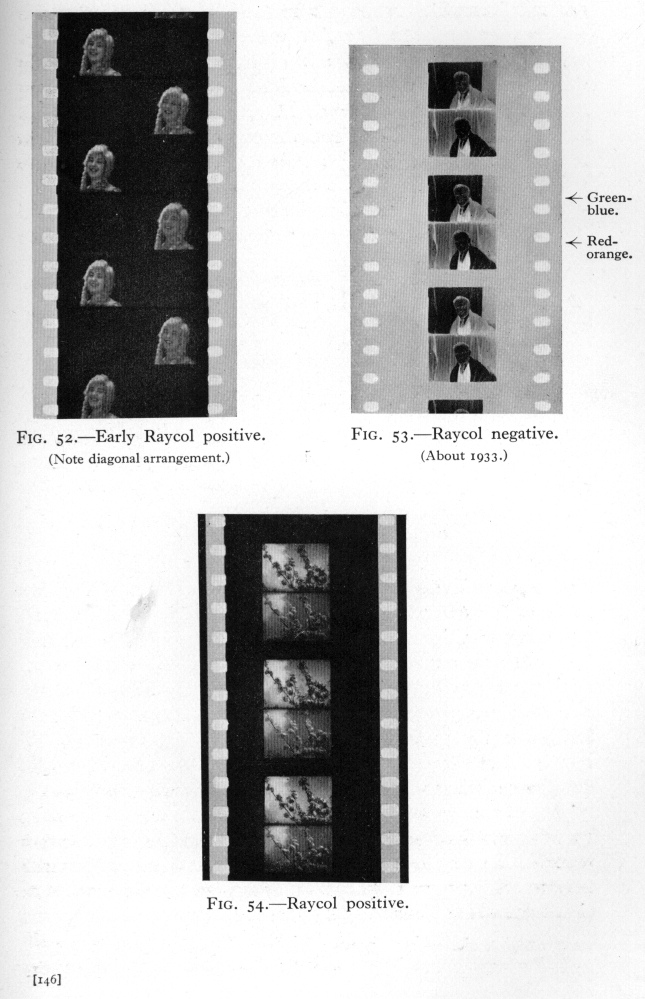
-
![]() Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
- Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
Select Category▼×
- All Categories
- Bibliography
- Chromogenic monopack
- Chromolytic multilayer
- Color separation
- Double-coated / bi-pack
- Edge Codes and Identification
- Hand coloring
- Other
- Printing / dye-transfer
- Printing / pigment process
- Screen processes
- Spatial synthesis (multiple lenses, beam splitter)
- Stencil coloring (pochoir, Pathécolor)
- Temporal synthesis (rotary filters)
- Theory
- Tinting
- Toning
-
![]() Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Source: Coe, Brian (1981): The History of Movie Photography. Westfield, N.J.: Eastview Editions.
- Schmidt, Richard / Kochs, Adolf (1943): Farbfilmtechnik. Eine Einführung für Filmschaffende. Berlin: Hesse, pp. 54-72. (Schriftenreihe der Reichsfilmkammer, 10.) (in German) [quote id='5']
- Schmidt, Richard / Kochs, Adolf (1943): Farbfilmtechnik. Eine Einführung für Filmschaffende. Berlin: Hesse, pp. 54-72. (Schriftenreihe der Reichsfilmkammer, 10.) (in German) [quote id='5']
9 Images in 1 Gallery
“Harmonicoior was developed by French chemist Maurice Combes. It was first formally demonstrated in London by Harmonicoior Films Ltd, of 4 Great Winchester Street, on the 23 March 1936 at the Curzon Soho with the film Talking Hands, produced at ...
-
![]() Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
- Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
- Source: Kistler, L. R. (1945): The Projection of Thomascolor Motion Pictures. In: International Projectionist, 20,7, Jul., pp. 12–14.
- Source: Kistler, L. R. (1945): The Projection of Thomascolor Motion Pictures. In: International Projectionist, 20,7, Jul., pp. 12–14.
- Left: Thomascolor camera lens mount for converting standard motion picture camera into Thomascolor. Right: A closeup of the Thomascolor projector lens mount for standard film projectors. The inventor points out that this is all that is needed to convert a standard projector to Thomascolor. Source: Anonymous (1944): Thomascolor. Four-Color Process For Motion Pictures. In: International Projectionist, 19,10, Oct., pp. 7–9.
5 Images
For this four-color process, the light beam was decomposed into four parts, each of which simultaneously exposed an area equal to one quarter of the 35mm frame of a black and white negative. This was obtained optically by placing a diaphragm and a ...
-
![]() Cross-section of the optical system displaying the different lenses, the prism and the four filters. Source: Pierotti, Federico (2016): Un'archeologia del colore nel cinema italiano. Dal Technicolor ad Antonioni. Pisa: Edizioni ETS, p. 71.
Cross-section of the optical system displaying the different lenses, the prism and the four filters. Source: Pierotti, Federico (2016): Un'archeologia del colore nel cinema italiano. Dal Technicolor ad Antonioni. Pisa: Edizioni ETS, p. 71.
- 35mm black and white film strip with four equal-sized images (left) and 16mm projector with Cristiani-Mascarini optical system. Source: Pierotti, Federico (2016): Un'archeologia del colore nel cinema italiano. Dal Technicolor ad Antonioni. Pisa: Edizioni ETS, p. 71.
2 Images
-
![]() Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. A History of Motion Picture Color Technology.
Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. A History of Motion Picture Color Technology.
- Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
2 Images
The procedure for obtaining the lenticular elements in relief required a series of steps: starting from three black and white positive color separations, obtained with any of the available methods, three matrices were printed, from which the film to ...
-
![]() Projection of lenticular film in Bocca-Rudatis. Refraction of light beams through lens. Source: Pierotti, Federico (2016): Un'archeologia del colore nel cinema italiano. Dal Technicolor ad Antonioni. Pisa: Edizioni ETS, p. 81.
Projection of lenticular film in Bocca-Rudatis. Refraction of light beams through lens. Source: Pierotti, Federico (2016): Un'archeologia del colore nel cinema italiano. Dal Technicolor ad Antonioni. Pisa: Edizioni ETS, p. 81.
1 Image
Three matrices in the subtractive primary colors are printed on the gelatin of the final print. Supposedly, the used dyes were particularly fast and able to prevent color bleeding. Pokorny started working on color cinematography in the 1920s, often ...
Dufaycolor was a regular line screen process whereby the incident light was filtered through a pattern of tiny color patches created by lines in red, green and blue, the so called réseau.
-
![]() Reversal Colour Positive. Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: A Colour Box (GB 1935, Len Lye).
Reversal Colour Positive. Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: A Colour Box (GB 1935, Len Lye).
- Microscopic image of the filter structure of a Dufaycolor film. The Emulsion has been removed. The visible structures are not silver grain but the structure of the filter layers. Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Microscopic images of Dufaycolor film with the focus set at different points within the emulsion and filter layers. The images have been chained to show a travelling through the 3-dimensional structure of the layers. Credit: David Pfluger, conversion to video by Martin Weiss, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
231 Images in 9 Galleries
-
![]() Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
3 Images
-
![]() Source: Dubray, J.A. (1933): The Morgana Process In: Journal of the Society of Motion Picture Engineers 21,5, 1933, pp. 403-412.
Source: Dubray, J.A. (1933): The Morgana Process In: Journal of the Society of Motion Picture Engineers 21,5, 1933, pp. 403-412.
1 Image
-
![]() Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
40 Images
Gasparcolor was the first three-color multi-layer monopack film available for practical use. It was a double-coated print film with a cyan layer on one side and two layers dyed magenta and yellow on the other side (see illustrations).
-
![]() Uit het rijk der kristallen (NDL 1927?, J.C. Mol). Credit: EYE Film Museum. Photographs of the Dufaycolor and Gasparcolor nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
Uit het rijk der kristallen (NDL 1927?, J.C. Mol). Credit: EYE Film Museum. Photographs of the Dufaycolor and Gasparcolor nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Kreise (English title Circles) (Oskar Fischinger, GER 1933-34) Oskar Fischinger's own nitrate print. Credit: Library of Congress, (c) Fischinger Trust, courtesy Center for Visual Music. Photograph Fischinger's own nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Credit: (c) Fischinger Trust, courtesy Center for Visual Music. Film: Allegretto by Oskar Fischinger (1936-1943).
- Credit: (c) Fischinger Trust, courtesy Center for Visual Music. Film: Gasparcolor tests by Oskar Fischinger, c. 1933-34.
- Credit: Cinémathèque suisse. Film: Komposition in Blau (Composition in Blue) AKA Lichtkonzert Nr. 1 (Light-Concert No. 1) (GER 1935, Oskar Fischinger).
- Credit: Cinémathèque suisse. © Fischinger Trust, courtesy Center for Visual Music. Film: Komposition in Blau (Composition in Blue) AKA Lichtkonzert Nr. 1 (Light-Concert No. 1) (GER 1935, Oskar Fischinger).
- Credit: Cinémathèque suisse. © Fischinger Trust, courtesy Center for Visual Music. Film: Komposition in Blau (Composition in Blue) AKA Lichtkonzert Nr. 1 (Light-Concert No. 1) (GER 1935, Oskar Fischinger).
- Source: Coe, Brian (1981): The History of Movie Photography. Westfield, N.J.: Eastview Editions.
- Color chart on Agfa Tripofilm. This was the raw stock used for Gasparcolor in Germany until about 1939. Source: Arens, Hans; Heymer, Gerd (1939): Die „Agfa-Farbentafel für Farbenphotographie“. In: Veröffentlichungen des wissenschaftlichen Zentral-Laboratoriums der photographischen Abteilung Agfa, Vol. 6, 1939, pp. 225-229. Leipzig: Hirzel. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 213.
398 Images in 24 Galleries
-
![]() Credit: Harvard Film Archive, George Huizinga Collection, item no. 10454. Film: Prehistoric Women (1951).
Credit: Harvard Film Archive, George Huizinga Collection, item no. 10454. Film: Prehistoric Women (1951).
- Credit: Harvard Film Archive, George Huizinga Collection, item no. 10454. Film: Prehistoric Women (1951).
- Source: Coe, Brian (1981): The History of Movie Photography. Westfield, N.J.: Eastview Editions.
- Reflection on Cinecolor print. Credit: Image courtesy of the 20th Century Fox Collection at the Academy Film Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger
- Reflection on Cinecolor 16 mm print. Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger
93 Images in 9 Galleries
The Roncarolo system required a camera capable of recording two panchromatic negatives (which became three or four in subsequent patents) through the use of a beam splitter and red and green filters.
The chromatic information registered on the two or ...
-
![]() Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
2 Images
“Agfacolor Plate (1932-1938): colored particles very small and not visible to the naked eye; clumps of particles of the same color give the image a pointillist effect (Fig. 2.63). Unlike with the autochromes, in which the grains are remarkably ...
-
![]() Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 72.
Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 72.
1 Image
“Agfacolor Film (1932–1934): individual colored particles cannot be seen with the naked eye, but clumps of grains of the same color give the image a pointillist effect (Fig. 2.70). There is no black pigment filler. The film has a thick base ...
-
![]() Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 76.
Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 76.
1 Image
“Chemicoior was the name under which the German Ufacolor Process was marketed in Britain. Ufacolor was also marketed under the name Spectracolor. The process used Agfa bipack negatives loaded with the emulsion sides facing and separated by a ...
-
![]() Source: Coe, Brian (1981): The History of Movie Photography. Westfield, N.J.: Eastview Editions. Film: Pagliacci (1937).
Source: Coe, Brian (1981): The History of Movie Photography. Westfield, N.J.: Eastview Editions. Film: Pagliacci (1937).
9 Images in 2 Galleries
With the fourth Technicolor process the company dominated the market for color films from the mid-1930s to the 1950s.
In a special camera, three b/w negative films were exposed through a beam-splitter that consisted of two prisms to form a cube. One ...
-
![]() Credit: Image courtesy of the Academy Film Archive. Film: Gone with the Wind (USA 1939, Victor Fleming). Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
Credit: Image courtesy of the Academy Film Archive. Film: Gone with the Wind (USA 1939, Victor Fleming). Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Film: Samson and Delilah (US 1949, Cecil B. DeMille), trailer.
- Photomicrograph, 50x. Credit: Norbert Wey, Institute of Pathology, University of Zurich.
- Photomicrograph, 100x. Credit: Norbert Wey, Institute of Pathology, University of Zurich.
1881 Images in 65 Galleries
The basic idea of the lenticular film was developed by the German Raphaël Liesegang in 1896 and applied to still photography by the French Rodolphe Berthon in 1908.
The lenticular process applies tiny cylindrical lenses embossed on the film support ...
-
![]() Color reconstruction. Credit: Gisela Harich-Hamburger, Diplomrestauratorin (FH).
Color reconstruction. Credit: Gisela Harich-Hamburger, Diplomrestauratorin (FH).
- Source: Heymer, Gerd (1933): Auflösungsvermögen und Farbwiedergabe in der Farbrasterphotographie. In: Veröffentlichungen des wissenschaftlichen Zentral-Laboratoriums der photographischen Abteilung Agfa, 3, 1933, pp. 188-207.
- Source: Weil, F. (1933): The Optical-Photographic Principles of the Agfacolor Process. In: Journal of the Society of Motion Picture Engineers, 20, (April, 1933), No. 4, p. 301-308.
- Both the Kodak and Agfa lenticular processes required the correct banded filter to be used with each different batch of panchromatic film. These two filters were for different batches of Agfacolor used in a Leica camera.. Source: Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ede, François (1994): Jour de fête ou la couleur retrouvée. Cahiers du Cinéma: Paris.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Magnification 5x, front. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification 10x, back. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification 20x, front. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Reflection on Agfacolor lenticular film. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. In: Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Reconstruction of lenticular film by Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland in the framework of their research project doLCE
- Agfacolor Lenticular sample from the Kodak Film Samples Collection at the National Science and Media Museum in Bradford. Credit: National Science and Media Museum Bradford. Photographs by Barbara Flueckiger in collaboration with Noemi Daugaard.
- Analog reconstruction by Giorgio Trumpy, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors
15 Images
“An American two-colour subtractive process still worked by the Consolidated Film Industries division of Republic Pictures Corporation. This concern was licensed by the owners of the “Prizma” patents, which it will be remembered was ...
-
![]() Mysore Yesterday and Tomorrow Credit: Image courtesy of the 20th Century Fox Collection at the Academy Film Archive. Photograph: Barbara Flueckiger.
Mysore Yesterday and Tomorrow Credit: Image courtesy of the 20th Century Fox Collection at the Academy Film Archive. Photograph: Barbara Flueckiger.
23 Images in 2 Galleries
“The Rotocolor process was an additive system for color cinematography. The process was announced in 1931 by H. Muller. According to an article in Film Daily, April 12, 1931, and The Motion Picture Herald, April 11, 1931, the process consisted of ...
-
![]() Screenshot from Mayorov, Nikolai (2012): Soviet Colours. Translated by Birgit Beumers. In: Studies in Russian & Soviet Cinema, 6:2, pp. 241–255. doi: 10.1386/srsc.6.2.241_1 Courtesy of Nikolai Mayorov.
Screenshot from Mayorov, Nikolai (2012): Soviet Colours. Translated by Birgit Beumers. In: Studies in Russian & Soviet Cinema, 6:2, pp. 241–255. doi: 10.1386/srsc.6.2.241_1 Courtesy of Nikolai Mayorov.
1 Image
“Coloratura. This is the process of Pathé Exchange at Bound Brook, N. J. Negatives are made by the bi-pack method. Prints are made on double-sided film and are dye-toned on one side and metallic-toned on the other. The double-sided film, ...
-
![]() Rota Farbenfilm Samples (Kodak Film Samples Collection). Credit: National Science and Media Museum Bradford. Photographs of the Rotacolor Prints by Josephine Diecke, SNSF project Film Colors. Technologies, Cultures, Institutions and Joëlle Kost, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
Rota Farbenfilm Samples (Kodak Film Samples Collection). Credit: National Science and Media Museum Bradford. Photographs of the Rotacolor Prints by Josephine Diecke, SNSF project Film Colors. Technologies, Cultures, Institutions and Joëlle Kost, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
13 Images in 2 Galleries
-
![]() Magnification of an image area. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
Magnification of an image area. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Color chart. Credit: Guido Seeber Nachlass, Deutsche Kinemathek, Berlin. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92.
- Credit: Guido Seeber Nachlass, Deutsche Kinemathek, Berlin. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Credit: Bundesarchiv-Filmarchiv, photo: Marian Stefanowski. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92. Film: Bunte Tierwelt. Studien in Hagebecks Tierpark in Stellingen (1931).
- Credit: Bundesarchiv-Filmarchiv, photo: Marian Stefanowski. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92. Film: Karneval (1936).
- Credit: Bundesarchiv-Filmarchiv, photo: Jeanpaul Goergen. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92. Film: Bunte Fischwelt (1936).
- Credit: Bundesarchiv-Filmarchiv, photo: Marian Stefanowski. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92. Film: Karneval (1936).
- Credit: Deutsches Filminstitut DIF (Vicas Nachlass), photo: Jeanpaul Goergen. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92. Film: Potsdam (1934).
- Credit: Bundesarchiv-Filmarchiv, photo: Marian Stefanowski. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92. Film: Farben machen froh (1938).
- Magnification 5x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification 10x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification 20x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. In:Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Magnification of an image area. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. In:Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Reflection on Ufacolor film. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. In:Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- An opened splice of an Ufacolor positive shows the two colors used in the process. Credit: David Pfluger. Source: David Pfluger’s collection.
136 Images in 7 Galleries
-
![]() Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
2 Images
-
![]() Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
3 Images
-
![]() Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
42 Images
“Public showings of the work done at this plant in Hollywood have been given to Los Angeles audiences.
The release prints are made on double sided film. Both sides are developed at one time and then toned red on one side and bluegreen on the ...
-
![]() Strange Birds (US 1930, Mack Sennett). Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph of the nitrate print: Barbara Flueckiger
Strange Birds (US 1930, Mack Sennett). Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph of the nitrate print: Barbara Flueckiger
- Magnification. Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Strange Birds (1930)
18 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
1 Image
“The Brewster Process.
(U.S.P. 1,752,477. 1930-)
Camera. – P. D. Brewster, an American inventor, who was one of the first to apply the bipack system to colour cinematography, has a number of patents to his credit covering various cameras and ...
-
![]() Dyes of Brewster color. Credit: Brian Pritchard.
Dyes of Brewster color. Credit: Brian Pritchard.
- Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
52 Images in 1 Gallery
Unlike other additive systems invented in previous years, Gualtierotti tried to avoid the phenomenon of chromatic aberration inherent in the use of multiple lenses or the creation of successive separation records. The proposed solution was based on ...
-
![]() Rotating filters permitting to adjust tonality and intensity of the colors. Source: Pierotti, Federico (2016): Un'archeologia del colore nel cinema italiano. Dal Technicolor ad Antonioni. Pisa: Edizioni ETS, p. 62
Rotating filters permitting to adjust tonality and intensity of the colors. Source: Pierotti, Federico (2016): Un'archeologia del colore nel cinema italiano. Dal Technicolor ad Antonioni. Pisa: Edizioni ETS, p. 62
1 Image
-
![]() Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 70.
Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 70.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 70.
- Photomicrograph (20x) of a Finlay screen. Credit: Courtesy of George Eastman House, International Museum of Photography and Film.
- Finlay box. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 39.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 39.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 40.
9 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
13 Images in 1 Gallery
“The Dutch Sirius Color process (1929) used a camera with a beamsplitting system behind the lens to expose a single film, the film passing through two gates at right angles to each other. The double-coated print film was dye-toned. The process ...
-
![]() Magnification, 20x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
Magnification, 20x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification, 10x. Credit: Photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification, 5x. Credit: Photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. In: Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Magnification of an image area. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Reflection on the Sirius film, front. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Reflection on the Sirius film, back. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
142 Images in 4 Galleries
“Harriscolor
In this method as in other methods of color photography, independent color value negatives are first obtained. The Harriscolor process can employ one of the following two methods: Either a camera wherein the dividing light prisms ...
-
![]() Credit: Technicolor Collection. George Eastman House Moving Image Department. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
Credit: Technicolor Collection. George Eastman House Moving Image Department. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Credit: Technicolor Collection. George Eastman House Moving Image Department. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Credit: Technicolor Collection. George Eastman House Moving Image Department. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
3 Images
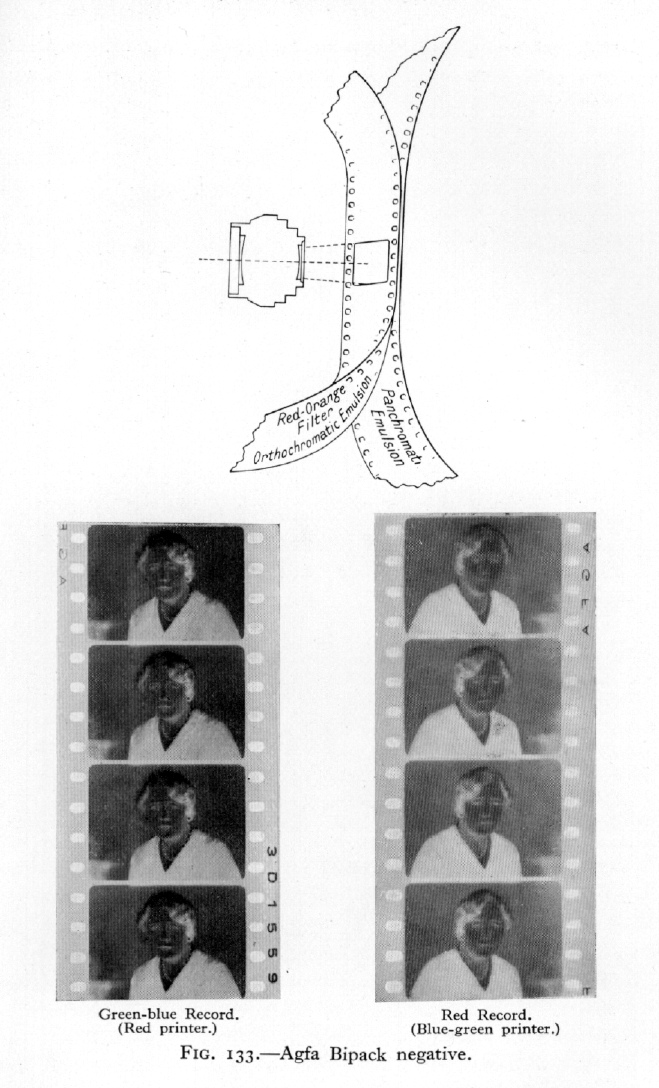
AGFA BIPACK FILM
The front film is orthochromatic and sensitive, therefore, to green and blue. The rear film is panchromatic and records red-orange only, there being a red-orange filter on the orthochromatic emulsion. In fact, this is a bipack of the ...
-
![]() Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
11 Images in 1 Gallery
Kodak Sonochrome was a specially prepared tinted film for sound film that did not interfere with the spectral sensitivity of the photo-electric cell for the reading of the optical sound track.
The 17 Sonochrome tints were dyed in mainly light hues ...
-
![]() Credit: Paolo Cherchi Usai. Source: Cherchi Usai, Paolo (2000): Silent Cinema. London: BFI.
Credit: Paolo Cherchi Usai. Source: Cherchi Usai, Paolo (2000): Silent Cinema. London: BFI.
- Source: The International Photographer, July 1929
- Source: The International Photographer, July 1929
- Source: The International Photographer, July 1929
- Source: The International Photographer, July 1929
79 Images in 3 Galleries
“LENTICULAR PROCESS
In 1896 R. E. Liesegang (Ahriman, 1896) suggested a photographic color process based upon the use of banded filters in the camera aperture.
[…]
In 1909 R. Berthon (British Patent 10,611; see also Berthon, 1910a, b) ...
-
![]() Kodacolor lenticular filter for the projector. Lichtspiel / Kinemathek Bern.
Kodacolor lenticular filter for the projector. Lichtspiel / Kinemathek Bern.
- Credit: Rudolf Gschwind, Imaging and Media Lab, University of Basel.
- Magnification of an area. Credit: Rudolf Gschwind, Imaging and Media Lab, University of Basel.
- Color reconstruction test. Credit: Rudolf Gschwind, Imaging and Media Lab, University of Basel.
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Microscopic linear lens structure of Kodacolor lenticular film. Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Acetate plastic base of Kodacolor lenticular film embedded in epoxide resin. The emulsion layer usually placed on the opposite side of the acetate base has been removed beforehand and is therefore not visible. Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Focal travelling through the 3-dimensional structure of Kodacolor lenticular film. In the beginning the linear lenticular structure is visible and towards the end the emulsion layer comes into focus and the granular structure defined by the density of the silver is visible. In this shot the lenticules were showing towards the light source and the emulsion towards the camera. This enables an undistorted recording of the emulsion layer. Credit: David Pfluger, editing by Martin Weiss, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Focal travelling through the 3-dimensional structure of Kodacolor lenticular film. In the beginning the linear lenticular structure is visible and towards the end the emulsion layer comes into focus. In this shot the lenticules were allocated towards the lens of the microscope and the light source at the side of the emulsion similar to the configuration in projection. As a consequence the graininess of the emulsion is not visible as with the film flipped to the other side. The structure is optically distorted perpendicular to the linear structure of the lenticules. Credit: David Pfluger, editing by Martin Weiss, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.